树莓派4B-搭建一个本地车牌识别服务器
实现目标:
一、设备自启后能够获得服务的ip与端口号,用于计算机连接设备;
二、计算机可以通过服务ip与端口访问设备服务;
三、上传需要处理的数据,返回结果反馈给用户;
四、上传到服务器的数据不会导致设备内存耗尽,自动删除多余的数据;
进阶(未实现):
五、提供用户登陆功能,设备支持唯一admin管理员用户。其他用户可注册;
六、提供登陆界面,用户通过登陆界面输入用户名与密码登录;
七、支持已处理的数据记录在设备数据库当中,提供web页面可查;
八、查询的历史数据支持查看:数据处理时间、处理前上传图片和处理后车牌结果。
使用到的工具与方法
一、systemctl自启服务
二、oled
二、python
三、flask
四、bootstrap框架
五、hyperlpr车牌识别的v1版本
实现过程:
一、配置自启服务,开机显示服务ip与端口
使用systemctl配置开机自启由oled显示ip与端口(在前面另一篇文章)。

二、将基于flask的web程序加入到run.sh执行脚本当中
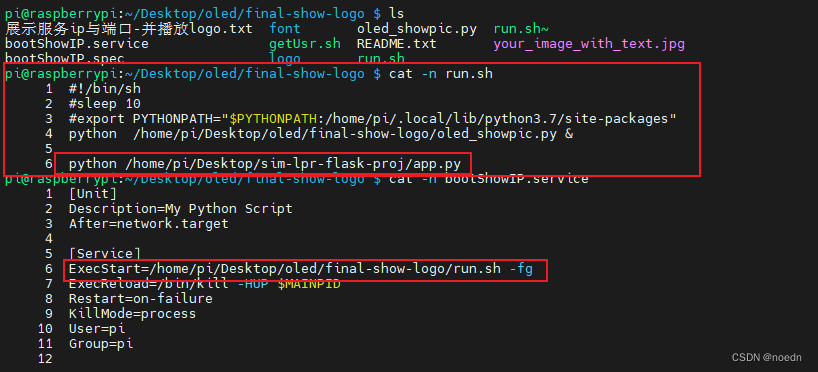
前提是bootShowIP.service文件已经放到/usr/lib/systemd/system目录当中并已启用:
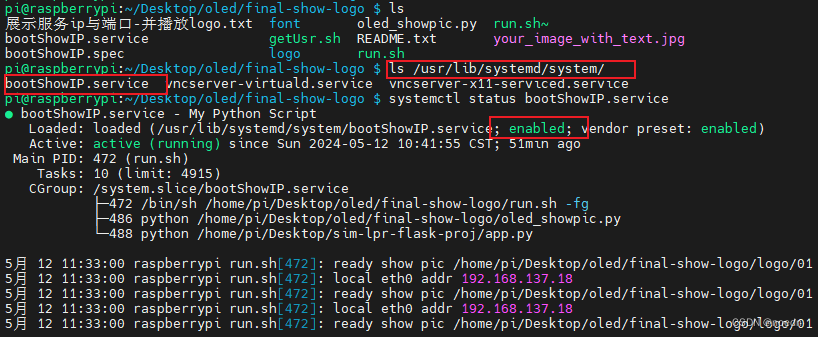
三、在将flask程序部署到树莓派上前,在本地进行了测试。
1、本地可以正常安装使用hyperlpr3,但是在设备上运行时提示由于无法安装onnxruntime导致的无法使用车牌识别功能。
2、无法安装onnxruntime可能是因为onnxruntime没有支持设备的处理器架构的版本。尝试安装hyperlpr v1成功:
python -m pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple hyperlpr #防止下载过慢,使用-i指定下载镜像 3、由于hyperlpr v1版本比较旧,依赖的numpy版本也比较旧,如果直接安装最新的numpy会导致无法使用:
尝试解决:
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple --upgrade --force-reinstall numpy 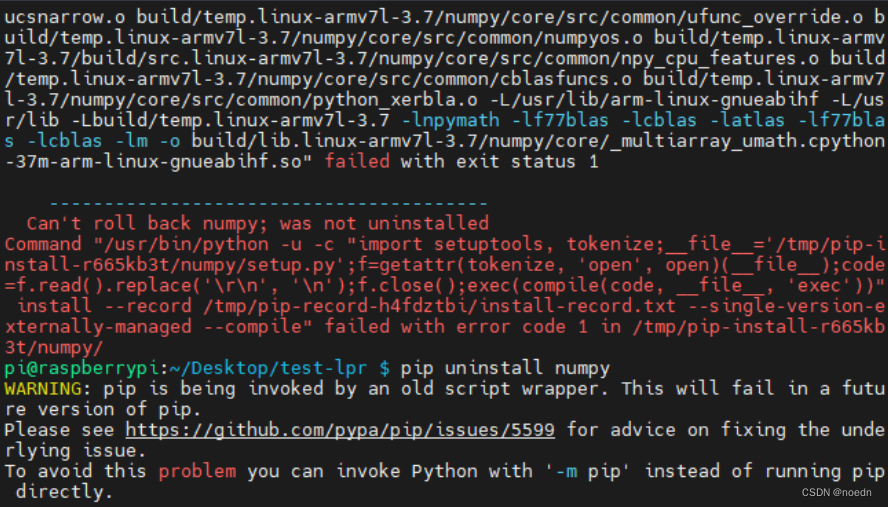
安装失败,按提示“Can't roll back numpy; was not uninstalled”,卸载pip uninstall numpy
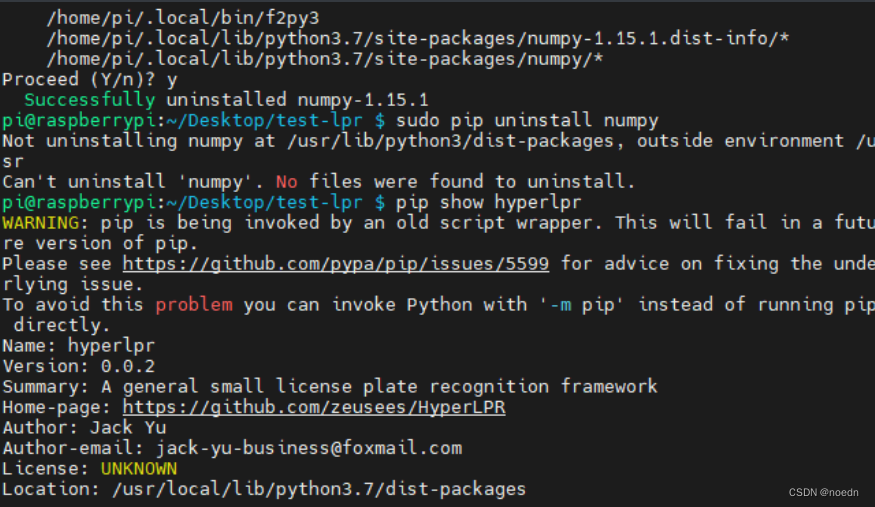
卸载之后发现hyperlpr正常了,并且已经存在numpy,可能是安装了多次
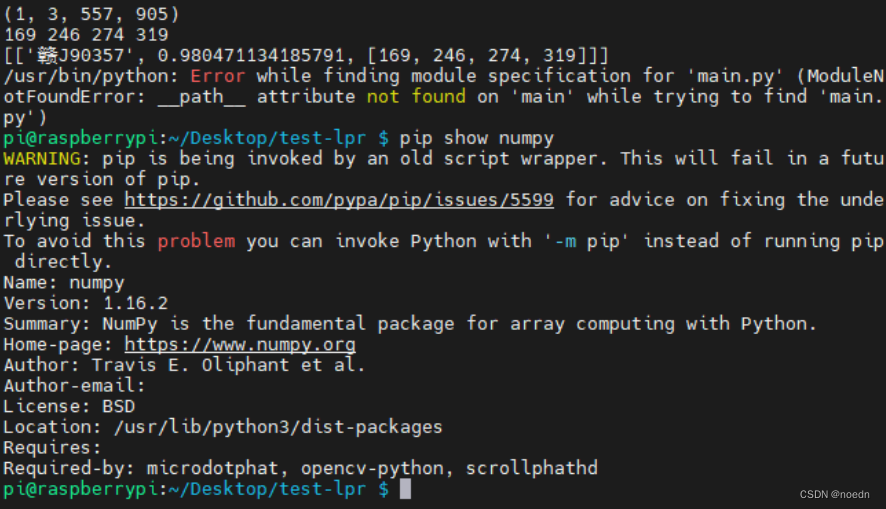
四、测试安装的hyperlpr模块正常后,将以hyperlpr作为后端的falsk程序部署到树莓派
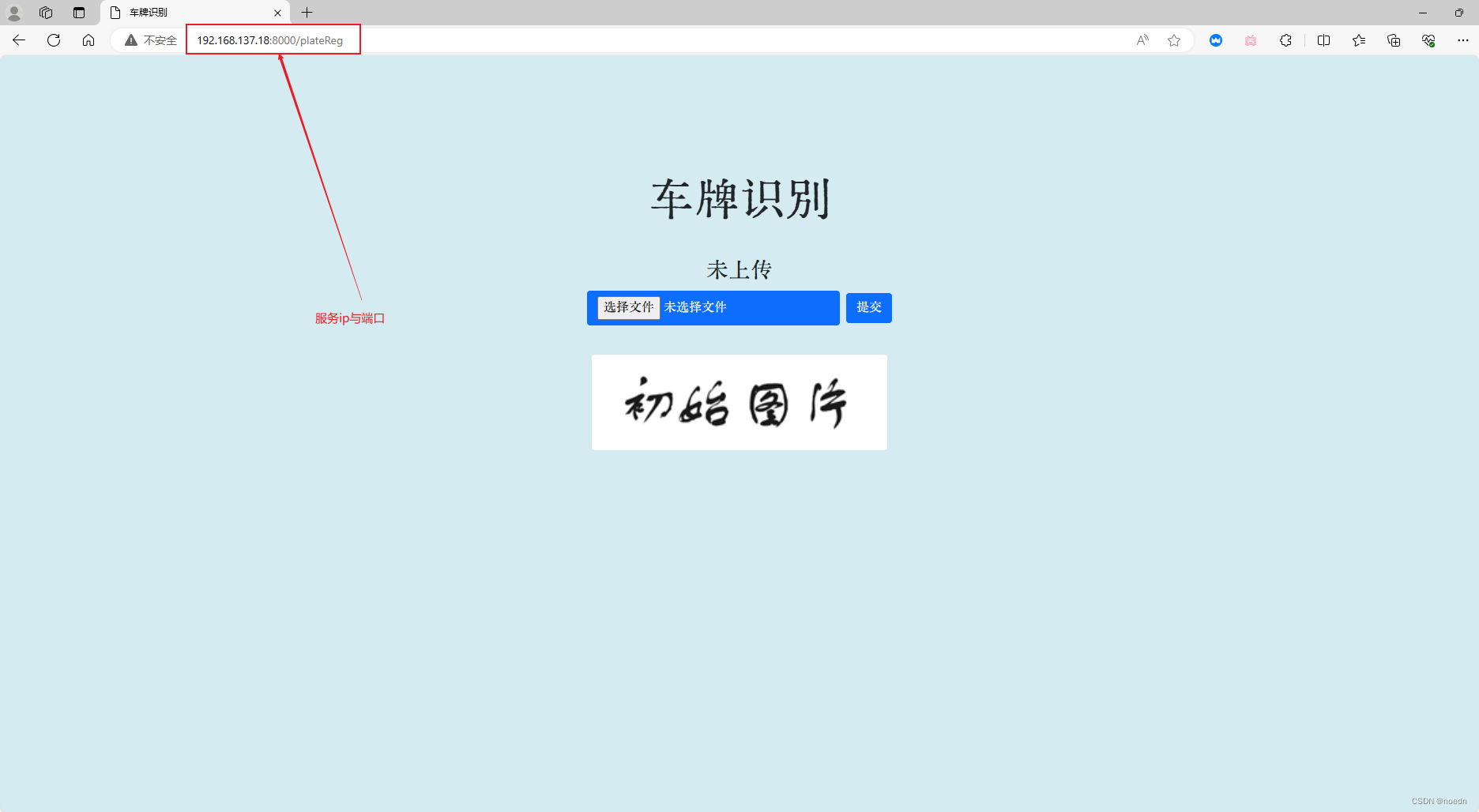
车牌识别系统主页:
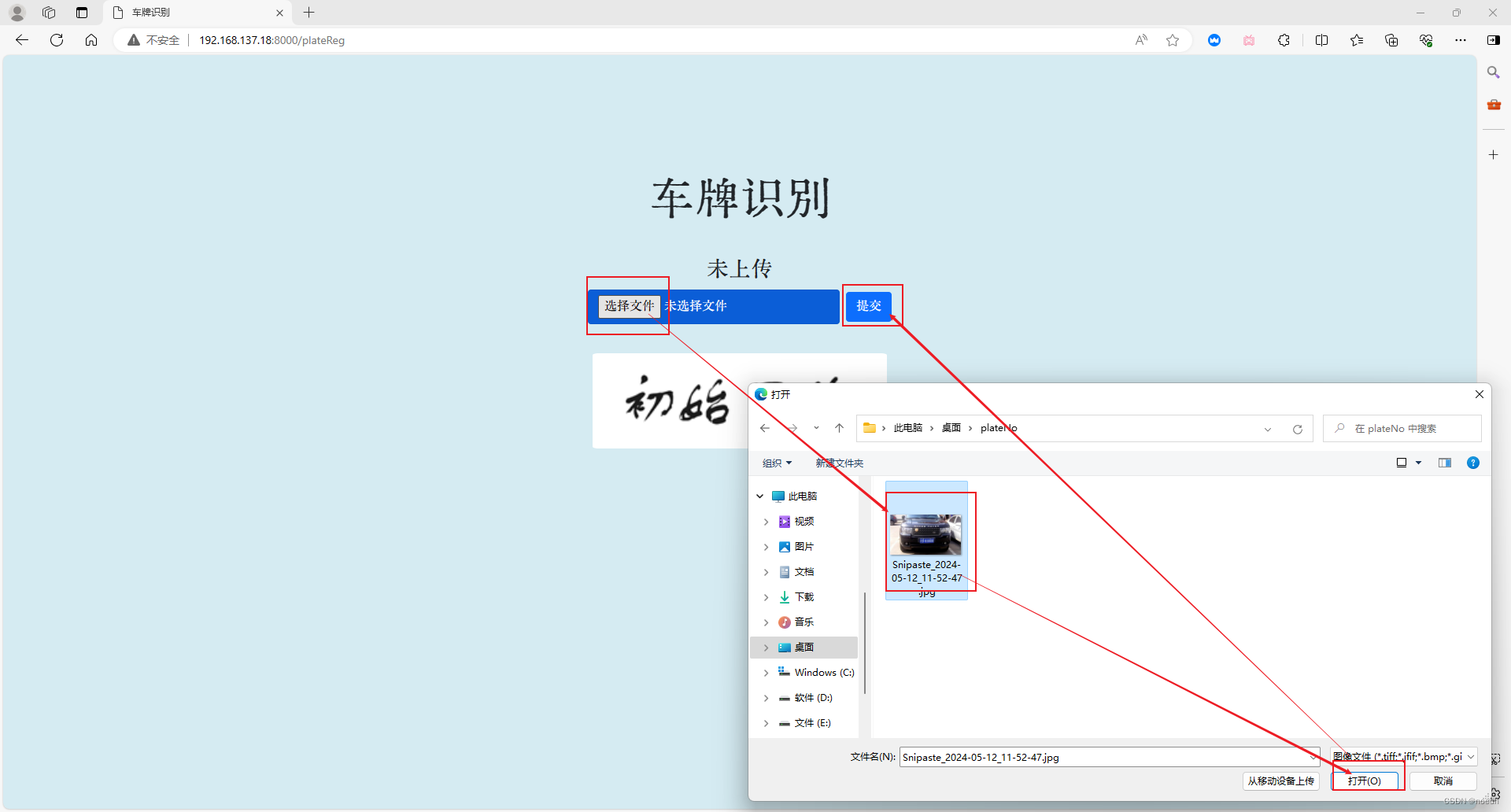
提交待识别车牌:
获取车牌识别结果与车牌抠图:

所有源代码
一、项目代码目录结构:
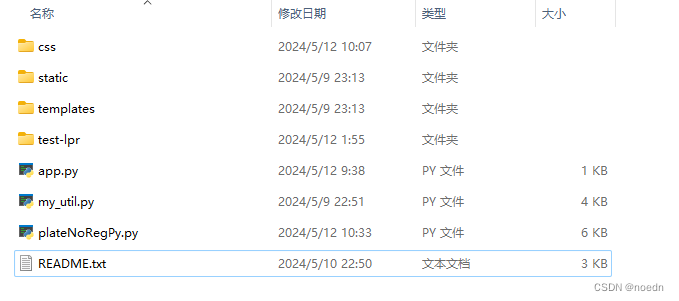
目录文件夹与文件作用说明:
1、css文件夹是boostrap框架的静态文件,用于控制web页面的样式,可以从bootstrap快捷简单的获得美观的表单;
