【C++】模版

目录
- 一、泛型编程
- 二、函数模板
- 2.1 函数模板概念
- 2.2 函数模板格式
- 2.3 函数模板的原理
- 2.4 函数模板的实例化
- 2.5 模板参数的匹配原则
- 三、类模板
- 3.1 类模板的定义格式
- 3.2 类模板的实例化
- 四、非类型模板参数
- 五、模板的特化
- 5.1 概念
- 5.2 函数模板特化
- 5.3 类模板特化
- 5.3.1 全特化
- 5.3.2 偏特化
- 5.3.3 类模板特化应用示例
- 六、模板分离编译
- 6.1 什么是分离编译
- 6.2 模板的分离编译
- 6.3 解决方法
- 七、模板总结
- 结尾
一、泛型编程
如何实现一个通用的交换函数呢?
void Swap(int& left, int& right) { int temp = left; left = right; right = temp; } void Swap(double& left, double& right) { double temp = left; left = right; right = temp; } void Swap(char& left, char& right) { char temp = left; left = right; right = temp; } ...... 使用函数重载虽然可以实现,但是有一下几个不好的地方:
- 重载的函数仅仅是类型不同,代码复用率比较低,只要有新类型出现时,就需要用户自己增加对应的函数
- 代码的可维护性比较低,一个出错可能所有的重载均出错
那能否告诉编译器一个模子,让编译器根据不同的类型利用该模子来生成代码呢?
如果在C++中,也能够存在这样一个模具,通过给这个模具中填充不同材料(类型),来获得不同材料的铸件(即生成具体类型的代码),那将会节省许多头发。巧的是前人早已将树栽好,我们只需在此乘凉。
泛型编程:编写与类型无关的通用代码,是代码复用的一种手段。模板是泛型编程的基础。
二、函数模板
2.1 函数模板概念
函数模板代表了一个函数家族,该函数模板与类型无关,在使用时被参数化,根据实参类型产生函数的特定类型版本。
2.2 函数模板格式
template
返回值类型 函数名(参数列表){}
template void Swap(T& left, T& right) { T temp = left; left = right; right = temp; } 注意:typename是用来定义模板参数关键字,也可以使用class(切记:不能使用struct代替class)
2.3 函数模板的原理
函数模板是一个蓝图,它本身并不是函数,是编译器用使用方式产生特定具体类型函数的模具。所以其实模板就是将本来应该我们做的重复的事情交给了编译器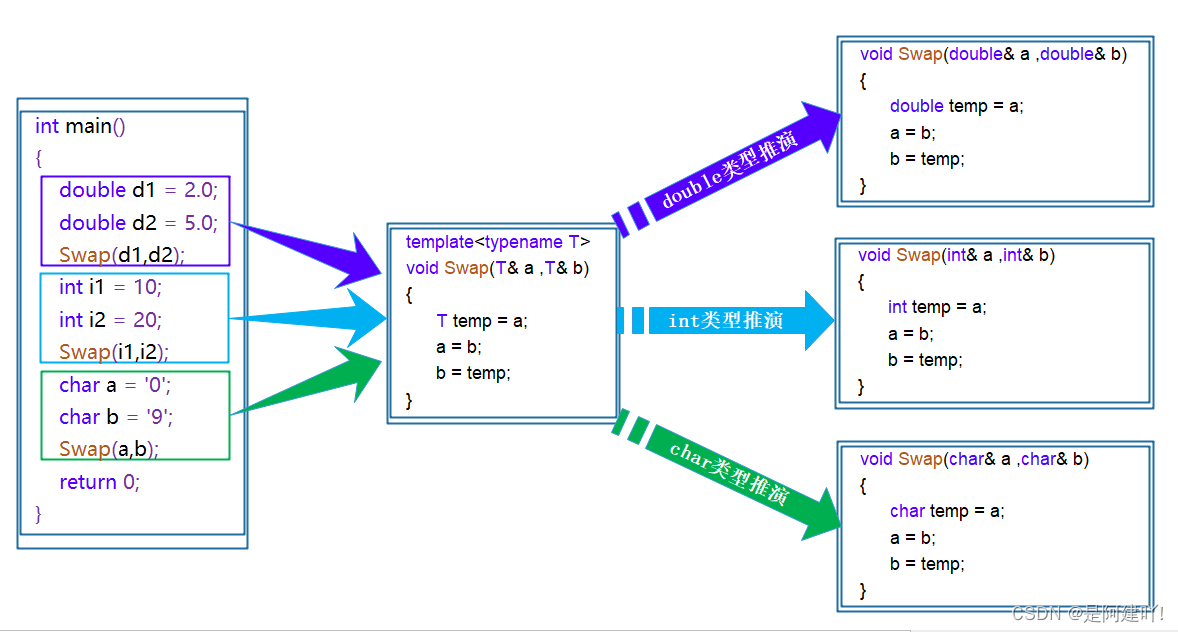
在编译器编译阶段,对于模板函数的使用,编译器需要根据传入的实参类型来推演生成对应类型的函数以供调用。比如:当用double类型使用函数模板时,编译器通过对实参类型的推演,将T确定为double类型,然后产生一份专门处理double类型的代码,对于字符类型也是如此。
