【数据结构】单链表 双向链表
目录
- 链表
- 链表的分类
- 单链表
- 单链表接口的实现
- 内部类
- 头插法
- 尾插法
- 任意位置插入
- 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
- 删除所有值为key的节点
- 得到单链表的长度
- 清空链表
- 单链表的优缺点
- 双向链表
- 双向链表接口的实现
- 内部类
- 头插法
- 尾插法
- 任意位置插入
- 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
- 删除所有值为key的节点
- 得到链表的长度
- 清空链表
- Java中的LinkedList
- 实现的接口
- 构造方法
- 常用方法
- 双向链表的优劣
- ArrayList和LinkedList对比
- 链表练习

链表
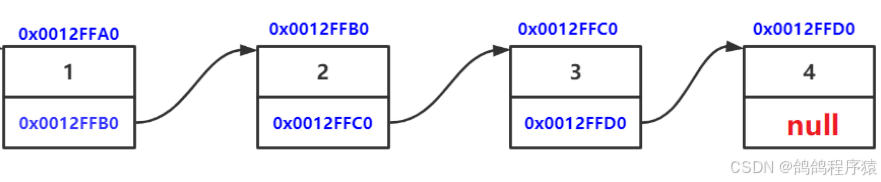
链表就是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
也是线性表。
数据域:存储数据元素信息的域。
指针域:存储直接后继的信息。
链表的分类
链表根据三个条件分类:
- 有头无头:有没有头结点,头结点的数据域是无用的。
- 是否循环:尾结点又指回头。
- 单向还是双向:指针域包不包含指向前面域的指针。
根据以上3个条件来分类(每一个条件选一),链表一共有8种。
单链表
单链表全称为:无头单向不循环链表。
单链表接口的实现
自己实现一个单链表(存储int数据类型),将单链表作为一个类,我们实现一些“接口”即成员方法来实现数据的增删查改。
// 1、无头单向非循环链表实现 public class SingleLinkedList { //头插法 public void addFirst(int data); //尾插法 public void addLast(int data); //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标 public boolean addIndex(int index,int data); //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中 public boolean contains(int key); //删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点 public void remove(int key); //删除所有值为key的节点 public void removeAllKey(int key); //得到单链表的长度 public int size(); //清空链表 public void clear(); } 内部类
因为我们需要使用数据域,指针域,在链表中一个一个串起来。那我们就将数据域指针域使用一个静态内部类来封装。只将第一个节点用head来表示。
注意:此处的head不是链表分类时的头,因为分类的头的数据域的数据是无效的而此处是有效的。
public class SingleLinkedList { static class ListNode{ public int val; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } } public ListNode head; } 头插法
实现思路:
将当前节点的下一个节点(next)指向头(head),再改头为当前节点。
public void addFirst(int data) { ListNode cur = new ListNode(data); cur.next = head; head = cur; } 尾插法
实现思路:
- 先判断链表是否为空,为空头指向尾插节点(因为尾插涉及尾结点的next,链表如果为空就会空指针异常)。
- 链表不为空,使用循环找到尾结点,next指向尾插节点。
public void addLast(int data){ if(head == null){ head = new ListNode(data); return; } ListNode cur = head; while(cur.next != null){ cur = cur.next; } cur.next = new ListNode(data); } 任意位置插入
实现思路:
- 先判断插入位置合法吗,不合法就抛异常。
- 头尾位置插入调用头插尾插函数即可。
- 中间节点插入找到前一个位置记录下来,当前位置记录下来, 在改插入节点和前一个节点的next。