2、static文件夹是字体(目录fonts)、web页面默认展示图片(目录src)、保存用户上传图片和经过处理的图片结果保存目录(目录img);
3、templates文件夹是web页面的html文件保存目录;
4、app.py文件是flask程序的入口函数文件;
5、mu_util.py文件是本人收集实现的一些工具函数文件;
6、plateNoRegPy.py文件是基于hyperlpr的车牌识别处理实现代码文件。
二、hyperlpr模块测试文件夹目录:

from hyperlpr import * import cv2 if __name__ == '__main__': image = cv2.imread("test.jpg") # 打印识别结果 lpr_result = HyperLPR_plate_recognition(image) print("[0]") print(lpr_result[0]) result = lpr_result[0] print("plateNo:") print(lpr_result[0][0]) print("location:") print("x1{},y1{},x2{},y2{}".format(result[2][0], result[2][1], result[2][2], result[2][3])) 三、css文件中的文件由bootstrap中下载
四、static文件夹
1、fonts文件夹
2、img文件夹,程序第一次使用前为空
3、src文件夹

五、templates文件夹
车牌识别 车牌识别
{# #} ![]() { name }}" alt="{{ name }}" class="default-img"> {% for d in data.predictions %}
{ name }}" alt="{{ name }}" class="default-img"> {% for d in data.predictions %} {{ d.label}}, 置信度:{{d.probability }}%
{% endfor %} {# { url_for('process_plateReg')}}" class="back-home">返回首页#} {# #} 六、app.py
from flask import Flask,render_template,request,redirect,send_file import os import plateNoRegPy app = Flask(__name__) # 设置配置 UPLOAD_FOLDER = os.path.join(app.root_path, 'static', 'img') app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'] = UPLOAD_FOLDER SOURCE_FOLDER = os.path.join(app.root_path, 'static', 'src') app.config['SOURCE_FOLDER'] = SOURCE_FOLDER # 注册路由和其他配置 app.register_blueprint(plateNoRegPy.blueprint) # 车牌图片识别蓝图注册 @app.route('/src/')#网页的所有文件都是来自服务器 def send_image(path): return send_file(path, mimetype='image/jpeg') @app.route('/') def hello_world(): # put application's code here return redirect('/plateReg')#跳转车牌识别 return 'Hello World!' if __name__ == '__main__': # app.run() app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8000)#服务访问ip与端口 七、plateNoRegPy.py