2.4 函数模板的实例化
用不同类型的参数使用函数模板时,称为函数模板的实例化。模板参数实例化分为:隐式实例化和显式实例化。
1. 隐式实例化:让编译器根据实参推演模板参数的实际类型
int main() { int a1 = 10, a2 = 20; double d1 = 10.0, d2 = 20.0; Add(a1, a2); Add(d1, d2); /* 该语句不能通过编译,因为在编译期间,当编译器看到该实例化时,需要推演其实参类型 通过实参a1将T推演为int,通过实参d1将T推演为double类型,但模板参数列表中只有一个T, 编译器无法确定此处到底该将T确定为int 或者 double类型而报错 注意:在模板中,编译器一般不会进行类型转换操作,因为一旦转化出问题,编译器就需要背黑锅 Add(a1, d1); */ // 此时有两种处理方式:1. 用户自己来强制转化 2. 使用显式实例化 Add(a1, (int)d1); Add((double)a1, d1); return 0; } 2. 显式实例化:在函数名后的<>中指定模板参数的实际类型
template T Add(const T& left, const T& right) { return left + right; } int main() { int a = 10; double b = 20.0; // 显式实例化 Add(a, b); return 0; } 如果类型不匹配,编译器会尝试进行隐式类型转换,如果无法转换成功编译器将会报错。
2.5 模板参数的匹配原则
- 一个非模板函数可以和一个同名的函数模板同时存在,而且该函数模板还可以被实例化为这个非模板函数
// 专门处理int的加法函数 int Add(int left, int right) { return left + right; } // 通用加法函数 template T Add(T left, T right) { return left + right; } int main() { Add(1, 2); // 与非模板函数匹配,编译器不需要特化 Add(1, 2); // 调用编译器特化的Add版本 return 0; } - 对于非模板函数和同名函数模板,如果其他条件都相同,在调动时会优先调用非模板函数而不会从该模板产生出一个实例。如果模板可以产生一个具有更好匹配的函数, 那么将选择模板
// 专门处理int的加法函数 int Add(int left, int right) { return left + right; } // 通用加法函数 template T1 Add(T1 left, T2 right) { return left + right; } int main() { Add(1, 2); // 与非函数模板类型完全匹配,不需要函数模板实例化 Add(1, 2.0); // 模板函数可以生成更加匹配的版本,编译器根据实参生成更加匹配的Add函数 return 0; } - 模板函数不允许自动类型转换,但普通函数可以进行自动类型转换
