趣味C语言——【猜数字】小游戏
🥰欢迎关注 轻松拿捏C语言系列,来和 小哇 一起进步!✊
🎉创作不易,请多多支持🎉
🌈感谢大家的阅读、点赞、收藏和关注💕
🌹如有问题,欢迎指正 感谢
目录
代码:
rand()
srand()
time()
设置随机数范围
🌟🌟产生a~b的随机数:
运用循环、选择语句和函数,我们可以制作一个简单的猜数字小游戏,
假定游戏规则是给出一个1~100间的随机数,我们在限定次数中去猜数字
代码:
#include #include #include void menu() { printf("---------------------------------\n"); printf("---------** 1.play game **-----\n"); printf("---------** 0.exit game **-----\n"); printf("---------------------------------\n"); } int main() { int input; srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));//程序中只需要调用一次就可以了 do { menu(); int r = rand() % 100 + 1; scanf("%d", &input); printf("%d", r); switch (input) { case 1: printf("游戏开始---->"); int count = 5; int guess = 0; while (count) { printf("你还有%d次机会\n", count); printf("请猜数字:\n"); scanf("%d", &guess); if (guess > r) printf("猜大了\n"); else if (guess < r) printf("猜小了\n"); else { printf("恭喜你,猜对了\n"); break; } count--; } if (count == 0) printf("全部猜错,游戏失败\n"); break; case 0: printf("退出游戏!"); break; default: printf("输入错误,请选择1或0\n"); } } while (input); return 0; } 运行截图:
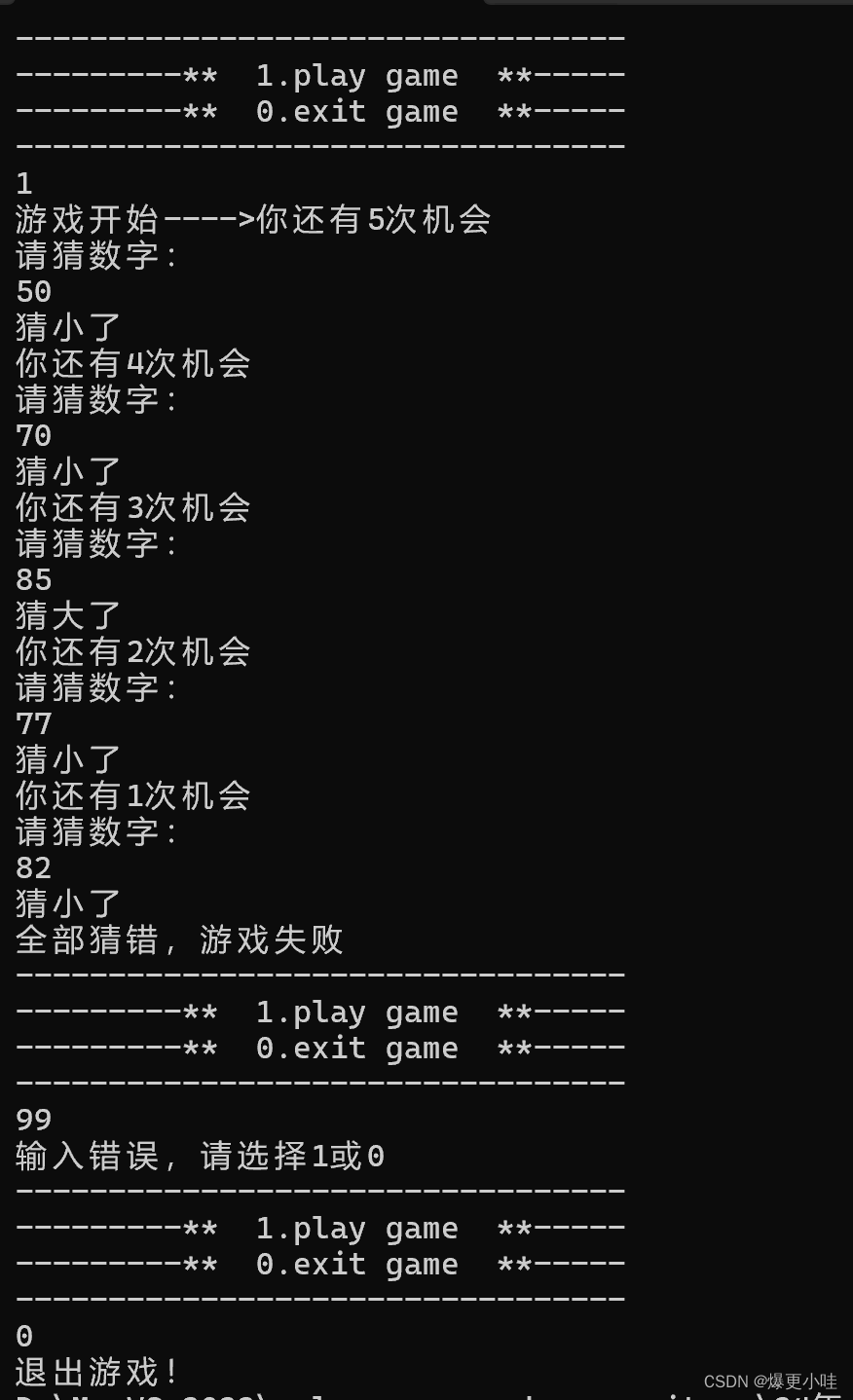
这里讲一下有关随机数生成的代码:
rand()
