前端 css3 媒体查询实现 响应式布局
创始人
2025-01-10 13:35:08
0次
什么是媒体查询?
媒体查询(Media Query)是CSS3新语法。
- 使用 @media 查询,可以针对不同的媒体类型定义不同的样式
- @media 可以针对不同的屏幕尺寸设置不同的样式
- 当你重置浏览器大小的过程中,页面也会根据浏览器的宽度和高度重新渲染页面
- 目前针对很多苹果手机、Android手机,平板等设备都用得到媒体查询
语法规范
@media mediatype and|not|only (media feature) { CSS-Code; }- 用 @media 开头 注意@符号
- mediatype 媒体类型
- 关键字 and not only
- media feature 媒体特性 必须有小括号包含
- mediatype 查询类型
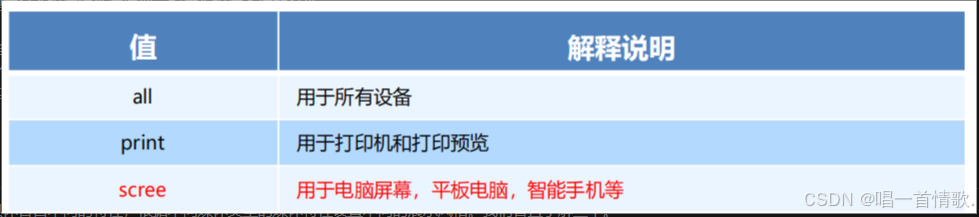
mediatype 查询类型
将不同的终端设备划分成不同的类型,称为媒体类型
关键字
关键字将媒体类型或多个媒体特性连接到一起做为媒体查询的条件。
- and:可以将多个媒体特性连接到一起,相当于“且”的意思。
- not:排除某个媒体类型,相当于“非”的意思,可以省略。
- only:指定某个特定的媒体类型,可以省略。
媒体特性
每种媒体类型都具体各自不同的特性,根据不同媒体类型的媒体特性设置不同的展示风格。我们暂且了解三个。
注意要加小括号,没有分号
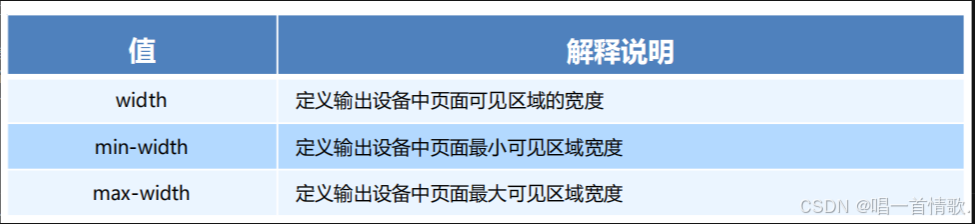
以上特性都是包含边界值的,比如min-width:100px就表示>=100px
案例:实现思路
① 按照从大到小的或者从小到大的思路
② 注意我们有最大值 max-width 和最小值 min-width都是包含等于的
③ 当屏幕小于540像素, 背景颜色变为蓝色 (x <= 539)
④ 当屏幕大于等于540像素 并且小于等于 969像素的时候 背景颜色为 绿色 ( 540=
注意: 为了防止混乱,媒体查询我们要按照从小到大或者从大到小的顺序来写,但是我们最喜欢的还是从小到大来写,这样代码更简洁