# 功能实现模型来源 # hyperlpr3在树莓派上可能无法安装 https://github.com/szad670401/HyperLPR?tab=readme-ov-file # https://github.com/szad670401/HyperLPR/tree/v1 import cv2 # import hyperlpr3 as lpr3 from hyperlpr import * from PIL import Image from flask import request, url_for, render_template, redirect, Blueprint, current_app from my_util import Logger, copy_file, delete_files import os import random # initialize our Flask application and the lpr object blueprint = Blueprint('processPlatNoImg', __name__) lprObject = None loger = Logger() default_pic_name = "defaultPlate.jpg" def init_default_source(): # 删除多余的图片 max_files_allowed = 30 #后续拷贝一个默认图片,加上上传图片,实际文件夹当中有32个文件 delete_files(current_app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], max_files_allowed) # 默认图片拷贝 source_path = os.path.join(current_app.config['SOURCE_FOLDER'], default_pic_name) dest_path = os.path.join(current_app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], default_pic_name) if not os.path.exists(dest_path) or not os.path.isfile(dest_path): copy_file(source_path, dest_path) # Instantiate object def load_object(): # 默认图片拷贝 source_path = os.path.join(current_app.config['SOURCE_FOLDER'], default_pic_name) dest_path = os.path.join(current_app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], default_pic_name) copy_file(source_path, dest_path) global lprObject lprObject = HyperLPR_plate_recognition ''' def load_object3(): # 默认图片拷贝 source_path = os.path.join(current_app.config['SOURCE_FOLDER'], default_pic_name) dest_path = os.path.join(current_app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], default_pic_name) copy_file(source_path, dest_path) global lprObject lprObject = lpr3.LicensePlateCatcher() ''' def prepare_image(image): loger.debug("Preparing image"+image) image = cv2.imread(image) return image def crop_image(image1, image2, x1, y1, x2, y2): # 打开图片 img = Image.open(image1) # 截取图片,参数为左上角和右下角的坐标 cropped_img = img.crop((x1, y1, x2, y2)) # 保存截取的图片 cropped_img.save(image2) loger.debug("recognize plateNo: " + image2) @blueprint.route('/plateReg', methods=['GET', 'POST']) # 访问的路径 def process_plateReg(): init_default_source() data = {"success": "未上传"} title = "Upload an image" name = default_pic_name if request.method == "POST": if request.files.get("image"): image1 = request.files["image"] imagePath = os.path.join(current_app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], image1.filename) image = image1.save(imagePath) loger.debug("接受车牌图片路径"+imagePath) processed_image = prepare_image(imagePath) data["predictions"] = [] ''' try: if lprObject == None: load_object3() loger.info("lpr object not initialzed") lpr3_results = lprObject(processed_image) except Exception as e: print("Exception load hyperlpr3", e) ''' try: if lprObject == None: load_object() loger.info("lpr object not initialzed") lpr_results = lprObject(processed_image) except Exception as e: print("Exception load hyperlpr", e) lpr_results = "" if len(lpr_results): print("lpr_results:") print(lpr_results[0]) result = lpr_results[0] # image2Name = "outputPlatNo" image2Name = result[0] + ".jpg" image2 = os.path.join(current_app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], image2Name) crop_image(imagePath, image2, result[2][0], result[2][1], result[2][2], result[2][3]) r = {"label": result[0], "probability": int(100*result[1])} else: image2Name = image1.filename r = {"label": "unkonw", "probability": int(0)} data["predictions"].append(r) # indicate that the request was a success data["success"] = "已上传" title = "predict" return render_template('plateNoReg.html', data=data, title=title, name=image2Name) return render_template('plateNoReg.html', data=data, title=title, name=name) 八、my_util.py
import os import sys import time import shutil import logging import time from datetime import datetime #进度条 def print_progress_bar(iteration, total, prefix='', suffix='', decimals=1, length=100, fill='█', print_end="\r"): """ 调用在Python终端中打印自定义进度条的函数 iteration - 当前迭代(Int) total - 总迭代(Int) prefix - 前缀字符串(Str) suffix - 后缀字符串(Str) decimals - 正数的小数位数(Int) length - 进度条的长度(Int) fill - 进度条填充字符(Str) print_end - 行尾字符(Str) """ percent = ("{0:." + str(decimals) + "f}").format(100 * (iteration / float(total))) filled_length = int(length * iteration // total) bar = fill * filled_length + '-' * (length - filled_length) print(f'\r{prefix} |{bar}| {percent}% {suffix}', end=print_end) # 打印新行,完成进度条 if iteration == total: print() class Logger(object): """ 终端打印不同颜色的日志 """ ch = logging.StreamHandler() # 创建日志处理器对象,在__init__外创建,是类当中的静态属性,不是__init__中的实例属性 # #创建静态的日志处理器可以减少内存消耗 # # 创建 FileHandler 实例,指定日志文件路径 # ch = logging.FileHandler(filename='app1.log') def __init__(self): self.logger = logging.getLogger() # 创建日志记录对象 self.logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # 设置日志等级info,其他低于此等级的不打印 def debug(self, message): self.fontColor('\033[0;37m%s\033[0m') self.logger.debug(message) def info(self, message): self.fontColor('\033[0;32m%s\033[0m') self.logger.info(message) def warning(self, message): self.fontColor('\033[0;33m%s\033[0m') self.logger.warning(message) def error(self, message): self.fontColor('\033[0;31m%s\033[0m') self.logger.error(message) def fontColor(self, color): formatter = logging.Formatter(color % '%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s') # 控制日志输出颜色 self.ch.setFormatter(formatter) self.logger.addHandler(self.ch) # 向日志记录对象中加入日志处理器对象 def delete_files(folder_path, max_files): """ 监控指定文件夹中的文件数量,并在超过max_files时删除最旧的文件。 """ print("进入删除图片文件夹"+folder_path) print("需要删除文件数量") print(max_files) if True: # 获取文件夹中的文件列表 files = os.listdir(folder_path) file_count = len(files) print(f"当前文件夹 {folder_path} 中的文件数量: {file_count}") # 如果文件数量超过max_files,则删除最旧的文件 if file_count > max_files: # 获取文件夹中所有文件的完整路径,并带上修改时间 file_paths_with_mtime = [(os.path.join(folder_path, f), os.path.getmtime(os.path.join(folder_path, f))) for f in files] # 按修改时间排序 sorted_files = sorted(file_paths_with_mtime, key=lambda x: x[1]) # 删除最旧的文件,直到文件数量在阈值以下 for file_path, mtime in sorted_files[:file_count - max_files]: try: os.remove(file_path) print(f"已删除文件: {file_path}") except OSError as e: print(f"删除文件时出错: {e.strerror}") def copy_file(src, dst): shutil.copy2(src, dst) # copy2会尝试保留文件的元数据 整体实现效果
项目代码仓库