三、类模板
3.1 类模板的定义格式
template class 类模板名 { // 类内成员定义 }; // 动态顺序表 // 注意:Vector不是具体的类,是编译器根据被实例化的类型生成具体类的模具 template class Vector { public: Vector(size_t capacity = 10) : _pData(new T[capacity]) , _size(0) , _capacity(capacity) {} // 使用析构函数演示:在类中声明,在类外定义。 ~Vector(); void PushBack(const T& data); void PopBack(); // ... size_t Size() { return _size; } T& operator[](size_t pos) { assert(pos < _size); return _pData[pos]; } private: T* _pData; size_t _size; size_t _capacity; }; // 注意:类模板中函数放在类外进行定义时,需要加模板参数列表 template Vector::~Vector() { if (_pData) delete[] _pData; _size = _capacity = 0; } 3.2 类模板的实例化
类模板实例化与函数模板实例化不同,类模板实例化需要在类模板名字后跟<>,然后将实例化的类型放在<>中即可,类模板名字不是真正的类,而实例化的结果才是真正的类
// Vector类名,Vector才是类型 Vector s1; Vector s2; 四、非类型模板参数
模板参数分类类型形参与非类型形参。
类型形参即:出现在模板参数列表中,跟在class或者typename之类的参数类型名称。
非类型形参,就是用一个常量作为类(函数)模板的一个参数,在类(函数)模板中可将该参数当成常量来使用。
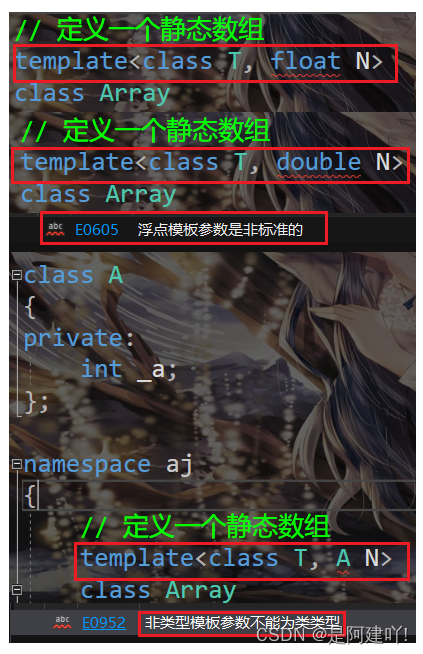
namespace aj { // 定义一个静态数组 template class Array { T& operator[](size_t position) { return _arr[position]; } const T& operator[](size_t position) { return _arr[position]; } bool empty() { return _size == 0; } size_t size() { return _size; } private: T _arr[N]; size_t _size; }; } 注意:
只有整形类型的对象可以作为非类型模版参数,浮点数、类对象以及字符串是不允许作为非类型模板参数的。
非类型的模板参数必须在编译期就能确认结果。
五、模板的特化
5.1 概念
通常情况下,使用模板可以实现一些与类型无关的代码,但对于一些特殊类型的可能会得到一些错误的结果,需要特殊处理,比如:实现了一个专门用来进行小于比较的函数模板