@media screen and (max-width:539px) { body{ background-color: blue; } } @media screen and (min-width:540px) and (max-width:969px) { body{ background-color: green; } } @media screen and (min-width:970px) { body{ background-color: red; } }由CSS的层叠性,可以省略第二个媒体查询的 and (max-width:969px),简写如下
@media screen and (max-width:539px) { body{ background-color: blue; } } @media screen and (min-width:540px) { body{ background-color: green; } } @media screen and (min-width:970px) { body{ background-color: red; } }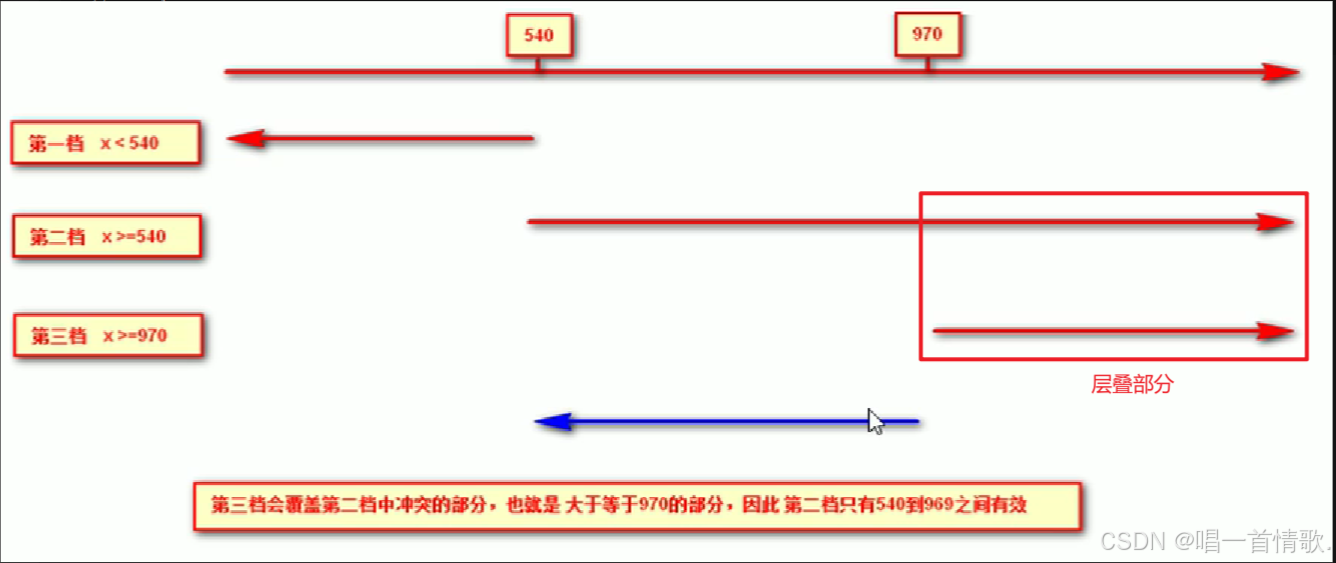
有个Bug:当width介于(539,540)时,页面没有样式
引入资源
当不同设备/页面宽度对应的样式有很多不同的时候,我们可以针对不同的媒体使用不同 stylesheets(样式表,即CSS文件)。原理就是直接在link中判断设备的尺寸,然后引用不同的css文件。
- 语法规范
2.示例
Document 1 2 style1.css
div{ width: 100%; height: 100px; } div:nth-child(1){ background-color: aqua; } div:nth-child(2){ background-color: green; }style2.css
