计算机视觉实战项目3(图像分类+目标检测+目标跟踪+姿态识别+车道线识别+车牌识别+无人机检测+A*路径规划+单目测距与测速+行人车辆计数等)
往期热门项目回顾:
计算机视觉项目大集合
改进的yolo目标检测-测距测速
路径规划算法
图像去雨去雾+目标检测+测距项目
交通标志识别项目
yolo系列-重磅yolov9界面-最新的yolo
姿态识别-3d姿态识别
深度学习小白学习路线
车辆跟踪及测距
- 该项目一个基于深度学习和目标跟踪算法的项目,主要用于实现视频中的目标检测和跟踪。
- 该项目使用了 YOLOv5目标检测算法和 DeepSORT
目标跟踪算法,以及一些辅助工具和库,可以帮助用户快速地在本地或者云端上实现视频目标检测和跟踪!
教程博客_传送门链接------->单目测距和跟踪
yolov5 deepsort 行人/车辆(检测 +计数+跟踪+测距+测速)
- 实现了局域的出/入 分别计数。
- 显示检测类别,ID数量。
- 默认是 南/北 方向检测,若要检测不同位置和方向,需要加以修改
- 可在 count_car/traffic.py 点击运行
- 默认检测类别:行人、自行车、小汽车、摩托车、公交车、卡车、船。
- 检测类别可在 objdetector.py 文件修改。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ALiLiLiYa/article/details/131819630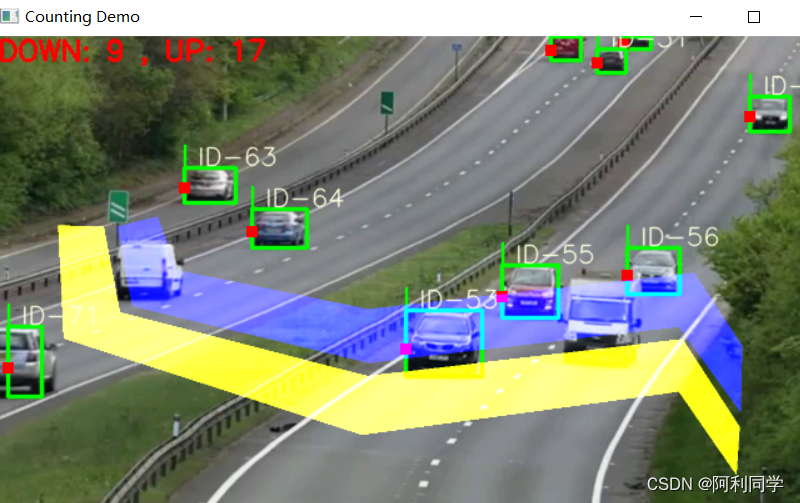
目标跟踪
- YOLOv5是一种流行的目标检测算法,它是YOLO系列算法的最新版本。
- YOLOv5采用了一种新的架构,可以在保持高准确性的同时提高检测速度。
- 在本文中,我们将介绍如何使用YOLOv5_deepsort算法来进行船舶跟踪和测距。
教程博客_传送门链接------->目标跟踪
车道线识别
- 本文主要讲述项目集成:从车道线识别、测距、到追踪,集各种流行模型于一体!
- 不讲原理,直接上干货!
- 把下文环境配置学会,受益终生!
- 各大项目皆适用
!