public boolean addIndex(int index,int data) throws IndexIllegalException{ try{ if(index < 0 || index > size()){ throw new IndexIllegalException("位置不合法"); } else if (index == 0) { addFirst(data); return true; } else if (index == size()) { addLast(data); return true; }else{ ListNode cur = head; ListNode pre = head; ListNode newNode = new ListNode(data); for (int i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { cur = cur.next; pre = pre.next; } newNode.next = cur.next; pre.next = cur; return true; } }catch(IndexIllegalException e){ e.printStackTrace(); return false; } } 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
使用循环遍历即可。
public boolean contains(int key){ ListNode cur = head; for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) { if(cur.val == key){ return true; } cur = cur.next; } return false; } 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
实现思路:
- 看链表是否为空,空直接返回。
- 先看头结点是不是要删的节点(因为删除会涉及被删节点的前一个节点),是直接将头指向下一个节点。
- 循环找到当前节点,让前一个节点next指向当前节点的next即可。
public void remove(int key){ if(head == null){ return; } else if (head .val == key) { head = head.next; return; } ListNode cur = head.next; ListNode pre = head; while(cur != null){ if(cur.val == key){ pre.next = cur.next; return; } cur = cur.next; pre = pre.next; } } 删除所有值为key的节点
跟删除一个节点一个逻辑只不过删除后不返回,并且头结点最后判断。
public void removeAllKey(int key){ if(head == null){ return; } ListNode cur = head.next; ListNode pre = head; while(cur != null){ if(cur.val == key){ pre.next = cur.next; cur = cur.next; }else { cur = cur.next; pre = pre.next; } } if(head.val == key){ head = head.next; } } 得到单链表的长度
直接循环遍历就行。
public int size(){ ListNode cur = head; int size = 0; while(cur != null){ cur = cur.next; size++; } return size; } 清空链表
直接循环将每一个节点置空,注意置空前要将头先向后走。
public void clear(){ ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null){ head = cur.next; cur = null; cur = head; } } 单链表的优缺点
优缺点如下:
- 优点:单向链表增加删除节点简单。
- 缺点:只能从头到尾遍历,只能找到后继。
双向链表
在Java的集合类中使用的是无头双向非循环链表。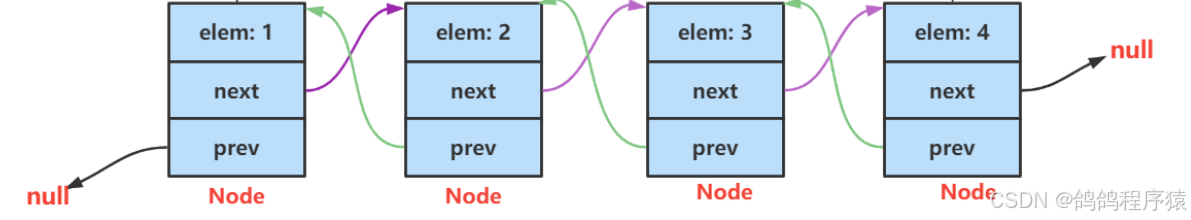
双向链表接口的实现
自己实现一个双向链表(存储int数据类型),将双向链表作为一个类,我们实现一些“接口”即成员方法来实现数据的增删查改。