div{ float: left; width: 50%; height: 100px; } div:nth-child(1){ background-color: aqua; } div:nth-child(2){ background-color: green; } 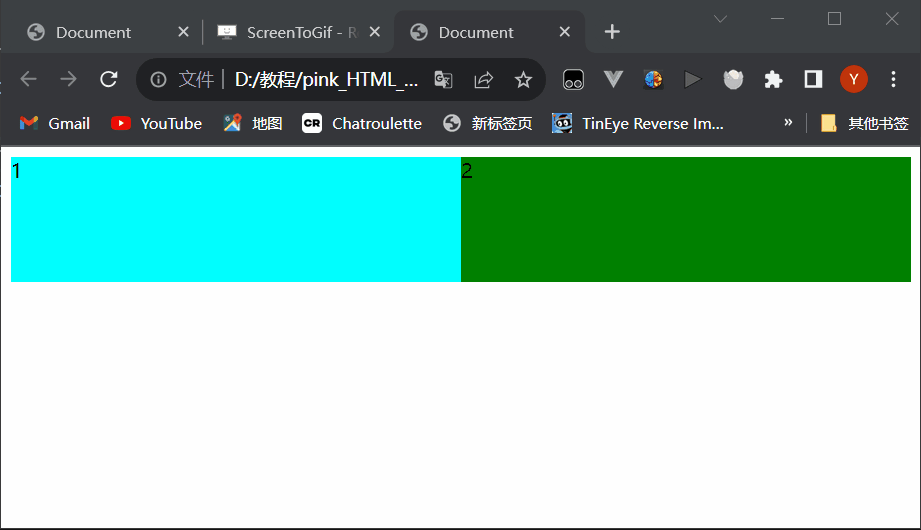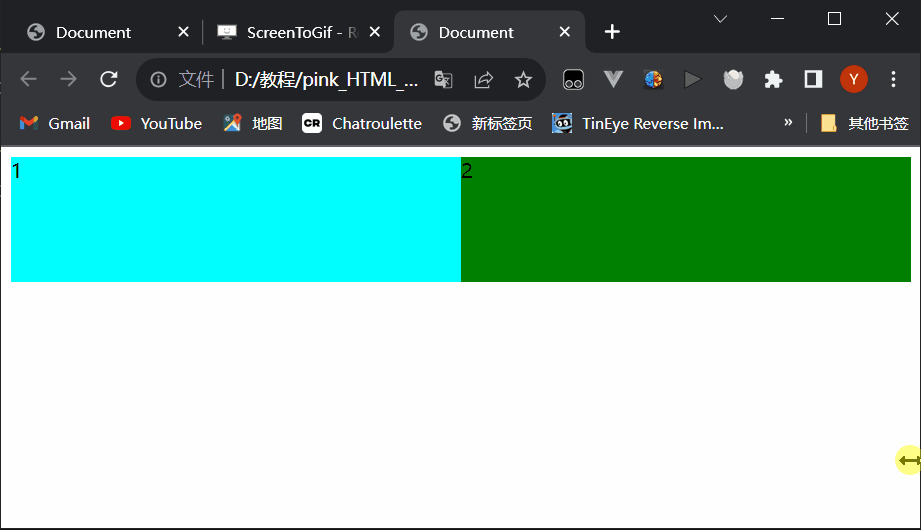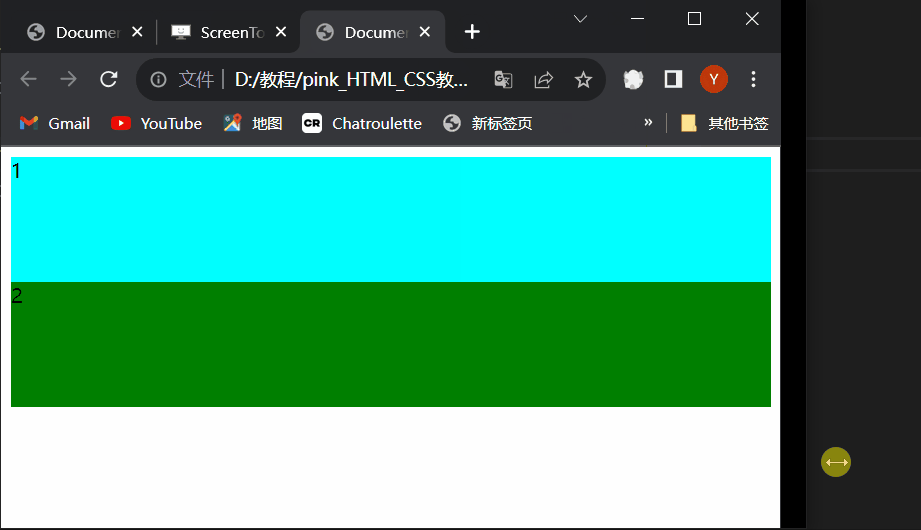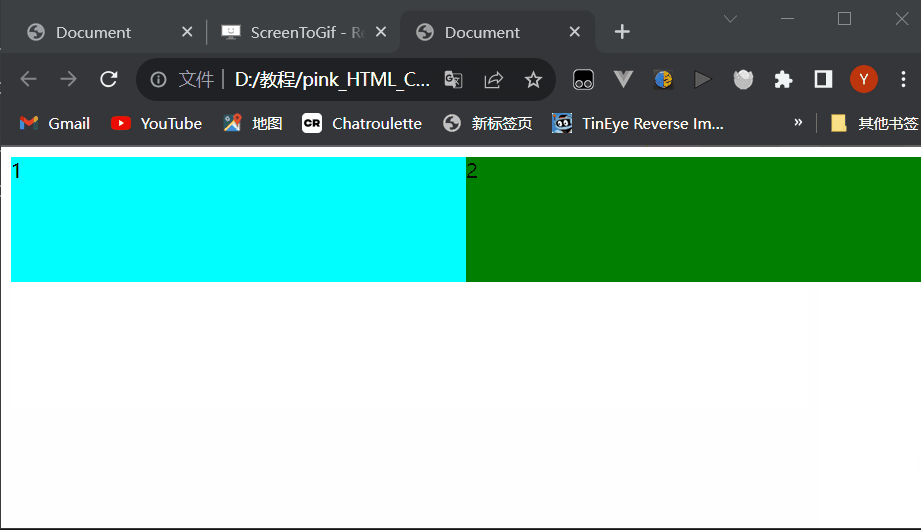
相关内容
热门资讯
通报开挂!情怀游戏字牌辅助,h...
>>您好:情怀游戏字牌辅助确实是有挂的,很多玩家在这款情怀游戏字牌辅助游戏中打牌都会发现很多用户的牌...
总算清楚“微信小程序嘟嘟十三张...
总算清楚“微信小程序嘟嘟十三张脚本”wepoker透视破解版(带开挂辅助安装透明挂教程) 【无需打开...
教程辅助“微信小程序蜀山四川辅...
教程辅助“微信小程序蜀山四川辅助器”真实有挂开挂辅助软件大神讲解微信小程序蜀山四川辅助器ai黑科技系...
盘点一款“手机字牌辅助脚本工具...
盘点一款“手机字牌辅助脚本工具”hhpoker有没有辅助辅助(带开挂辅助下载攻略方法);无需打开直接...
教程辅助“潮汕汇app透视软件...
教程辅助“潮汕汇app透视软件”揭秘有挂开挂辅助平台分享教程;无需打开直接搜索薇:136704302...
透视教学“陕麻圈内购破解辅助”...
透视教学“陕麻圈内购破解辅助”pokemmo手机辅助软件(带开挂辅助安装扑克教程);无需打开直接搜索...
教程辅助“打两圈辅助软件”真实...
较多好评“微乐万能挂官网”开挂(透视)辅助教程 了解更多开挂安装加(136704302)微信号是一款...
玩家必看秘籍“新荣耀平台辅助”...
玩家必看秘籍“新荣耀平台辅助”wepoker辅助软件价格(带开挂辅助神器黑科技教程);亲,wepok...
教程辅助“游戏茶苑辅助器”有挂...
游戏茶苑辅助器 无需打开直接搜索微信:136704302本司针对手游进行,选择我们的四大理由: 1、...
重大通报“闲来游戏辅助软件”w...
闲来游戏辅助软件是一款可以让一直输的玩家,快速成为一个“必胜”的ai辅助神器,有需要的用户可以加我微...