int rand (void);
使用要包含头文件
rand() 函数会返回一个伪随机数,伪随机数范围是0~RAND_MAX(大部分编译器上为32767)
#include #include int main() { printf("%d\n", rand()); printf("%d\n", rand()); printf("%d\n", rand()); printf("%d\n", rand()); printf("%d\n", rand()); return 0; } 第一次运行:
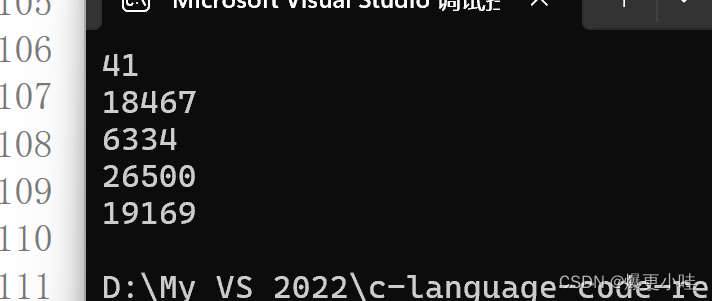
第二次运行:
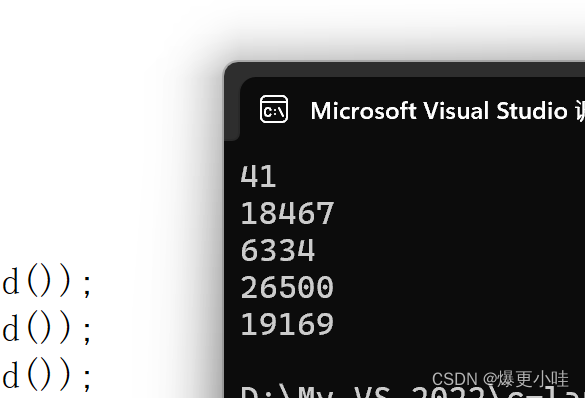
可以看到两次运行产生的随机数是一样的,这并没有实现真正的随机。
这是因为rand()函数产生的随机数是根据一个叫种子的基准值来计算的,而rand函数的种子默认为1。
所以要产生随机数我们还需要让种子也变化起来,
这里就需要srand()函数了
srand()
使用要包含头文件
void srand (unsigned int seed);
在调用rand函数前调用srand函数,通过srand函数的参数seed可以设置rand函数的种子,使种子变化起来。
srand函数通常不需要在程序中频繁调用。
在大多数情况下,你只需要在程序开始时调用一次srand函数,来设置随机数生成器的种子。
time()
使用要包含头文件
time_t time (time_t* timer);
time函数会返回程序运行时间到1970年1月1日0时0分0秒的时间差(也叫时间戳)
time函数的参数 timer 如果是非NULL的指针的话,函数也会将这个返回的差值放在timer指向的内存 中带回去。
如果 timer 是NULL,就只返回这个时间的差值。
所以我们可以搭配这三个函数使用来产生真正的随机数:
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
rand();
设置随机数范围
上面游戏中我们需要产生1~100的随机数,
写的 int r = rand()%100 + 1;
如果要产生0~99的随机数:
rand()%100;
产生100~200的随机数:
100+rand()%101或写成100+rand()%(200-100+1)
🌟🌟产生a~b的随机数:
a + rand()%(b-a+1)

🎉🎉🎉本文内容结束啦,希望各位大佬多多指教!
🌹🌹感谢大家三连支持
💕敬请期待下篇文章吧~

