Elasticsearch从0到1保姆级教学附带代码(适合小白白们学习)
文章目录
- 概要
- Elasticsearch
- 1. 关于各种数据库的使用
- 2. 关系型数据库中的索引
- 3. 安装与启动elasticsearch
- 访问elasticsearch
- 5. 使用elasticsearch分词
- 6. elasticsearch文档的相关概念
- 7.使用elasticsearch添加数据
- 7.1添加文档(使用elasticsearch随机生成的ID)
- 7.2. 查看文档
- 7.3. 修改文档
- 7.4. 删除
- 8. elasitcsearch中的字段的数据类型
- 9. 搜索
- 9.1. 准备测试数据
- 9.2. 简单的搜索
- 9.3. 高级搜索
- 10. 基于Spring Boot的elasticsearch编程
- 10.1. 添加依赖
- 10.2. 处理文档数据
- 10.3. 编写数据访问接口
概要
Elasticsearch是一个开源的分布式搜索和分析引擎,它构建在Apache Lucene库之上。它专注于提供快速、弹性和可靠的全文搜索、结构化搜索、分析和可视化功能。
以下是关于Elasticsearch的一些重要特点和概念:
- 分布式架构:Elasticsearch被设计为在多台服务器上运行,并自动管理数据的分片和复制。这使得它能够处理大规模的数据,并提供高可用性和容错性。
- 全文搜索:Elasticsearch使用倒排索引技术,可以高效地进行全文搜索。它支持各种查询类型,包括匹配、模糊搜索、范围搜索等。
- 实时数据:Elasticsearch对数据的更改几乎是实时的,通常在毫秒级别内就可以被索引并可查询。这使得它非常适合需要及时反馈的应用场景,如日志分析、监控数据处理等。
- 多语言支持:Elasticsearch提供了广泛的语言客户端,使得开发人员可以使用自己熟悉的语言与之交互,如Java、Python、Node.js等。
- 弹性扩展:Elasticsearch支持水平扩展,可以通过添加更多的节点来增加存储容量和负载能力。它还提供了自动分片和负载均衡机制,使得数据在集群中的分布更加均匀。
- 多种数据类型支持:除了文本数据,Elasticsearch也可以处理结构化数据和地理位置数据。它支持各种数据类型的索引和查询,包括字符串、数字、日期、布尔值、数组等。
- 易于使用的API:Elasticsearch提供了RESTful风格的API,可以使用HTTP协议与之进行交互。这使得开发人员可以轻松地索引、查询、修改和删除数据。
- 数据聚合与分析:Elasticsearch提供了丰富的聚合功能,可以对数据进行统计、分组、筛选和排序等操作。同时,它还集成了Kibana工具,用于可视化和分析数据。
- 总而言之,Elasticsearch是一个功能强大、易于使用和高度可扩展的搜索和分析引擎。它在大数据、日志分析、企业搜索、电子商务等领域都有广泛的应用。
Elasticsearch
1. 关于各种数据库的使用
- 关于MySQL:是关系型数据库,能清楚的表示数据之间的关系,并且,是基于磁盘存储的,可以使用相对较低的成本存储大量的数据
- 关于Redis:是基于K-V结构的在内存中读写数据的数据库(虽然也会自动同步到磁盘),能够明显的提高查询效率(通常设计预期不低于10万QPS),进而还可以保护关系型数据库,并且,通常是使用专门的服务器或集群,也可以作为整个集群中的共享内存资源
- 关于elasticsearch:用于解决搜索问题的非关系型文档数据库
2. 关系型数据库中的索引
- 在关系型数据库中,索引(index)是一种单独的、物理层面的对数据库中的一列或多列的值进行排序检索的一种数据结构。
- 如果没有做任何优化的处理,当MySQL这类数据库中的数据量较多时,查询效率会非常低下,这是因为在执行查询时,MySQL会把当前表中所有的数据全部检查一遍,检查每条数据是否匹配当前的查询规则!另外,MySQL是基于磁盘存储的,数据不会非常整齐的集中存储在磁盘的某个位置,而是散列的分布的磁盘的不同位置所以,在查询时,会需要频繁的执行IO操作,最终,实际表现查询效率非常低!
