稀疏3D检测-Sparse4Dv1v2v3
0. Multi-view 3D detection
LSS(Lift-Splat-Shoot)利用深度估计将图像特征提升到3D空间,并将特征拍到BEV平面。后续工作将lift-splats操作应用于3D检测领域。
Bevformer将时序信息以BEV特征cat一起引入时序信息。
DETR3D中通过预测的3D点投影到图像平面后获取图像特征,并且将deformable attention(Deformable DETR)应用于多视觉检测中。
PETR系列方法中,2D图像特征转换成3D的感知特征。对于每个instance feature,采用global cross attention来实现多视角的特征融合。由于融合模块计算复杂度仍与特征图尺寸相关,因此其仍然属于dense算法的范畴,对高分辨率的图像特征输入不够友好。
Sparse4D系列在3D空间中设置显式anchor,将它们投影到图像视图中以聚合局部特征,并通过迭代方式细化anchor。
Sparse 系列
资源:
SparseDrive:https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.19620
git: https://github.com/swc-17/SparseDrive/
Sparse4D: https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.10581
Sparse4Dv2: https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14018
Sparese4Dv3: https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.11722
git: https://github.com/linxuewu/Sparse4D
Sparse4D
1 sparse4D v1 & v2
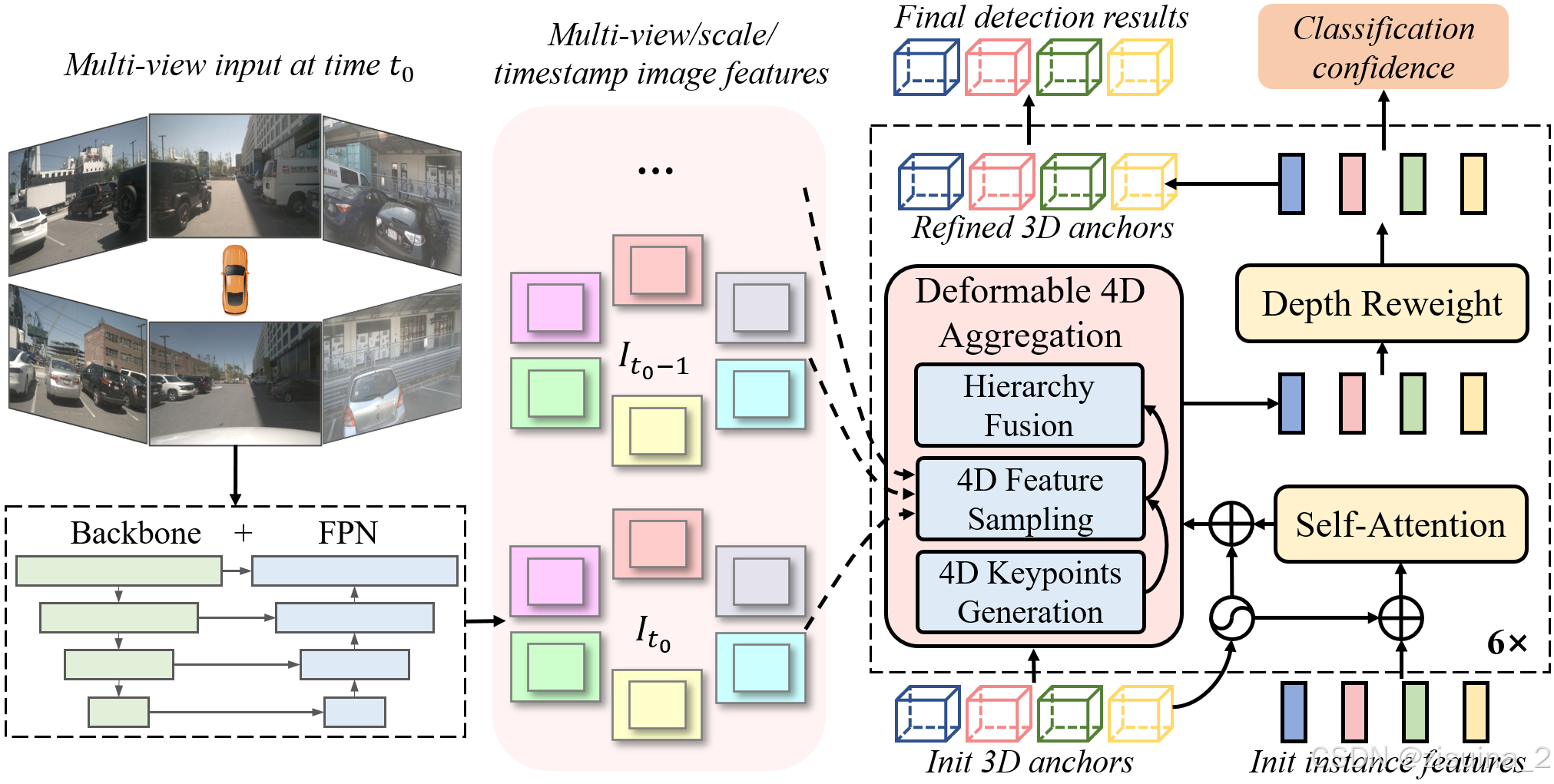
1.1 v1 Deformable 4D Aggregation
- 4D 关键点生成:基于每个instance 的3D anchor信息, 可以生成一系列3D关键点,分为固定关键点和可学习关键点。我们将固定关键点设置为anchor box的各面中心点及其立体中心点,可学习关键点坐标通过instance feature接一层全连接网络得到。在Sparse4D 中,采用了7个固定关键点 + 6个可学习关键点的配置fix_scare和learned scale(FC)。然后,结合instance 自身的速度信息以及自车的速度信息,对这些3D关键点进行运动补偿,获得其在历史时刻中的位置。结合当前帧和历史帧的3D关键点,获得了每个instance 的4D 关键点。默认base anchor使用了nuscenes_kmeans900.npy,其中聚类了x,y,z,其余whlyaw都是默认1,其余0.
- 4D 特征采样:在获得每个instance在当前帧和历史帧的3D关键点后,根据相机的内外参将其投影到对应的多视角多尺度特征图上进行双线性插值采样。从而得到Multi-Keypoint,Multi-Timestamp, Multi-Scale, Multi-View 的特征表示;[points_2d, attention weights, feature]进入deformable_aggregation_function,融合有两个function{add,cat}。
- 层级化特征融合:在采样得到多层级的特征表示后,需要进行层级化的特征融合,分为了三层:
- Fuse Multi-Scale/View:对于一个关键点在不同特征尺度和视角上的投影,采用了加权求和的方式,权重系数通过将instance feature和anchor embed输入至全连接网络中得到;
- Fuse Multi-Timestamp:对于时序特征,采用了简单的recurrent策略(concat + linear)来融合;LinearFusionModule