class Date { public: // 获取某年某月的天数 int GetMonthDay(int year, int month) { static int MonthDay[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0)) { return 29; } return MonthDay[month]; } // 全缺省的构造函数 Date(int year = 1970, int month = 1, int day = 1) :_year(year) , _month(month) , _day(day) {} bool operator<(const Date& d)const { if (_year < d._year) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day) { return true; } else { return false; } } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; template bool Less(const T& t1, const T& t2) { return t1 < t2; } int main() { cout << Less(520, 521) << endl; // 结果正确 Date date1(2023, 8, 8); Date date2(2023, 6, 6); cout << Less(date1, date2) << endl; // 结果正确 Date* p1 = new Date(2023, 8, 8); Date* p2 = new Date(2023, 6, 6); cout << Less(*p1, *p2) << endl; // 结果正确 // 这里我们需要比较的是指针指向的内容,而不是指针本身 // 并且由于Date是new出来的,并不能保证先new的对象地址一定小 // 所以比较的结果是随机的,并不是我们所需要的结果 cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl; // 结果错误 return 0; } 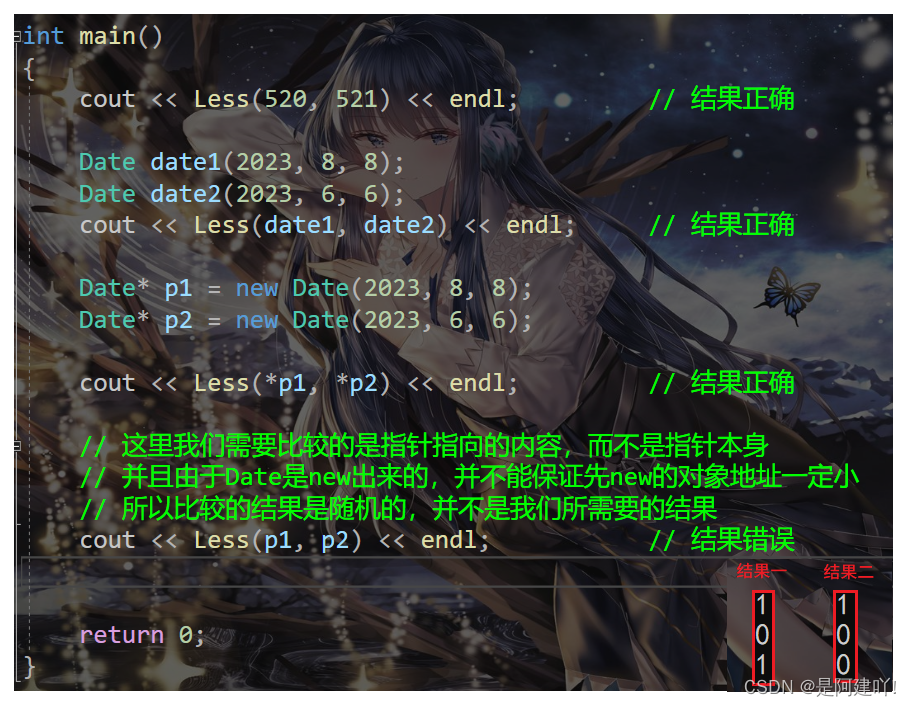
可以看到,Less绝对多数情况下都可以正常比较,但是在特殊场景下就得到错误的结果。上述示例中,p1指向的d1显然小于p2指向的d2对象,但是Less内部并没有比较p1和p2指向的对象内容,而比较的是p1和p2指针的地址,这就无法达到预期而错误。
此时,就需要对模板进行特化。即:在原模板类的基础上,针对特殊类型所进行特殊化的实现方式。模板特化中分为函数模板特化与类模板特化。
5.2 函数模板特化
函数模板的特化步骤:
- 必须要先有一个基础的函数模板
- 关键字template后面接一对空的尖括号<>