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name (column_name[, column_name_2 ...]); 例如:
CREATE INDEX idx_username ON account_user (username); 对于某张表的某个字段的索引,只需要创建1次即可!
当创建索引后,索引对应的列的查询效率都可以在毫秒级完成!
注意:在创建索引时,表中的数据越多,创建索引的耗时越多!
删除索引的语法格式是:
DROP INDEX index_name ON table_name; 找出数据对应的“页码”,并直接翻到对应的那一页,就能把数据全部找出来!所以,整体效率非常之高!
索引的本质是一种B+Tree结构(是一种树型结构)的数据,在MySQL中,InnoDB存储引擎中页的大小是16KB,如果使用BIGINT类型的主键,每个主键需要占用8字节,在B+Tree中的指针是4~8字节,每个指针与主键形成一个节点,则每个节点将占用最多16字节,每页最少可以存储1024个节点,深度为3的B+Tree最多可以存储1024 * 1024 * 1024个节点,大约是1000 * 1000 * 1000 = 1000000000个节点(10亿),所以,每个B+Tree可以维护约10亿个节点,如果表中的数据量不超过10亿条,都只需要最多执行3次IO操作,就可以找出数据的位置。
在数据库,即使你没有显式的创建索引,某些字段的查询效率可能也非常高,因为索引还有其它种类,包括:
- PRIMARY KEY:主键索引
- UNIQUE:唯一索引
- INDEX:普通索引
- FULLTEXT:全文索引
基于索引的特性,使用时,必须注意:
- 索引不会包含有NULL值的列
- 数据量非常少的表没有必要创建索引,例如绝大部分字典表,或数据量不多且修改频率也非常低的表也没有必要创建索引,例如资讯平台的“栏目”或“类别”、小型应用中“用户的角色”
- 数据经常变化的字段不要创建索引,因为会频繁的更新索引,导致更新效率低下
- 查询时需要计算字段值时,索引是无效的,例如:where age + 10 > 30时,age列的索引是无效的
- 左侧的模糊查询无法使用索引,因为索引是基于对这一列的数据进行排序得到的
- 其实,在开发实践中,所有模糊查询都是不允许使用的
除了以上限制以外,不同的企业的开发规范可能提出更高的要求:
- 类型为text的字段不允许使用索引
- 类型为varchar且字段值可能很长的字段,也不允许使用索引
- 其它
3. 安装与启动elasticsearch
无论是哪个操作系统,只需要下载elasticsearch的压缩包即可,将其解压,执行bin目录下的elasticsearch即可启动elasticsearch服务:
启动成功后,看到的结果大致是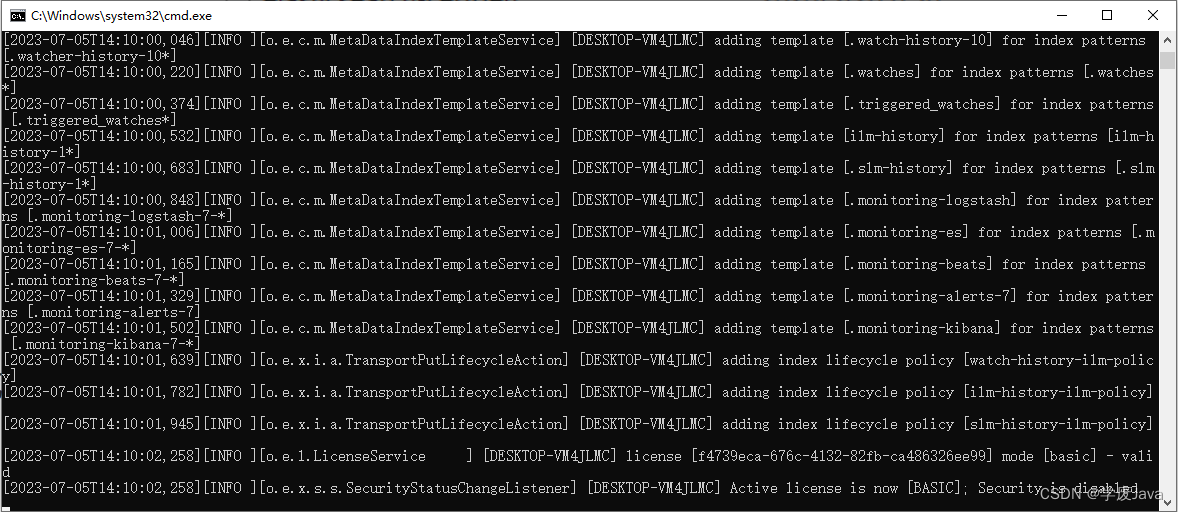
在使用elasticsearch的过程中,以上窗口不可以关闭!