- Fuse Multi-Keypoint:最后,采用求和的方式融合同一个instance不同keypoint的特征;
实例由三部分表示,分别是anchor、实例特征和anchor embedding(anchor, instance feature and anchor embedding)。
- anchor是结构化信息,表示实例的状态,具有实际的物理意义。两部分组成。默认使用
- instance feature是从图像中提取的高阶语义特征,主要来自图像编码器。
- 而anchor embedding就是anchor的特征编码,用一个小的anchor编码器Ψ将anchor的结构化信息映射到高维空间。
![[Image]](/uploadfile/202501/b33b1e1e3be444.png)
1.2 v2 Instance Temporal Propagation:
anchor中加入了时序动态补偿,在Sparse4D-V2中,将decoder分为单帧层和时序层。单帧层以新初始化的instance作为输入,输出一部分高置信度cls得分的instance至时序层;时序层的instance除了来自于单帧层的输出以外,还来自于历史帧(上一帧)。我们将历史帧的instance投影至当前帧,其中,instance feature保持不变,anchor box通过自车运动和目标速度投影至当前帧,anchor embed通过对投影后的anchor进行编码得到。StreamPETR 中,采用了隐式的query时序转换方式,即把velocity、ego pose、timestamp都编码成特征,然后再和query feature做一些乘加操作;
1.3 v2 Efficient Deformable Aggregation
对Deformable Aggregation运算速率进行优化。对deformable aggregation模块进行了底层的分析和优化,让其并行计算效率显著提升,显存占用大幅降低。
1.4 v2 Camera Parameter Encoding
将相机参数进行编码,将相机投影矩阵通过全连接网络映射到高维特征空间得到camera embed。在计算deformable aggregation中的attention weights 𝑊 时,我们不仅考虑instance feature和anchor embed,还加上了camera embed。DeformableFeatureAggregation中进行添加。
1.5 v2Dense Depth Supervision
加入depth辅助监督,在实验中,发现基于稀疏的方法在早期训练阶段缺乏足够的收敛能力和速度。为了缓解这一问题,我们还引入了以点云为监督的多尺度密集深度估计方法作为辅助训练任务。而在推理过程中,这个分支网络将不会被激活,不影响推理效率。
2 Sparse4D-v3(2023.11):
在V3中针对sparse快速收敛:改善denosing,增加quality模块。对于特征混肴:提出了Decopled Attention
2.1 Temporal Instance Denoising
训练的instance包括learnable,noisy。其中noisy的包含temporal,nontemporal elements。时序增加了denosing, 在传统denosing上正负样本分配机制有可能存在歧义,使用bipartite graph进行分配,时序上,会在单帧选择M′ group进入下一帧的训练。每组实例的相互独立性,噪声实例和正常实例之间没有特征交互,这与 DN-DETR 不同。
Mask制作,左边DN-DETR,PETR系列的mask,右边是sparse4D的mask生成方式:![[Image]](/uploadfile/202501/7584fd2a60d293e.png)
正负样本的制作DN-DETR
