解密Spring Boot:深入理解条件装配与条件注解

文章目录
- 一、条件装配概述
- 1.1 条件装配的基本原理
- 1.2 条件装配的作用
- 二、常用注解
- 2.1 @ConditionalOnClass
- 2.2 @ConditionalOnBean
- 2.3 @ConditionalOnProperty
- 2.4 @ConditionalOnExpression
- 2.5 @ConditionalOnMissingBean
- 三、条件装配的实现原理
- 四、实际案例
一、条件装配概述
1.1 条件装配的基本原理
条件装配的基本原理是根据特定的条件来决定是否应用特定的配置或组件。在 Spring Boot 中,条件装配是通过条件注解来实现的。
条件注解是一种特殊的注解,用于标记在配置类、组件类或方法上。它们根据某些条件的结果来决定是否应用相应的配置或组件。
条件注解的基本原理:
- 条件判断:Spring 在处理配置类或组件时,会对标记了条件注解的类或方法进行条件判断。
- 条件匹配:条件注解中定义的条件匹配器会根据特定的条件,如类路径是否存在、Bean 是否存在、属性是否被设置等,对环境进行判断,如果条件满足则返回 true,否则返回 false。
- 条件注解处理器:Spring 容器会使用条件注解处理器来处理条件注解,根据条件匹配的结果来决定是否应用相应的配置或组件。
- 应用配置或组件:根据条件注解的处理结果,Spring 容器会决定是否应用相应的配置或组件。如果条件满足,则进行相应的配置或组件的注册和初始化;如果条件不满足,则忽略该配置或组件。
1.2 条件装配的作用
条件装配的作用在于根据特定的条件来决定是否应用特定的配置或组件,从而实现灵活性和可配置性。
条件装配实现的作用:
- 环境适配:通过条件装配,可以根据当前的运行环境(如开发环境、测试环境、生产环境)或者配置(如不同的数据库、不同的服务提供商)来动态地选择合适的配置或组件,从而使应用程序适应不同的环境。
- 可插拔性:条件装配可以根据应用程序的需求动态地选择性地应用不同的配置或组件,使得应用程序的功能可以根据需求进行扩展或者替换,从而增强了应用程序的可插拔性和可扩展性。
- 简化配置:通过条件装配,可以根据特定的条件自动地应用相应的配置或组件,而无需手动配置或编写复杂的条件判断逻辑,从而简化了配置过程,提高了配置的易用性和可维护性。
- 优化性能:通过条件装配,可以根据特定的条件选择性地应用相应的配置或组件,避免不必要的资源消耗,从而优化了应用程序的性能和资源利用率。
二、常用注解
2.1 @ConditionalOnClass
@ConditionalOnClass是 Spring Boot 中的一个条件注解,用于在类路径中存在指定的类时才会应用相应的配置。
定义了一个灵活的条件注解 ConditionalOnClass,它可以根据类路径中特定类的存在与否来决定是否应用相应的配置或组件。
示例和用法说明:
/** * 只有当应用程序的类路径中存在 RedisTemplate 类时,RedisConfiguration 类中定义的 redisTemplate() 方法才会被注册为 Bean,并被 Spring 容器管理 * 如果类路径中不存在 RedisTemplate 类,则该配置类中的 Bean 将被忽略 */ @Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate.class}) public class RedisConfiguration { @Bean public RedisTemplate redisTemplate() { RedisTemplate redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>(); // 配置 RedisTemplate 的相关属性 return redisTemplate; } } 2.2 @ConditionalOnBean
@ConditionalOnBean是 Spring Framework 中的一个条件注解,它的作用是在容器中存在指定的 Bean 时,才会应用相应的配置或组件。如果指定的 Bean 不存在,则该配置或组件将被忽略。
定义了一个具有多个属性的注解 ConditionalOnBean,可以用于指定条件判断所依赖的类、名称、注解等信息,以及搜索依赖 Bean 的策略和泛型容器中的参数化类型。

示例和用法说明:
- 基本用法:
/** * MyService 类被标记为 @ConditionalOnBean(MyBean.class),这意味着只有当容器中存在 MyBean 类型的 Bean 时,MyService 才会被创建并添加到容器中 */ @Configuration public class MyConfiguration { @Bean public MyBean myBean() { return new MyBean(); } @ConditionalOnBean(MyBean.class) @Bean public MyService myService() { return new MyService(); } } - 多个 Bean 的情况:
/** * MyService 类被标记为 @ConditionalOnBean({MyBean.class, AnotherBean.class}),这意味着只有当容器中同时存在 MyBean 和 AnotherBean 类型的 Bean 时,MyService 才会被创建并添加到容器中 */ @Configuration public class MyConfiguration { @Bean public MyBean myBean() { return new MyBean(); } @Bean public AnotherBean anotherBean() { return new AnotherBean(); } @ConditionalOnBean({MyBean.class, AnotherBean.class}) @Bean public MyService myService() { return new MyService(); } } - 使用名称来指定 Bean:
/** * MyService 类被标记为 @ConditionalOnBean(name = {"myBean", "anotherBean"}),这意味着只有当容器中同时存在名称为 "myBean" 和 "anotherBean" 的 Bean 时,MyService 才会被创建并添加到容器中 */ @Configuration public class MyConfiguration { @Bean(name = "myBean") public MyBean myBean() { return new MyBean(); } @Bean(name = "anotherBean") public AnotherBean anotherBean() { return new AnotherBean(); } @ConditionalOnBean(name = {"myBean", "anotherBean"}) @Bean public MyService myService() { return new MyService(); } } 2.3 @ConditionalOnProperty
@ConditionalOnProperty注解是 Spring Framework 中的条件注解之一,用于基于配置属性的存在与否来决定是否应用某个配置。
定义了一个具有多个属性的注解 ConditionalOnProperty,它可以用于根据配置文件中的属性值来决定是否应用某个配置。
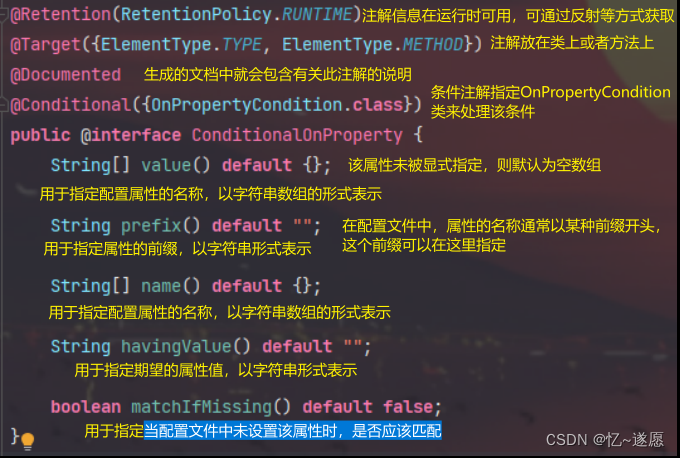
示例和说明:
/** * @ConditionalOnProperty 注解指定了一个名为myapp.feature.enabled 的属性,当这个属性存在并且其值为"true"时,MyFeatureConfiguration 配置类中的配置会生效 * havingValue 参数指定了期望的属性值,如果没有指定havingValue,则默认匹配任何非空值 * matchIfMissing 参数指定了当配置文件中未设置该属性时,是否应该匹配。如果设置为 true,则表示当属性不存在时也匹配,这样可以设置默认行为 */ @Configuration @ConditionalOnProperty( name = "myapp.feature.enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true ) public class MyFeatureConfiguration { } myapp.feature.enabled=true 2.4 @ConditionalOnExpression
@ConditionalOnExpression是 Spring 框架中的一个条件注解,在应用配置时根据 SpEL表达式的结果来决定是否进行配置。它允许我们使用更灵活的表达式来控制配置的条件。
定义了一个具有一个属性的注解 ConditionalOnExpression,它可以根据 SpEL 表达式的结果来决定是否应用某个配置。

示例和说明:
/** * 检查配置文件中的 my.config.enabled 属性是否等于 'true' * 如果等于 'true',则表达式结果为 true`,MyBean 实例将会被创建 * 否则,表达式结果为 false,配置将被忽略,不会创建 MyBean 实例 */ @Configuration public class MyConfig { @Bean @ConditionalOnExpression("#{environment.getProperty('my.config.enabled') == 'true'}") public MyBean myBean() { // 配置生效时创建 MyBean 实例 return new MyBean(); } } 2.5 @ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean是一个 Spring Boot 中常用的条件注解,它的作用是:当容器中不存在指定的 Bean 时,才会进行配置。
定义了一个具有多个属性的注解 ConditionalOnMissingBean,用于根据存在或缺少特定类型的 bean 来决定是否应用某个配置。

示例和说明:
/** * 使用 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 注解来判断容器中是否已经存在了 MyService 类型的 Bean * 如果不存在,则创建一个 MyServiceImpl 实例并返回 * 否则,不进行任何操作。 */ @Configuration public class MyConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(MyService.class) public MyService myService() { return new MyServiceImpl(); } } 三、条件装配的实现原理
条件装配的实现原理主要基于Spring的IoC容器和@Conditional注解。
在Spring的IoC容器中,BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor是两个核心的接口,它们允许我们在bean的创建和配置过程中添加额外的逻辑。(想要了解源码,读者可以查看我前面的博文)
条件装配的实现原理:
- @Conditional注解:这个注解可以标记在类、方法或注解上,用于指定在特定的条件满足时才创建和配置bean。
@Conditional注解需要一个Class类型的参数,这个参数需要实现Condition接口。 - Condition接口:这是一个函数式接口,它定义了一个
matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata)方法。- 这个方法返回一个boolean值,表示条件是否满足。如果返回true,则Spring容器会创建和配置相应的bean;如果返回false,则不会创建和配置。