启动成功后,你可以通过浏览器访问 http://localhost:9200,结果如下: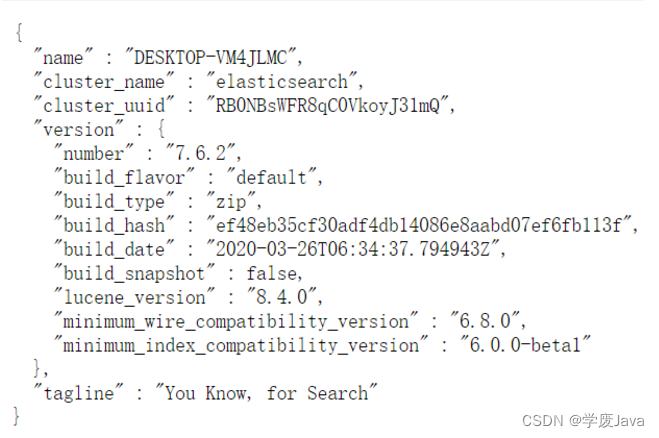
访问elasticsearch
elasticsearch提供的访问方式是基于RESTful的,你可以使用任何一个可以提交REST请求的工具来访问elasticsearch,例如常见的测试工具PostMan等。
在IntelliJ IDEA中,你可以创建以.http为扩展名的HttpRequest文件,通过这类文件来提交REST请求,例如:
然后,在文件中编写请求: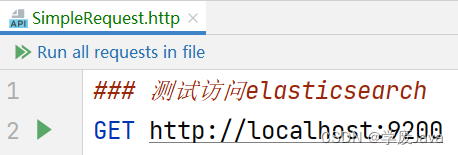
直接点击请求左侧的绿色小箭头即可发起请求,执行效果如下: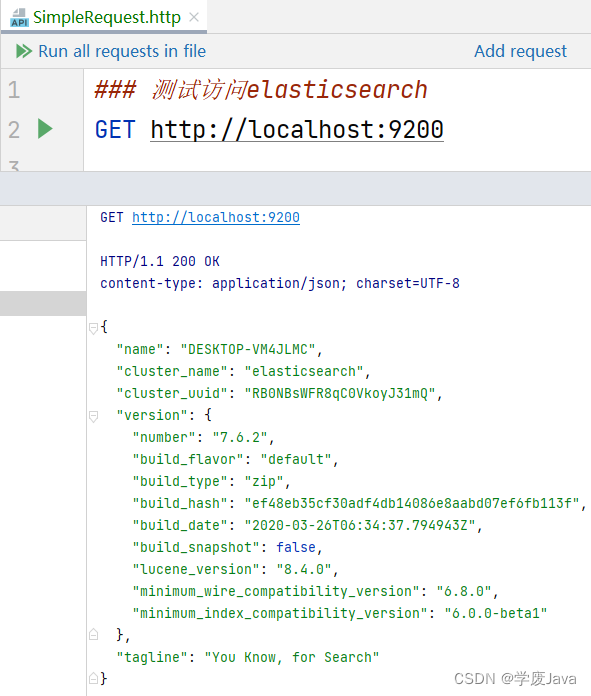
5. 使用elasticsearch分词
- 向 http://localhost:9200/_analyze 提交请求即可分词,请求参数必须是名为text的,参数值就是你希望分词的词组或词句,例如
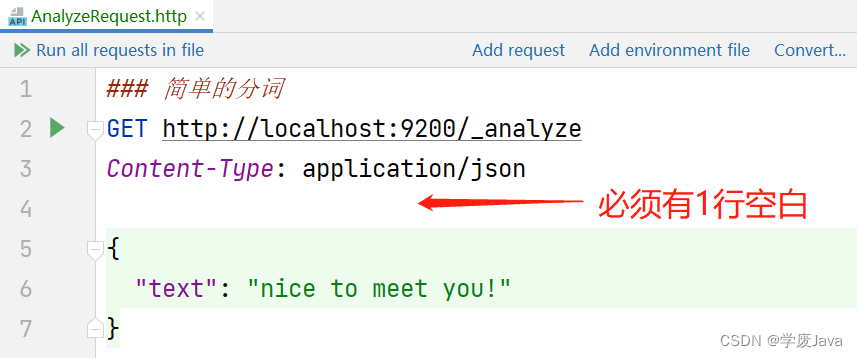
在同一个.http文件中,可以编写多个请求,但是,后续的请求的代码必须使用 ### 和前序的请求分开,不能只使用1个 #!
