利用Jackson封装常用的JsonUtil工具类
创始人
2025-01-16 16:10:23
0次
在实际开发中,我们对于 JSON 数据的处理,通常有这么几个第三方工具包可以使用:
- gson:谷歌的
- fastjson:阿里巴巴的
- jackson:美国FasterXML公司的,Spring框架默认用的
由于以前一直用习惯了阿里的 fastjson,最近突然改为 jackson ,不是太习惯,所以手写一个工具类,应付一下工作中常用的一些方法。
1. 引入依赖包
在 pom.xml 文件中加入以下依赖
com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-databind 2.14.2 2. 编写 JsonUtil 工具类
package com.yuhuofei.utils; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ArrayNode; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; /** * @Description 由于习惯了用fastjson处理JSON数据,突然改成用jackson,有些不适应,所以打算用jackson封装出类似fastjson里的方法进行使用 * @ClassName JsonUtil * @Author yuhuofei * @Date 2023/8/19 14:36 * @Version 1.0 */ @Slf4j public class JsonUtil { private static ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); // 时间日期格式 private static final String STANDARD_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"; //以静态代码块初始化 static { //对象的所有字段全部列入序列化 objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.ALWAYS); //取消默认转换timestamps形式 objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false); //忽略空Bean转json的错误 objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false); //所有的日期格式都统一为以下的格式,即yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss objectMapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat(STANDARD_FORMAT)); //忽略 在json字符串中存在,但在java对象中不存在对应属性的情况。防止错误 objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false); } /**===========================以下是从JSON中获取对象====================================*/ public static T parseObject(String jsonString, Class object) { T t = null; try { t = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, object); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { log.error("JsonString转为自定义对象失败:{}", e.getMessage()); } return t; } public static T parseObject(File file, Class object) { T t = null; try { t = objectMapper.readValue(file, object); } catch (IOException e) { log.error("从文件中读取json字符串转为自定义对象失败:{}", e.getMessage()); } return t; } //将json数组字符串转为指定对象List列表或者Map集合 public static T parseJSONArray(String jsonArray, TypeReference reference) { T t = null; try { t = objectMapper.readValue(jsonArray, reference); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { log.error("JSONArray转为List列表或者Map集合失败:{}", e.getMessage()); } return t; } /**=================================以下是将对象转为JSON=====================================*/ public static String toJSONString(Object object) { String jsonString = null; try { jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(object); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { log.error("Object转JSONString失败:{}", e.getMessage()); } return jsonString; } public static byte[] toByteArray(Object object) { byte[] bytes = null; try { bytes = objectMapper.writeValueAsBytes(object); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { log.error("Object转ByteArray失败:{}", e.getMessage()); } return bytes; } public static void objectToFile(File file, Object object) { try { objectMapper.writeValue(file, object); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { log.error("Object写入文件失败:{}", e.getMessage()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /**=============================以下是与JsonNode相关的=======================================*/ //JsonNode和JSONObject一样,都是JSON树形模型,只不过在jackson中,存在的是JsonNode public static JsonNode parseJSONObject(String jsonString) { JsonNode jsonNode = null; try { jsonNode = objectMapper.readTree(jsonString); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { log.error("JSONString转为JsonNode失败:{}", e.getMessage()); } return jsonNode; } public static JsonNode parseJSONObject(Object object) { JsonNode jsonNode = objectMapper.valueToTree(object); return jsonNode; } public static String toJSONString(JsonNode jsonNode) { String jsonString = null; try { jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(jsonNode); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { log.error("JsonNode转JSONString失败:{}", e.getMessage()); } return jsonString; } //JsonNode是一个抽象类,不能实例化,创建JSON树形模型,得用JsonNode的子类ObjectNode,用法和JSONObject大同小异 public static ObjectNode newJSONObject() { return objectMapper.createObjectNode(); } //创建JSON数组对象,就像JSONArray一样用 public static ArrayNode newJSONArray() { return objectMapper.createArrayNode(); } /**===========以下是从JsonNode对象中获取key值的方法,个人觉得有点多余,直接用JsonNode自带的取值方法会好点,出于纠结症,还是补充进来了*/ public static String getString(JsonNode jsonObject, String key) { String s = jsonObject.get(key).asText(); return s; } public static Integer getInteger(JsonNode jsonObject, String key) { Integer i = jsonObject.get(key).asInt(); return i; } public static Boolean getBoolean(JsonNode jsonObject, String key) { Boolean bool = jsonObject.get(key).asBoolean(); return bool; } public static JsonNode getJSONObject(JsonNode jsonObject, String key) { JsonNode json = jsonObject.get(key); return json; } } 3. 测试
新建一个 User 类
package com.yuhuofei.entity; import lombok.Data; import java.io.Serializable; /** * @Description * @ClassName User * @Author yuhuofei * @Date 2023/8/19 14:49 * @Version 1.0 */ @Data public class User implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Integer id; private String name; private String passWord; } 新建一个测试类
import com.yuhuofei.entity.User; import com.yuhuofei.utils.JsonUtil; /** * @Description * @ClassName TestJsonUtil * @Author yuhuofei * @Date 2023/8/19 14:58 * @Version 1.0 */ public class TestJsonUtil { public static void main(String[] args) { String jsonString = "{\"id\":11,\"name\":\"小明\",\"passWord\":\"123456\"}"; User user = JsonUtil.parseObject(jsonString, User.class); System.out.println(user); } } 执行 main 方法测试,可以看到在控制台正确地输出了结果。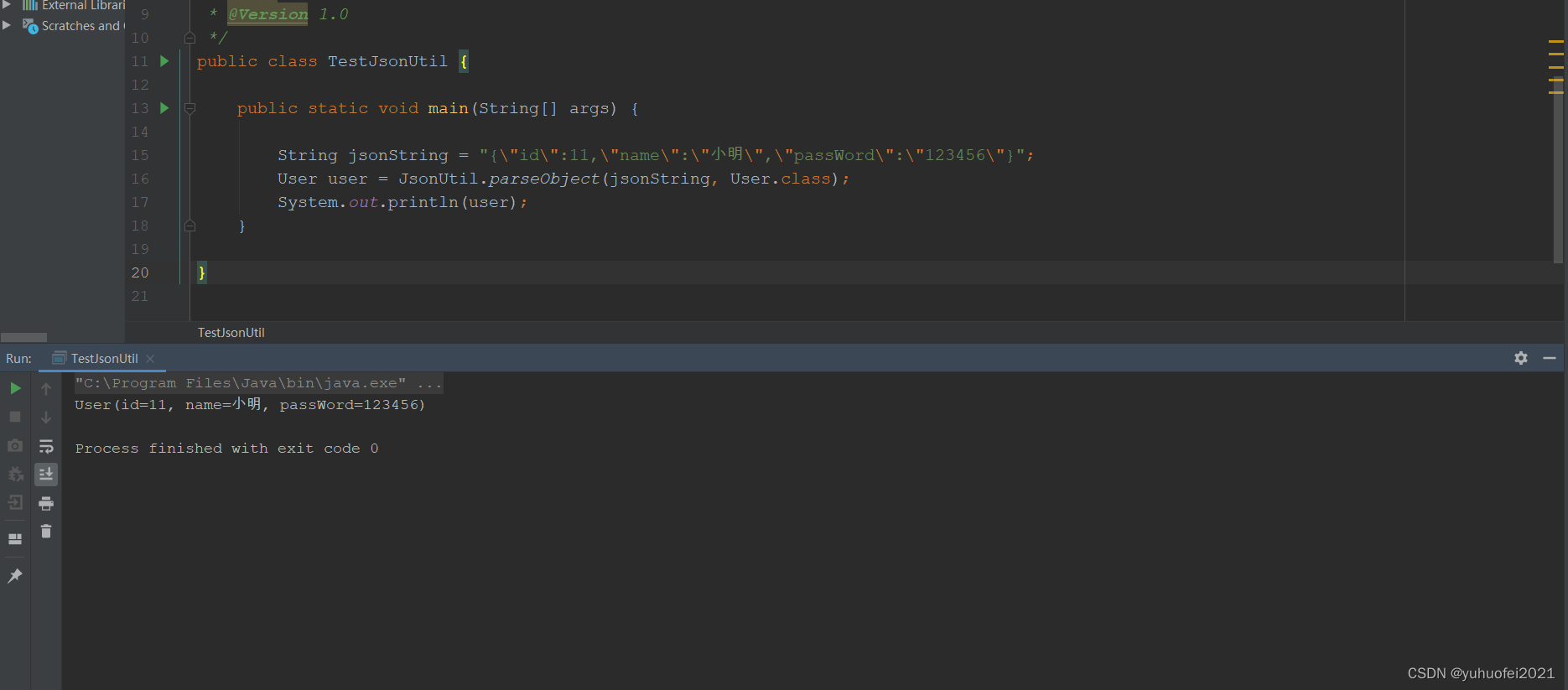
相关内容
热门资讯
wepower有外挂!hhpo...
wepower有外挂!hhpoker德州有挂(透视)存在挂教程(有挂猫腻)-哔哩哔哩;1、超多福利:...
wepokeai机器人!wej...
wepokeai机器人!wejoker透视方法(透视)细节揭秘(确实有挂)-哔哩哔哩;亲真的是有正版...
wepokeai代打的胜率!p...
wepokeai代打的胜率!pokermaster脚本(透视)黑科技教程(有挂秘笈)-哔哩哔哩是一款...
wepoke黑科技!德普之星透...
wepoke黑科技!德普之星透视辅助软件是真的(透视)教你攻略(有挂方略)-哔哩哔哩是一款可以让一直...
wepoke是真的有挂!hh ...
wepoke是真的有挂!hh poker辅助有用(透视)细节方法(有挂功能)-哔哩哔哩;最新版202...
wepokeai代打逻辑!po...
wepokeai代打逻辑!pokemmo手机版脚本免费(透视)透明教程(真的有挂)-哔哩哔哩;是一款...
wepoke有app软件!we...
wepoke有app软件!wepoker辅助工具(透视)透牌教程(有挂分析)-哔哩哔哩;wepoke...
wepok软件透明挂!哈糖大菠...
【福星临门,好运相随】;wepok软件透明挂!哈糖大菠萝软件下载(透视)2025新版教程(揭秘有挂)...
七分钟了解!新畅游互娱科技(辅...
七分钟了解!新畅游互娱科技(辅助挂)详细透视开挂辅助新2025版(切实真的有挂)-哔哩哔哩;1、首先...
wepokeai代打逻辑!德州...
wepokeai代打逻辑!德州hhpoker脚本(透视)辅助教程(有挂秘笈)-哔哩哔哩;是一款可以让...