- 两个参数提供了关于Spring容器和当前正在评估的bean的元数据信息。
- 自动配置:在Spring Boot中,条件装配被广泛应用于自动配置。
- Spring Boot会根据我们在
pom.xml文件中引入的依赖,自动配置相应的bean。 - 这是通过一系列的
AutoConfiguration类实现的,这些类上通常会使用@ConditionalOnClass、@ConditionalOnMissingBean等注解来指定条件。
- Spring Boot会根据我们在
四、实际案例
假设正在开发一个在线商城的 Spring Boot 应用程序,其中包含了用户管理和订单管理两个模块。现在,希望在用户注册时发送一封欢迎邮件,但是如果用户已经在系统中存在,则不发送邮件。
ps:使用条件注解
@ConditionalOnMissingBean来实现这一定制化功能。
- 创建一个邮件服务接口
EmailService和实现类WelcomeEmailService。
/** * 邮件服务接口 */ public interface EmailService { void sendWelcomeEmail(String email); } /** * 发送欢迎邮件 */ @Service public class EmailServiceImpl implements EmailService { @Override public void sendWelcomeEmail(String email) { // 发送欢迎邮件的逻辑 System.out.println("Sending welcome email to: " + email); } } - 创建一个用户服务类
UserService,在用户注册时调用邮件服务发送欢迎邮件。
public interface UserService { public void registerUser(String email); } /** * 在用户注册时检查是否已经存在该用户,如果不存在则发送欢迎邮件 */ @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private final UserMapper userMapper; private final EmailService emailService; @Autowired public UserServiceImpl(UserMapper userMapper, EmailService emailService) { this.userMapper = userMapper; this.emailService = emailService; } @Override public void registerUser(String email) { if(!userMapper.existsByEmail(email)) { userMapper.save(email); emailService.sendWelcomeEmail(email); }else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Email already exists"); } } } - 创建一个
UserRepository实现,它使用HashSet来模拟存储用户信息。
/** * 不想使用数据库,直接使用HashSet来模拟存储用户信息的email * 使用一个HashSet来存储注册过的email,HashSet不允许存储重复的元素 * @author LEK */ @Repository public class UserMapper { private final Set registeredEmails = new HashSet<>(); public boolean existsByEmail(String email) { return registeredEmails.contains(email); } public void save(String email) { if (Objects.nonNull(email) && !email.isEmpty()) { registeredEmails.add(email); } } } - 使用
@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解来确保只有在容器中不存在EmailService的实现类时才会注入WelcomeEmailService。这样,如果用户在系统中已经存在,就不会发送欢迎邮件。
@Configuration public class EmailConfig { /** * 邮件配置 * */ @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(EmailService.class) public EmailServiceImpl email() { return new EmailServiceImpl(); } } - 新建
UserServiceImplTest测试类,由于是使用HashSet来模拟运行,每次启动都是不存在的,然后手动一下。
@SpringBootTest public class UserServiceImplTest { @Autowired private UserService userService; @Test public void testRegisterExistingUser() { String existingEmail = "existing@example.com"; userService.registerUser(existingEmail); // 注册已存在的用户,预期会抛出 IllegalArgumentException userService.registerUser(existingEmail); } } - 运行效果。
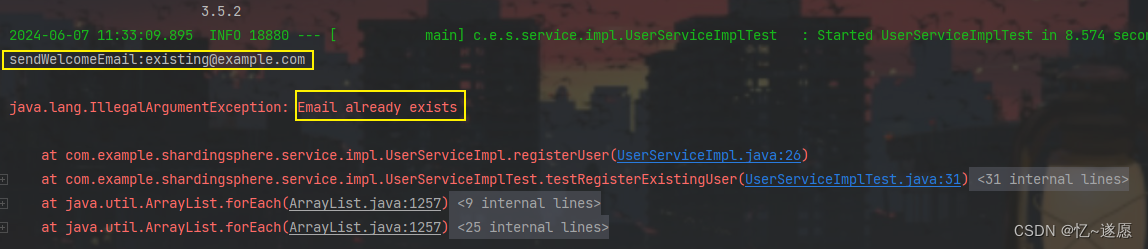
哪儿有勤奋,哪儿就有成功