也可以对中文进行分词,但是,默认的分词对中文的支持非常不好,它只会将每个汉字作为一个词!
示例代码:
### 简单的分词:中文 GET http://localhost:9200/_analyze Content-Type: application/json { "text": "很高兴认识你!" } 可以在elasticsearch中安装插件,以更好的支持中文的分词,经典的中文分词插件就是ik分词器。
你只需要找到elasticsearch文件夹下的plugins文件夹(如下图所示):
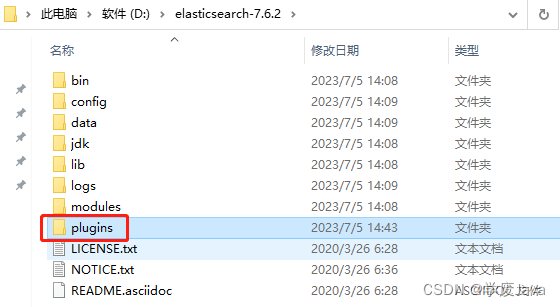
然后,将IK分词器的文件夹粘贴到plugins的子级即可,并且,你可以自由的修改IK分词器文件夹的名称,例如: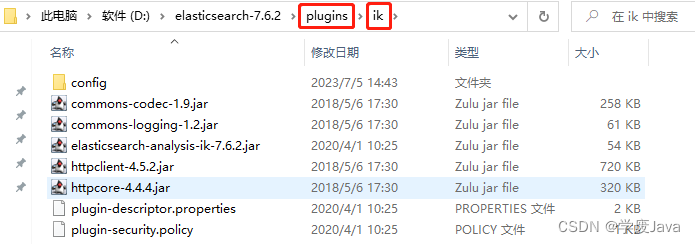
以上配置完成后,需要重启elasticsearch才会应用新的分词器!
接下来,在提交请求时,可以在请求参数列表中添加analyzer参数,取值可以是IK分词器中的ik_smart或ik_max_word,例如:
### 使用IK的分词:智能 GET http://localhost:9200/_analyze Content-Type: application/json { "analyzer": "ik_smart", "text": "很高兴认识你!" } ### 使用IK的分词:最大词量(最细粒度) GET http://localhost:9200/_analyze Content-Type: application/json { "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "text": "很高兴认识你!" } 使用IK分词器时,还可以自造词!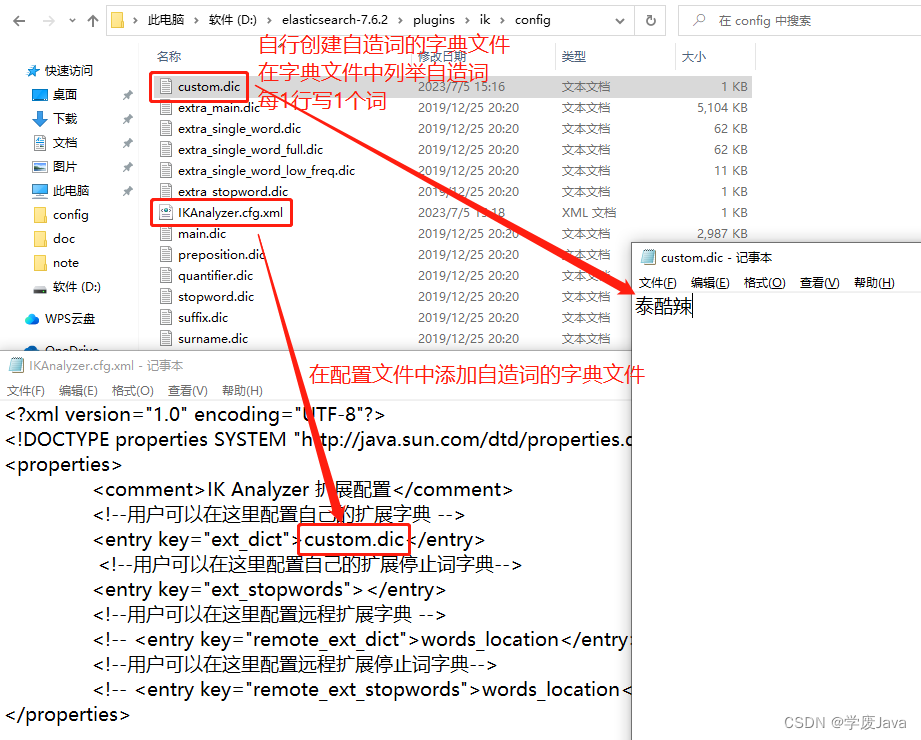
6. elasticsearch文档的相关概念
索引(index / indices)
- 相当于MySQL中的Database
类型(type / types)
- 相当于MySQL中的Table,可以自行创建“类型”,或,如果不关心“类型”,则使用_doc表示类型名
文档(document / documents)
- 相当于MySQL中的一行行的数据,在elasticsearch中每个数据都是由JSON格式组织的
字段(field / fields)
- 相当于MySQL中的Column
7.使用elasticsearch添加数据
7.1添加文档(使用elasticsearch随机生成的ID)
POST http://localhost:9200/{索引名}/{类型名}
提示:添加文档时,如果索引不存在,会自动创建索引;如果类型不存在,会自动创建类型!
请求示例:
### 添加文档(新增数据),将随机生成此数据在ES中的ID POST http://localhost:9200/index_crud/_doc Content-Type: application/json { "id": 1, "title": "这是放在ES中的第1篇文章", "sort": 80, "gmtCreate": "2023-07-01" } 添加文档(新增数据),并自行指定ID
请求URL的格式(此处对ID值并没有严格的要求):PUT http://localhost:9200/{索引名}/{类型名}/{文档ID}
请求示例:
### 添加文档(新增数据),并自行指定ID,此处对ID值并没有严格的要求 PUT http://localhost:9200/index_crud/_doc/No9527 Content-Type: application/json { "id": 9527, "title": "这是放在ES中的第2篇文章", "sort": 90, "gmtCreate": "2023-07-02" } 7.2. 查看文档
查看当前索引中的所有文档
请求URL的格式:GET http://localhost:9200/{索引名}/_search
请求示例:
### 查看当前索引中的所有文档 GET http://localhost:9200/index_crud/_search 根据ID访问文档
请求URL的格式:GET http://localhost:9200/{索引名}/_doc/{文档ID}
- 提示:如果是elasticsearch自动生成的ID,你可以通过“查看所有文档”来获取ID值,或者,此前添加文档时,返回的结果中也会包含ID值。
请求示例:
### 根据ID访问文档(此前添加文档时使用的自定义ID) GET http://localhost:9200/index_crud/_doc/No9527 7.3. 修改文档
修改文档【1】
请求URL的格式:PUT http://localhost:9200/{索引名}/_doc/{文档ID}
提示:以上请求与“指定ID的添加文档”是相同的!
注意:此类操作会使用请求参数替换原有的整个数据,如果原数据有5个属性,请求参数只有2个属性,执行后,数据将只有本次请求的2个属性!
请求示例:
PUT http://localhost:9200/index_crud/_doc/No9527 Content-Type: application/json { "id": 9527, "title": "这是放在ES中的第2篇文章", "sort": 90, "gmtCreate": "2023-07-02" } 修改文档【2】
请求URL的格式:POST http://localhost:9200/{索引名}/_doc/{文档ID}/_update
提示:这种修改文档的方式只会修改原数据中与本次请求参数对应的属性
注意:如果原数据中没有本次请求的参数属性,则会在原数据上添加新的属性!