reference_points += noise (if noise ratio > 0.5 positive else negtive) reference_points += noise (if noise ratio > 0.5 positive else negtive) 生成了2倍的dn reference_points
作者认为上述的随机干扰存在歧义,这些样本不够负样本,制作noise_neg这部分的noise的干扰会更大
reference_points = [reference_points, box_target + noise_neg] 并且即使是Denosing也使用box_cost和匈牙利算法制作了正样本
2.2 增加quality训练分支
![[Image]](/uploadfile/202501/433142cb6517d6f.png)
现有的基于稀疏方法的主要估计cls置信度来衡量正样本和负样本与真实值的对齐情况。优化目标是最大化所有正样本的分类置信度。然而,不同正样本之间的匹配质量差异显著,因此,论文分类置信度并不是评估预测边界框质量的理想指标。为了帮助网络理解正样本的质量,一方面加速收敛,另一方面合理化预测排名,我们引入了预测质量估计任务。对于3D检测任务,我们定义了两个质量指标:中心点(centerness)和偏航度(yawness)
第0维度 位置的质量 CELOSS
cns_target = torch.norm( box_target[..., [X, Y, Z]] - box[..., [X, Y, Z]], p=2, dim=-1 ) cns_target = torch.exp(-cns_target) 第1维度 角度质量 GassianFocalLoss
yns_target = ( torch.nn.functional.cosine_similarity( box_target[..., [SIN_YAW, COS_YAW]], box[..., [SIN_YAW, COS_YAW]], dim=-1, ) > 0 ) 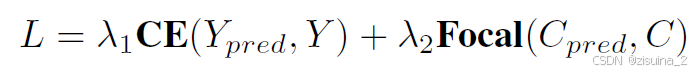
2.3 Decoupled Attention
![[Image]](/uploadfile/202501/83d99aabdd7ba.png)
Sparse4D中有两个instance attention模块,1)instance self-attention和2)temporal instance cross-attention。在这两个attention模块中,将instance feature和anchor embed相加作为query与key,在计算attention weights时一定程度上会存在特征混淆的问题。解耦注意力机制的提出。![[Image]](/uploadfile/202501/eed4befff0b7f.png)
if self.decouple_attn: self.fc_before = nn.Linear( self.embed_dims, self.embed_dims * 2, bias=False ) self.fc_after = nn.Linear( self.embed_dims * 2, self.embed_dims, bias=False ) if self.decouple_attn: query = torch.cat([query, query_pos], dim=-1) if key is not None: key = torch.cat([key, key_pos], dim=-1) query_pos, key_pos = None, None if value is not None: value = self.fc_before(value) return self.fc_after( self.layers[index]( query, key, value, query_pos=query_pos, key_pos=key_pos, **kwargs, ) ) 2.4 Validation
![[Image]](/uploadfile/202501/460bf6af9f42af2.png)