// 2、无头双向链表实现 public class LinkedList { //头插法 public void addFirst(int data); //尾插法 public void addLast(int data); //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标 public boolean addIndex(int index,int data); //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中 public boolean contains(int key); //删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点 public void remove(int key); //删除所有值为key的节点 public void removeAllKey(int key); //得到链表的长度 public int size(); //情空链表 public void clear(); } 内部类
因为我们需要使用数据域,指针域,在链表中一个一个串起来。那我们就将数据域指针域使用一个静态内部类来封装。只将第一个节点用head来表示,最后一个节点用last表示。
注意:此处的head不是链表分类时的头,因为分类的头的数据域的数据是无效的而此处是有效的。
static class ListNode{ public int val; public ListNode prev; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } } public ListNode head; public ListNode last; 头插法
实现思路:
- 如果当前链表为空就直接将头尾指向当前节点。
- 如果不是先将插入节点的下一个指向头,头的前一个指向插入节点,头指向插入节点。
public void addFirst(int data){ ListNode cur = new ListNode(data); if(head == null){ head = last = cur; return; } cur.next = head; head.prev = cur; head = cur; } 尾插法
实现思路:
- 看链表是否为空,为空直接头和尾指向插入节点。
- 链表不为空,将尾结点的next指向插入节点,将插入节点的prev指向尾结点,将尾结点改为插入节点。
public void addLast(int data){ ListNode cur = new ListNode(data); if(last == null){ head = last = cur; return; } last.next = cur; cur.prev = last; last = cur; } 任意位置插入
实现思路:
- 判断位置是否合法,不合法抛异常。
- 插入位置为头尾,对应调用头插方法,尾插方法。
- 找到插入位置对应节点,将插入节点前驱prev改为对应节点前驱,对应节点前驱改为插入节点,插入节点后继next改为对应节点。
public boolean addIndex(int index,int data) throws IndexIllegalException{ try{ if(index < 0 || index > size()){ throw new IndexIllegalException("插入位置不合法"); } else if (index == 0) { addFirst(data); return true; } else if (index == size()) { addLast(data); return true; }else { ListNode cur = head; ListNode newNode = new ListNode(data); for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { cur = cur.next; } newNode.prev = cur.prev; cur.prev = newNode; newNode.next = cur; return true; } }catch (IndexIllegalException e){ e.printStackTrace(); return false; } } 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
直接循环遍历就行。
public boolean contains(int key){ ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ if(cur.val == key){ return true; } cur = cur.next; } return false; } 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