请求示例:
POST http://localhost:9200/index_crud/_doc/No9527/_update Content-Type: application/json { "doc": { "commentCount": 637 } } 7.4. 删除
根据ID删除文档
请求URL的格式:DELETE http://localhost:9200/{索引名}/{类型名}/{文档ID}
注意:如果尝试删除的文档不存在,则会响应404错误!
请求示例:DELETE http://localhost:9200/index_crud/_doc/No9527
删除整个索引
请求URL的格式:DELETE http://localhost:9200/{索引名}
注意:将会删除这个索引中的所有类型及各类型中的数据!
注意:如果尝试删除的索引不存在,则会响应404错误!
请求示例:DELETE http://localhost:9200/index_crud
8. elasitcsearch中的字段的数据类型
在elasticsearch中,文档的各个字段都是有数据类型的,大致有:
- 字符串类型:text、keyword
- text类型被处理时,默认会被分词
- 默认类型
- keyword类型被处理时,默认不会被分词
- text类型被处理时,默认会被分词
- 数值类型:byte、short、integer、long、float、double等
- 布尔类型:boolean
- 日期类型:date
- 二进制类型:binary
- 其它(可参考org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType的枚举值)
当向elasticsearch中添加文档时,如果对应的索引没有设置数据类型,则会自动设置数据类型!
可以查询索引信息,来观察各字段的数据类型!请求URL的格式为:
### 查看索引的基本信息 GET http://localhost:9200/{索引名} 请求示例:
### 查看索引的基本信息 GET http://localhost:9200/index_search 也可以专门的创建索引,并在创建时指定各字段的数据类型,请求方式大致是:
PUT http://localhost:9200/{索引名} Content-Type: application/json { "mappings": { "properties": { "{字段名1}": { "type": "{数据类型1}" }, "{字段名2}": { "type": "{数据类型2}" }, ... "{字段名n}": { "type": "{数据类型n}" } } } } 请求示例:
### 创建索引,并配置各字段的数据类型 PUT http://localhost:9200/index_search Content-Type: application/json { "mappings": { "properties": { "id": { "type": "long" }, "title": { "type": "text" }, "desc": { "type": "keyword" }, "sort": { "type": "integer" }, "price": { "type": "integer" } } } } 9. 搜索
9.1. 准备测试数据
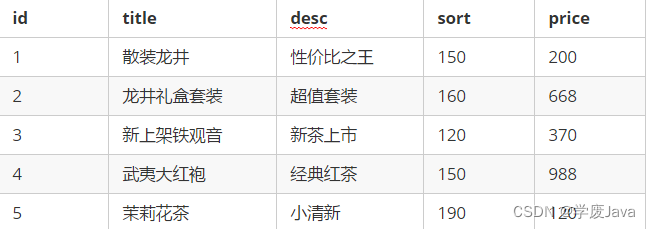
- 将以上测试数据存入到名为index_search索引中,则代码为:
### 添加测试数据-1 PUT http://localhost:9200/index_search/_doc/1 Content-Type: application/json { "id": 1, "title": "散装龙井", "desc": "性价比之王", "sort": 150, "price": 200 } ### 添加测试数据-2 PUT http://localhost:9200/index_search/_doc/2 Content-Type: application/json { "id": 2, "title": "龙井礼盒套装", "desc": "超值套装", "sort": 160, "price": 668 } ### 添加测试数据-3 PUT http://localhost:9200/index_search/_doc/3 Content-Type: application/json { "id":3, "title": "新上架铁观音", "desc": "新茶上市", "sort": 120, "price": 370 } ### 添加测试数据-4 PUT http://localhost:9200/index_search/_doc/4 Content-Type: application/json { "id": 4, "title": "武夷大红袍", "desc": "经典红茶", "sort": 150, "price": 988 } ### 添加测试数据-5 PUT http://localhost:9200/index_search/_doc/5 Content-Type: application/json { "id": 5, "title": "茉莉花茶", "desc": "小清新", "sort": 190, "price": 120 } 9.2. 简单的搜索
请求URL的格式:GET http://localhost:9200/{索引名}/_search?q={字段名:关键字}
注意:执行以上搜索时,会自动对关键字进行分词,例如,关键是“套装”时,“散装”也会出现在结果中,因为会对“套装”进行分词,得到“套装”、“套”、“装”这些词,而“散装”也包含了“装”,所以,会出现在结果中!