- 函数名后跟一对尖括号,尖括号中指定需要特化的类型
- 函数形参表: 必须要和模板函数的基础参数类型完全相同,如果不同编译器可能会报一些奇怪的错误。
class Date { public: // 获取某年某月的天数 int GetMonthDay(int year, int month) { static int MonthDay[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0)) { return 29; } return MonthDay[month]; } // 全缺省的构造函数 Date(int year = 1970, int month = 1, int day = 1) :_year(year) , _month(month) , _day(day) {} bool operator<(const Date& d)const { if (_year < d._year) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day) { return true; } else { return false; } } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; template bool Less( T t1, T t2) { return t1 < t2; } // 特化 template<> bool Less(Date* t1, Date* t2) { return *t1 < *t2; } int main() { cout << Less(520, 521) << endl; // 结果正确 Date date1(2023, 8, 8); Date date2(2023, 6, 6); cout << Less(date1, date2) << endl; // 结果正确 Date* p1 = new Date(2023, 8, 8); Date* p2 = new Date(2023, 6, 6); cout << Less(*p1, *p2) << endl; // 结果正确 // 这里p1和p2的类型为Date* // 那么调用Less函数时会调用特化后的版本,而不会再显示实例化 cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl; // 结果正确 return 0; } 注意:一般情况下如果函数模板遇到不能处理或者处理有误的类型,为了实现简单通常都是将该函数直接给出。
template bool Less( T t1, T t2) { return t1 < t2; } // 特化 template<> bool Less(Date* t1, Date* t2) { return *t1 < *t2; } // 直接给出 bool Less(Date* t1, Date* t2) { return *t1 < *t2; } 该种实现简单明了,代码的可读性高,容易书写,因为对于一些参数类型复杂的函数模板,特化时特别给出,因此函数模板不建议特化。
