音视频入门基础:H.264专题(13)——FFmpeg源码中通过SPS属性获取视频色彩格式的实现
一、引言
通过FFmpeg命令可以获取到H.264裸流文件的色彩格式(又译作色度采样结构、像素格式):
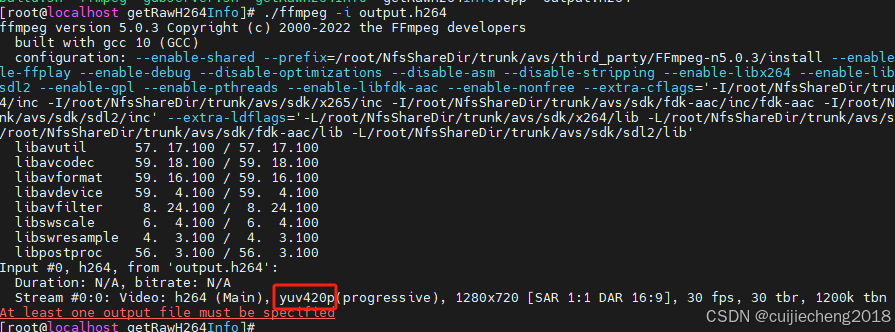
在vlc中也可以获取到色彩格式(vlc底层也使用了FFmpeg进行解码):
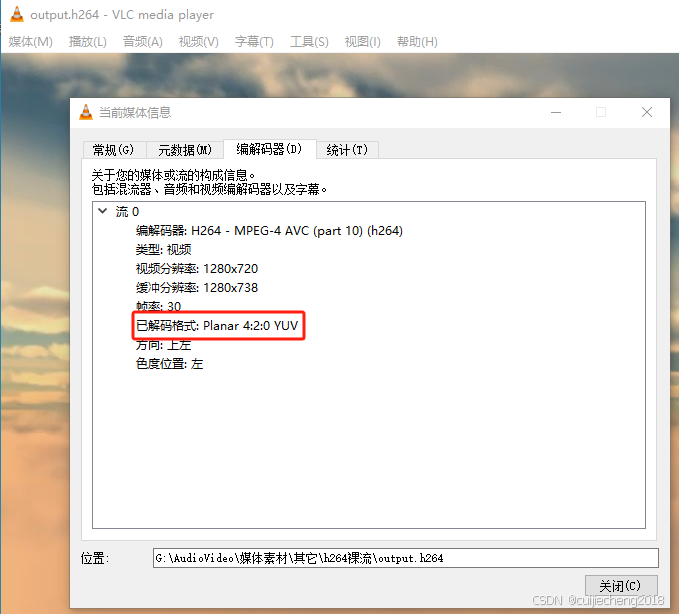
这个色彩格式就是之前的文章《音视频入门基础:像素格式专题(4)——YUV简介》中描述的像素格式。所以FFmpeg和vlc是怎样获取到H.264编码的视频的色彩格式呢?它们其实是通过SPS中的属性chroma_format_idc获取的。
二、H.264官方文档对chroma_format_idc的描述
chroma_format_idc属性在H.264官方文档《T-REC-H.264-202108-I!!PDF-E.pdf》第44页中定义:
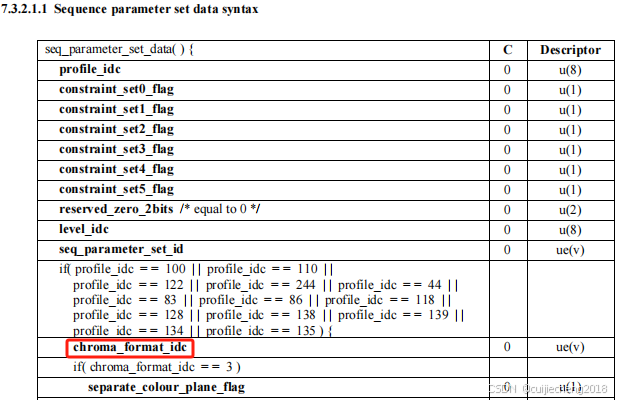
根据H.264官方文档《T-REC-H.264-202108-I!!PDF-E.pdf》第22页,当chroma_format_idc = 0时,色彩格式为单色;chroma_format_idc = 1时,色彩格式为YUV 4:2:0;chroma_format_idc = 2时,色彩格式为YUV 4:2:2;chroma_format_idc = 3时,色彩格式为YUV 4:4:4:
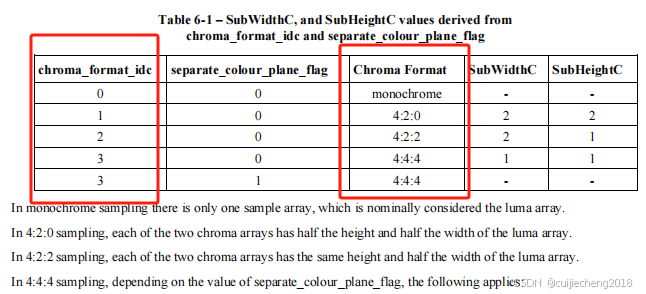
根据H.264官方文档第74页,chroma_format_idc的值应该在0到3的范围内(包括0和3)。当chroma_format_idc不存在时,应推断其值为1(4:2:0的色度格式)。
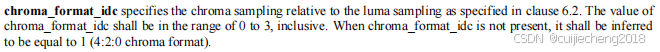
也就是说,只有当profile_idc等于下面红框里的这些值时,chroma_format_idc才会存在。如果profile_idc不是这些值,chroma_format_idc的值就是1,表示色彩格式为YUV 4:2:0:
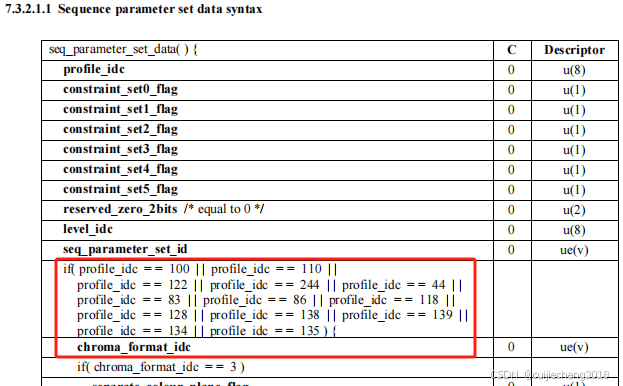
三、计算色彩格式的例子
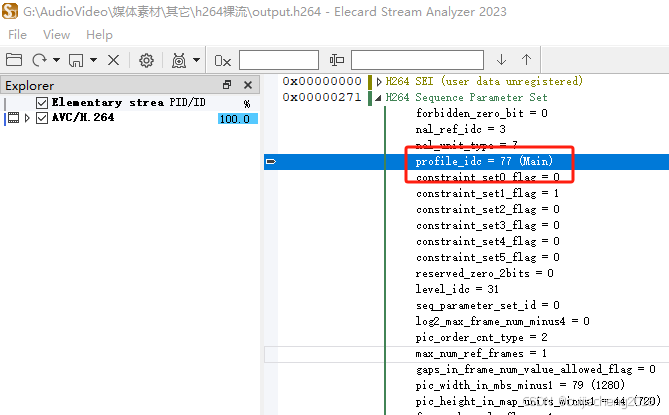
下面以某个视频文件为例,讲述怎么计算它的色彩格式。用Elecard Stream Analyzer工具打开一个用H.264编码的视频文件,看到其profile_idc值为77。由于profile_idc不是上图红框里的那些值,所以chroma_format_idc值为1,所以该视频的色彩格式为YUV 4:2:0:
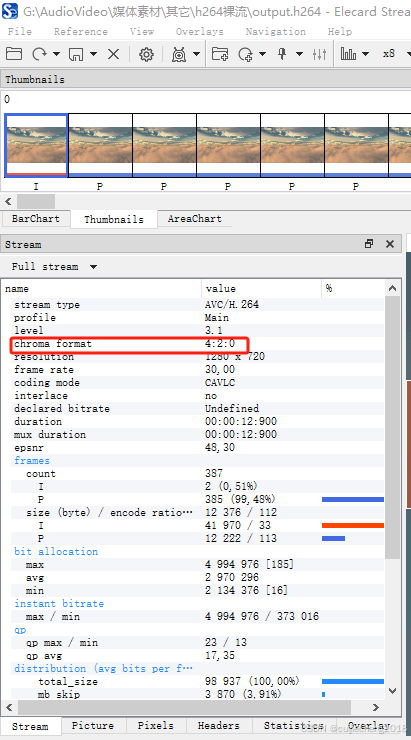
用Elecard StreamEye工具可以看到该视频的色彩格式确实为YUV 4:2:0,证明我们的计算是正确的:
四、FFmpeg源码中获取色彩格式的实现
从文章《音视频入门基础:H.264专题(10)——FFmpeg源码中,存放SPS属性的结构体和解码SPS的函数分析》中,我们可以知道,FFmpeg源码中通过ff_h264_decode_seq_parameter_set函数解码SPS,从而拿到SPS中的属性。
在ff_h264_decode_seq_parameter_set函数中有如下代码,通过下面的这部分代码拿到SPS中的chroma_format_idc:
int ff_h264_decode_seq_parameter_set(GetBitContext *gb, AVCodecContext *avctx, H264ParamSets *ps, int ignore_truncation) { //... if (sps->profile_idc == 100 || // High profile sps->profile_idc == 110 || // High10 profile sps->profile_idc == 122 || // High422 profile sps->profile_idc == 244 || // High444 Predictive profile sps->profile_idc == 44 || // Cavlc444 profile sps->profile_idc == 83 || // Scalable Constrained High profile (SVC) sps->profile_idc == 86 || // Scalable High Intra profile (SVC) sps->profile_idc == 118 || // Stereo High profile (MVC) sps->profile_idc == 128 || // Multiview High profile (MVC) sps->profile_idc == 138 || // Multiview Depth High profile (MVCD) sps->profile_idc == 144) { // old High444 profile sps->chroma_format_idc = get_ue_golomb_31(gb); //... }else { sps->chroma_format_idc = 1; //... } //... }然后在FFmpeg源码的源文件libavcodec/h264_parser.c的parse_nal_units函数中,通过如下代码,得到色彩格式:
static inline int parse_nal_units(AVCodecParserContext *s, AVCodecContext *avctx, const uint8_t * const buf, int buf_size) { //... for (;;) { switch (nal.type) { case H264_NAL_SPS: ff_h264_decode_seq_parameter_set(&nal.gb, avctx, &p->ps, 0); break; //... case H264_NAL_IDR_SLICE: //... switch (sps->bit_depth_luma) { case 9: if (sps->chroma_format_idc == 3) s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P9; else if (sps->chroma_format_idc == 2) s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P9; else s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P9; break; case 10: if (sps->chroma_format_idc == 3) s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P10; else if (sps->chroma_format_idc == 2) s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P10; else s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P10; break; case 8: if (sps->chroma_format_idc == 3) s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P; else if (sps->chroma_format_idc == 2) s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P; else s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P; break; default: s->format = AV_PIX_FMT_NONE; } //... } //... } }