请求示例:
### 搜索:按照title的“套装”进行搜索 GET http://localhost:9200/index_search/_search?q=title:套装 ### 搜索:按照desc的“红茶”进行搜索 GET http://localhost:9200/index_search/_search?q=desc:红茶 注意:执行以上搜索时,如果搜索的字段是text类型,会自动对关键词进行分词,如果字段是keyword,则不会分词,仅有完全匹配的数据才会被搜索到!
9.3. 高级搜索
### 搜索:简单的自定义query搜索,如果不写query,相当于SQL里没有where,则搜索全部数据,或者,将match部分配置为:"match_all": {} GET http://localhost:9200/index_search/_search Content-Type: application/json { "query": { "match": { "title": "套装" } } } ### 搜索:多个条件的搜索,must >>> AND / should >>> OR / must_not >>> != GET http://localhost:9200/index_search/_search Content-Type: application/json { "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "match": { "title": "套装" } }, { "match": { "desc": "超值套装" } } ] } } } ### 搜索:指定查询字段列表的搜索 GET http://localhost:9200/index_search/_search Content-Type: application/json { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "_source": [ "id", "title", "price" ] } ### 搜索:指定排序规则的搜索,通过与query同级的sort属性来配置规则,如果希望升序,则字段的属性为空对象即可 GET http://localhost:9200/index_search/_search Content-Type: application/json { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "sort": [ { "price": {}, "id": { "order": "desc" } } ] } ### 搜索:分页搜索,通过与query同级的from属性表示从第几条开始,0表示第1条,以此类推,另外再通过size属性表示搜索多少条数据 GET http://localhost:9200/index_search/_search Content-Type: application/json { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "from": 2, "size": 2 } ### 搜索:高亮显示,通过与query同级的highlight标签进行配置,会在搜索结果中生成与数据结果同级的highlight对象,默认会在匹配的文本上添加em标签 GET http://localhost:9200/index_search/_search Content-Type: application/json { "query": { "match": { "title": "套装" } }, "highlight": { "fields": { "title": {} }, "pre_tags": "", "post_tags": "" } } 10. 基于Spring Boot的elasticsearch编程
10.1. 添加依赖
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch 10.2. 处理文档数据
在基于Spring Data Elasticsearch的开发时,需要在存入/读取时使用的数据类型上添加相关注解:
- @Document:添加在类上,通过此注解的indexName属性配置此类数据在elasticsearch中的索引名称
- @Id:添加在类中被作为主键的属性上,表示此属性的值将作为数据在elasticsearch中的ID
- @Field:添加在类中不被作为主键的属性上,此注解并不是必须的,即使没有在属性上添加此注解进行配置,后续框架和elasticsearch也能自动处理数据类型,重点考虑那些会被用于搜索匹配的属性,特别是字符串类型的,到底配置为@Field(type = FieldType.Text)还是@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
示例:
package server.content.pojo.vo.search; import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType; import java.io.Serializable; import java.time.LocalDateTime; /** * 用于处理搜索功能的文章数据的VO类 */ @Data @Document(indexName = "article") // http://localhost:9200/article public class ArticleSearchVO implements Serializable { /** * 数据ID */ @Id private Long id; /** * 作者ID */ private Long authorId; /** * 作者名字 */ private String authorName; /** * 标题 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Text) private String title; /** * 摘要 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Text) private String brief; } 10.3. 编写数据访问接口
在基于Spring Boot的项目中,添加了spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch后,当需要处理elasticsearch编程时,只需要自定义接口,实现Spring Data框架中的Repository接口即可,实现接口时必须指定2个泛型,第1个是文档对应数据类型,第2个是主键的数据类型,例如:
public interface IArticleSearchRepository extends Repository { } 