5.3 类模板特化
5.3.1 全特化
全特化即是将模板参数列表中所有的参数都确定化。
template class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class(T1, T2)" << endl; } private: T1 _t1; T2 _t2; }; template<> class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class(double, int)" << endl; } private: double _t1; int _t2; }; int main() { Class c1; Class c2; return 0; } 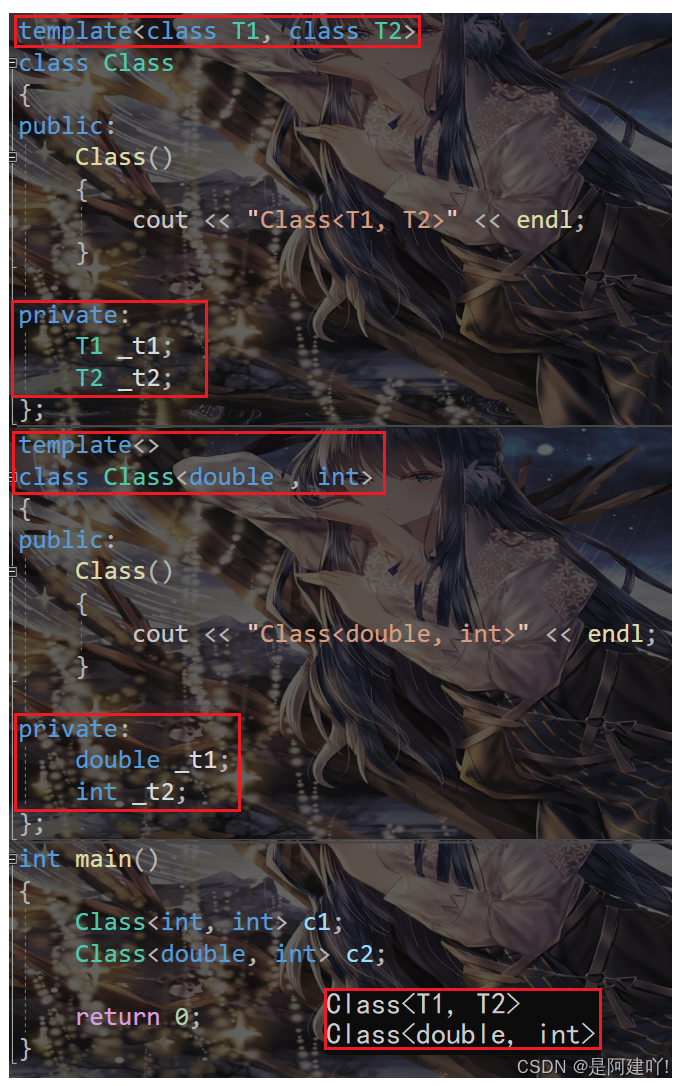
5.3.2 偏特化
偏特化:任何针对模版参数进一步进行条件限制设计的特化版本。比如对于以下模板类:
template class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class(T1, T2)" << endl; } private: T1 _t1; T2 _t2; }; template class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class(double, T1)" << endl; } private: double _t1; int _t2; }; int main() { Class c1; Class c2; return 0; } 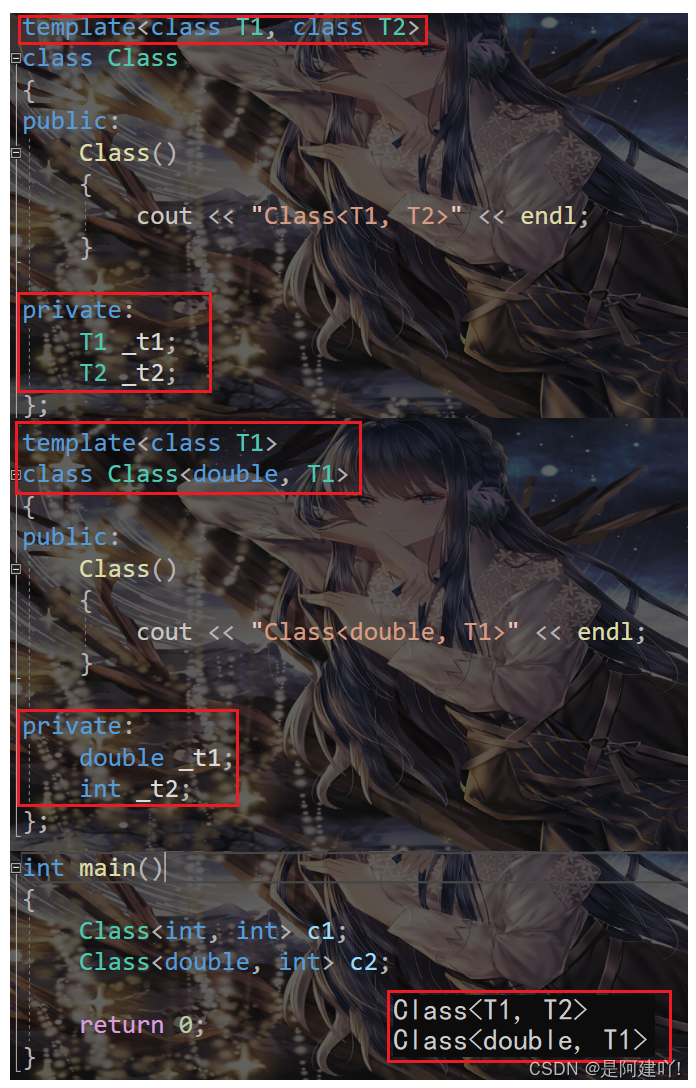
偏特化有以下两种表现方式:
- 部分特化
将模板参数类表中的一部分参数特化
template class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class" << endl; } private: T1 _t1; T2 _t2; }; // 将第一个参数特化为double template class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class" << endl; } private: double _t1; T1 _t2; }; - 参数更进一步的限制
偏特化并不仅仅是指特化部分参数,而是针对模板参数更进一步的条件限制所设计出来的一个特化版本