实现思路:
- 先判断头节点是不是要删的节点,是将下一个节点前驱prev置为空,头指向下一个节点,返回。
- 循环遍历除头尾节点外的节点,找到被删节点,将该节点前一个节点的后继next改为该节点的下一个节点,该节点后一个节点的前驱prev改为该节点的前一个,返回。
- 如果都不是,判断尾节点,将尾结点的前一个节点的后继next置为空,尾结点改为前一个节点,返回。
public void remove(int key){ ListNode cur = head; if(head.val == key){ head.next.prev = null; head = head.next; return; } else { while(cur.next != null){ if(cur.val == key){ cur.prev.next = cur.next; cur.next.prev = cur.prev; return; } cur = cur.next; } if (last.val == key) { last.prev.next = null; last = last.prev; return; } } } 删除所有值为key的节点
- 先循环遍历除头尾节点外的节点,找到被删节点,将该节点前一个节点的后继next改为该节点的下一个节点,该节点后一个节点的前驱prev改为该节点的前一个。
- 判断头节点是不是要删的节点,是将下一个节点前驱prev置为空,头指向下一个节点。
- 判断尾节点,将尾结点的前一个节点的后继next置为空,尾结点改为前一个节点。
public void removeAllKey(int key){ ListNode cur = head.next; while(cur.next != null){ if(cur.val == key){ cur.prev.next = cur.next; cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } cur = cur.next; } if(head.val == key){ head.next.prev = null; head = head.next; } if (last.val == key) { last.prev.next = null; last = last.prev; } } 得到链表的长度
直接循环遍历即可。
public int size(){ ListNode cur = head; int size = 0; while(cur != null){ size++; cur = cur.next; } return size; } 清空链表
实现思路:
- 先循环遍历将每一个节点前驱prev后继next置为空。
- 最后将头head和为last置为空。
public void clear(){ ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ ListNode curNext = cur.next; cur.prev = null; cur.next = null; cur = curNext; } head = null; last = null; } } Java中的LinkedList
在Java中用集合类LinkedList来表示双向链表。
实现的接口
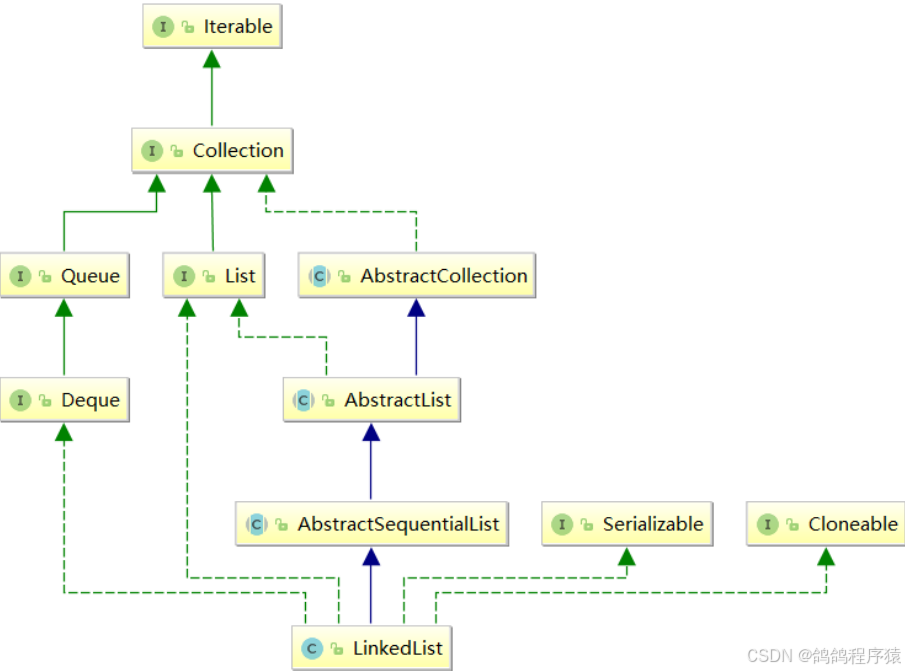
接口说明:
- 没有实现RandomAccess接口,不能随机访问。
- 实现了Cloneable接口,可克隆。
- Serializable接口表示支持序列化。
构造方法
Java中提供了两个构造方法。
| 方法 | 方法用途介绍 |
|---|---|
| LinkedList() | 无参构造 |
| public LinkedList(Collection c) | 使用其他集合容器中元素构造List |
常用方法
提供的常用方法与上面实现的差不多。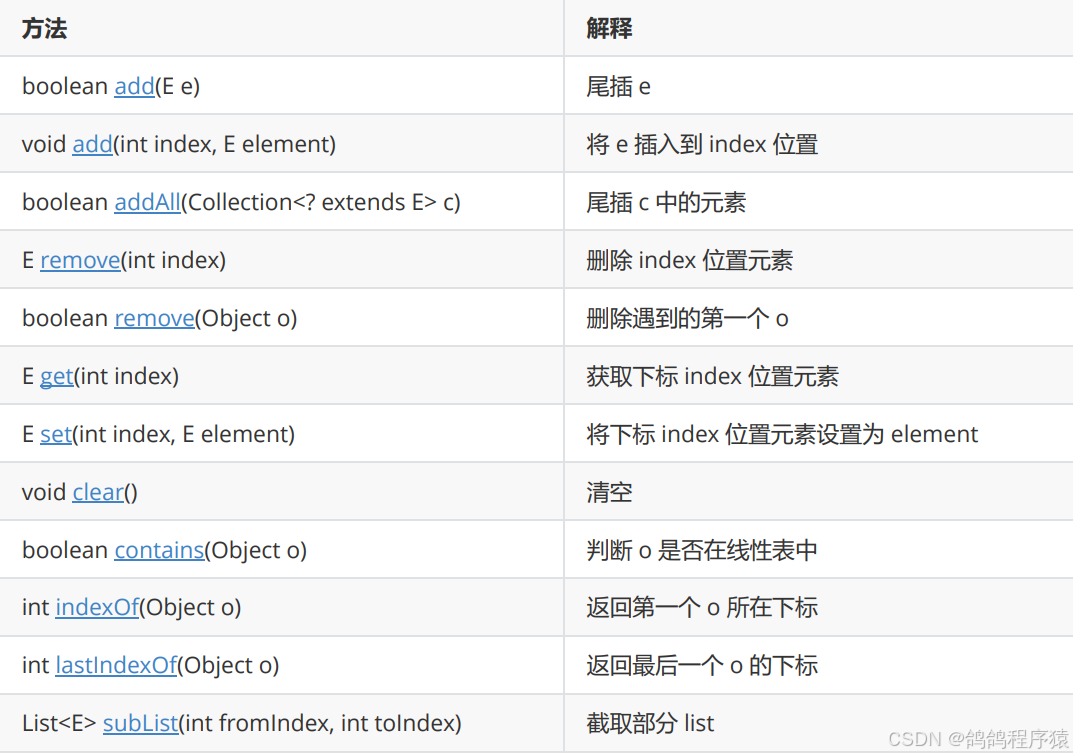
双向链表的优劣
优缺点如下:
- 优点:可以找到前驱和后继,可进可退。
- 确点:删除节点复杂,需要多分配一个指针域。
ArrayList和LinkedList对比
对比如下图: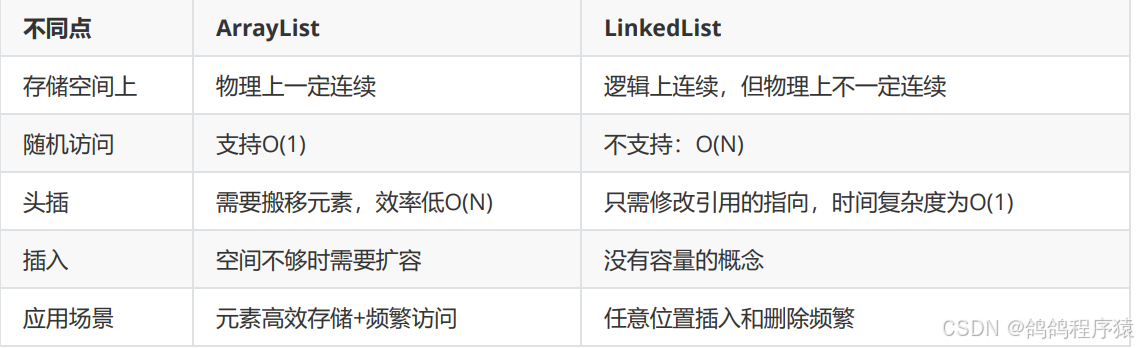
链表练习
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
反转一个单链表
链表的中间节点
合并两个有序链表
链表分割
链表的回文结构
相交链表
环形链表