template class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class" << endl; } private: T1 _t1; T2 _t2; }; template class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class" << endl; } private: double _t1; T1 _t2; }; template class Class { public: Class() { cout << "Class" << endl; } private: T1 _t1; T2 _t2; }; template class Class { public: Class(const T1& t1 , const T2& t2) :_t1(t1) ,_t2(t2) { cout << "Class" << endl; } private: const T1& _t1; const T2& _t2; }; int main() { Class c1; // 调用基本的类模版 Class c2; // 调用特化double的类模版 Class c3; // 调用特化为指针版本的类模版 Class c4(1,2); // 调用特化为引用版本的类模版 return 0; } 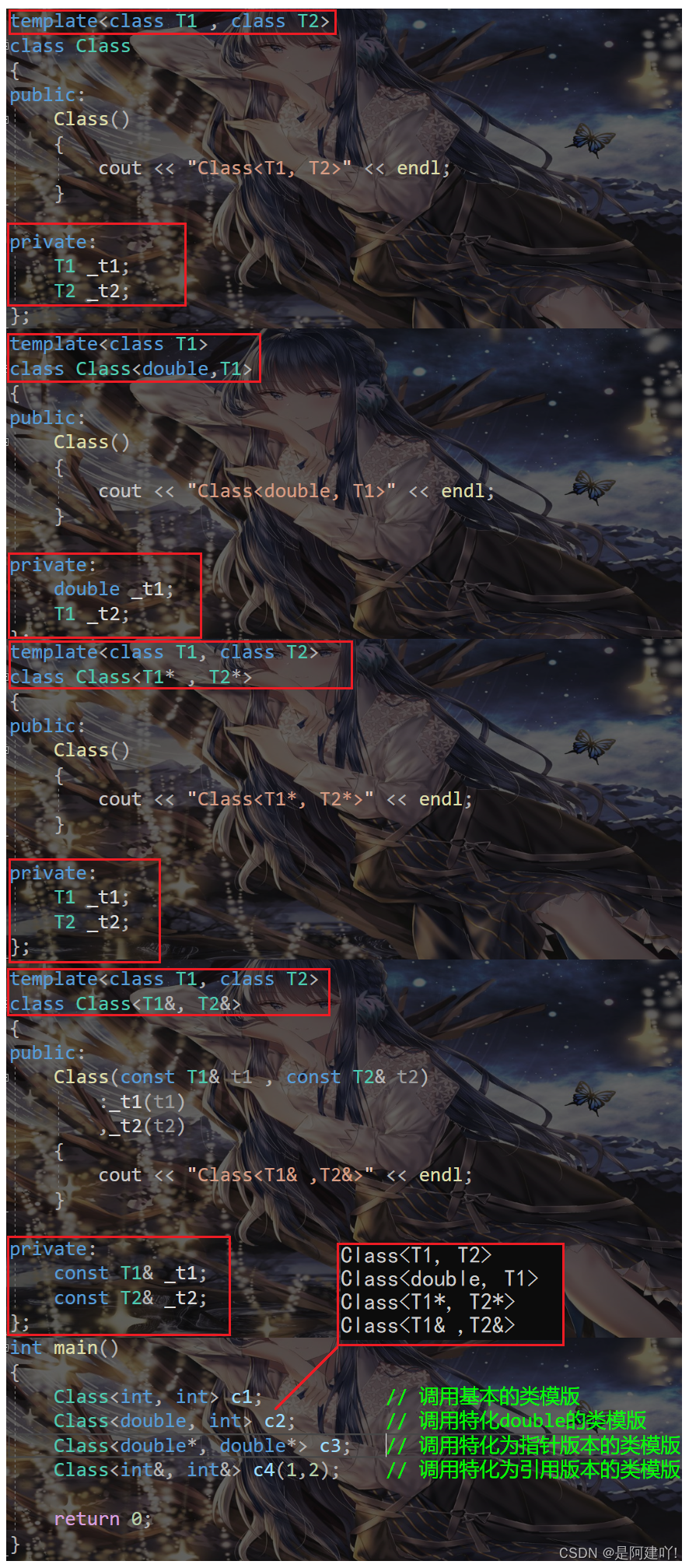
5.3.3 类模板特化应用示例
有如下专门用来按照小于比较的类模板Less:
#include #include class Date { public: // 获取某年某月的天数 int GetMonthDay(int year, int month) { static int MonthDay[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0)) { return 29; } return MonthDay[month]; } // 全缺省的构造函数 Date(int year = 1970, int month = 1, int day = 1) :_year(year) , _month(month) , _day(day) {} bool operator<(const Date& d)const { if (_year < d._year) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day) { return true; } else { return false; } } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; template struct Less { bool operator()(const T& t1, const T& t2)const { return t1 < t2; } }; int main() { Date d1(2000, 1, 1); Date d2(1949, 10, 1); Date d3(2023, 8, 8); vector v; v.push_back(d1); v.push_back(d2); v.push_back(d3); sort(v.begin(), v.end(), Less()); Date* p1 = new Date(2000, 1, 1); Date* p2 = new Date(1949, 10, 1); Date* p3 = new Date(2023, 8, 8); vector vv; vv.push_back(p1); vv.push_back(p2); vv.push_back(p3); sort(vv.begin(), vv.end(), Less()); return 0; } 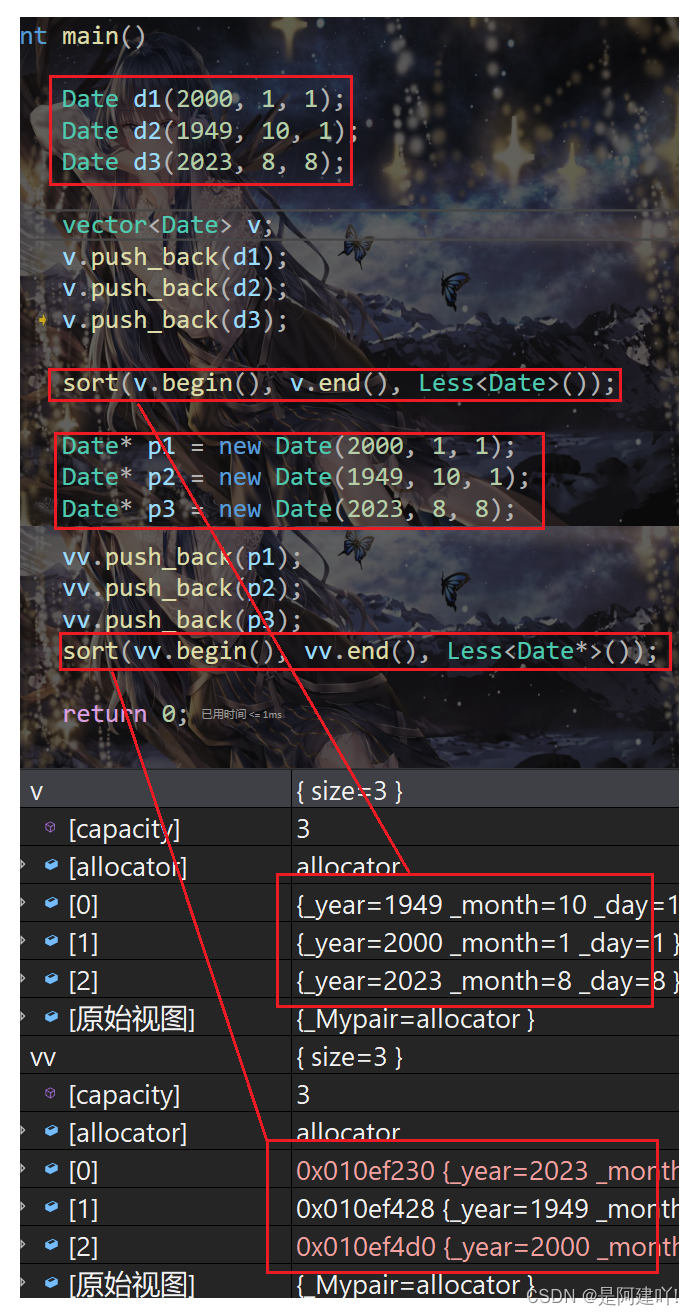
上述代码使用sort排序Date对象时可以正常完成,但是由于后面Date对象是new出来的,并不会因为先new地址就会小,所以使用sort排序时,会按照指针的大小进行排序,那么结果就是错误的。可以使用类模版特化来解决该问题。
template struct Less { bool operator()(const T& t1, const T& t2)const { return t1 < t2; } }; // 只要是Date类型的指针就解引用再进行比较 template<> struct Less { bool operator()(Date* t1, Date* t2)const { return *t1 < *t2; } }; // 只要是指针就进行解引用再进行比较 template struct Less { bool operator()(T* t1,T* t2)const { return *t1 < *t2; } }; 六、模板分离编译
6.1 什么是分离编译
一个程序(项目)由若干个源文件共同实现,而每个源文件单独编译生成目标文件,最后将所有目标文件链接起来形成单一的可执行文件的过程称为分离编译模式。
6.2 模板的分离编译
假如有以下场景,模板的声明与定义分离开,在头文件中进行声明,源文件中完成定义:
// a.h template T Add(const T& left, const T& right); // a.cpp template T Add(const T& left, const T& right) { return left + right; } // main.cpp #include"a.h" int main() { Add(1, 2); Add(1.0, 2.0); return 0; } 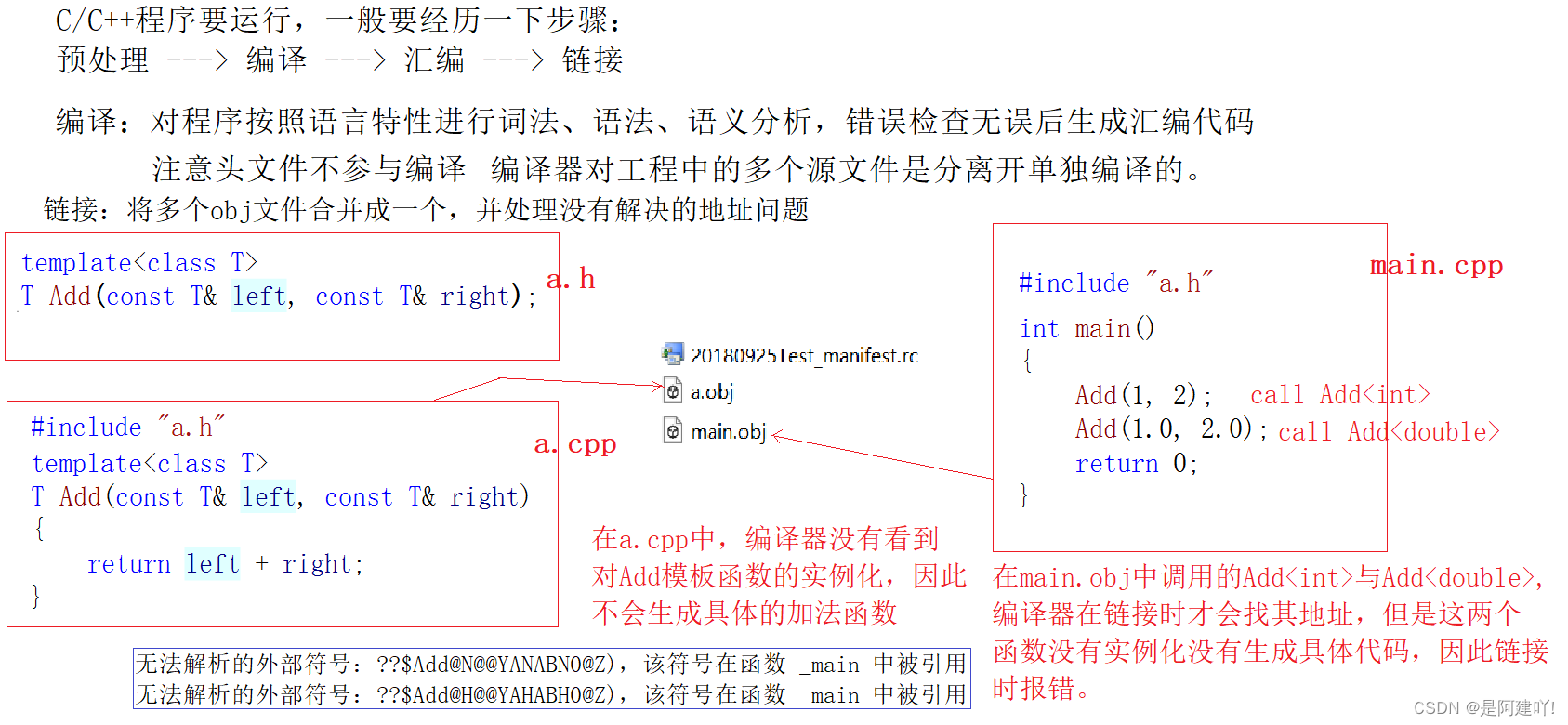
6.3 解决方法
- 将声明和定义放到一个文件 “xxx.hpp” 里面或者xxx.h其实也是可以的。推荐使用这种。
- 模板定义的位置显式实例化。这种方法不实用,不推荐使用。
七、模板总结
【优点】
- 模板复用了代码,节省资源,更快的迭代开发,C++的标准模板库(STL)因此而产生
- 增强了代码的灵活性
【缺陷】
- 模板会导致代码膨胀问题,也会导致编译时间变长
- 出现模板编译错误时,错误信息非常凌乱,不易定位错误
结尾
如果有什么建议和疑问,或是有什么错误,大家可以在评论区中提出。
希望大家以后也能和我一起进步!!🌹🌹
如果这篇文章对你有用的话,请大家给一个三连支持一下!!🌹🌹