教程博客_传送门链接------->车道线识别+目标检测
看下本项目的效果:
语义分割
- MMsegmentation是一个基于PyTorch的图像分割工具库,
- 它提供了多种分割算法的实现,包括语义分割、实例分割、轮廓分割等。
- MMsegmentation的目标是提供一个易于使用、高效、灵活且可扩展的平台,以便开发者可以轻松地使用最先进的分割算法进行研究和开发
教程博客_传送门链接------->语义分割

姿态识别
人
- 体姿态估计是计算机视觉中的一项重要任务
- 具有各种应用,例如动作识别、人机交互和监控。
- 近年来,基于深度学习的方法在人体姿态估计方面取得了显著的性能。
- 其中最流行的深度学习方法之一是YOLOv7姿态估计模型
。
程博客_传送门链接------->:姿态识别https://blog.csdn.net/ALiLiLiYa/article/details/129482358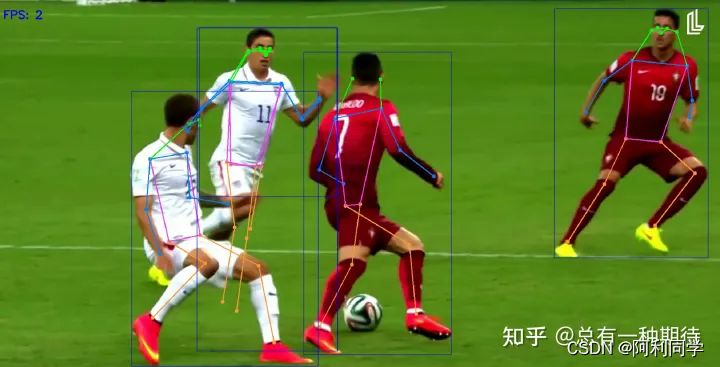
图像分类
- 在本教程中,您将学习如何使用迁移学习训练卷积神经网络以进行图像分类。您可以在 cs231n 上阅读有关迁移学习的更多信息。
- 本文主要目的是教会你如何自己搭建分类模型,耐心看完,相信会有很大收获。废话不多说,直切主题…
- 首先们要知道深度学习大都包含了下面几个方面:
1.加载(处理)数据
2.网络搭建
3.损失函数(模型优化)
4 模型训练和保存
- 把握好这些主要内容和流程,基本上对分类模型就大致有了个概念。
**教程博客_传送门链接--------->:图像分类
交通标志识别
本
- 项目是一个基于 OpenCV 的交通标志检测和分类系统
- 可以在视频中实时检测和分类交通标志。检测阶段使用图像处理技术,
- 在每个视频帧上创建轮廓并找出其中的所有椭圆或圆形。它们被标记为交通标志的候选项。
教程博客_传送门链接------->交通标志识别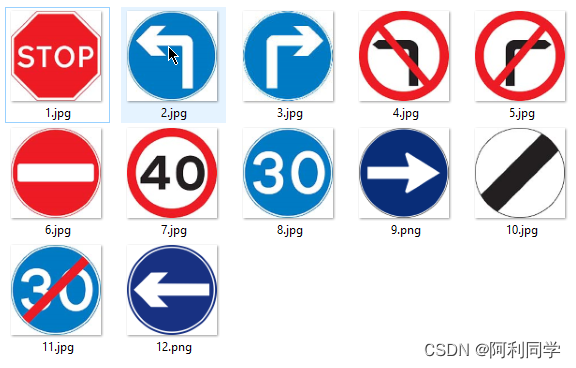
表情识别、人脸识别
- 面部情绪识别(FER)是指根据面部表情识别和分类人类情绪的过程。
- 通过分析面部特征和模式,机器可以对一个人的情绪状态作出有根据的推断。
- 这个面部识别的子领域高度跨学科,涉及计算机视觉、机器学习和心理学等领域的知识
。
教程博客_传送门链接------->表情识别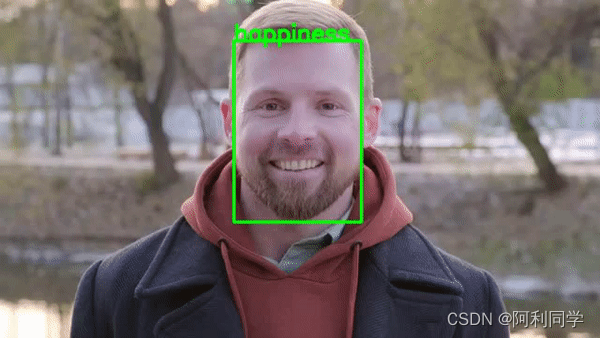
疲劳检测
- 瞌睡经常发生在汽车行驶的过程中
- 该行为害人害己,如果有一套能识别瞌睡的系统,那么无疑该系统意义重大!
教程博客_传送门链接------->疲劳检测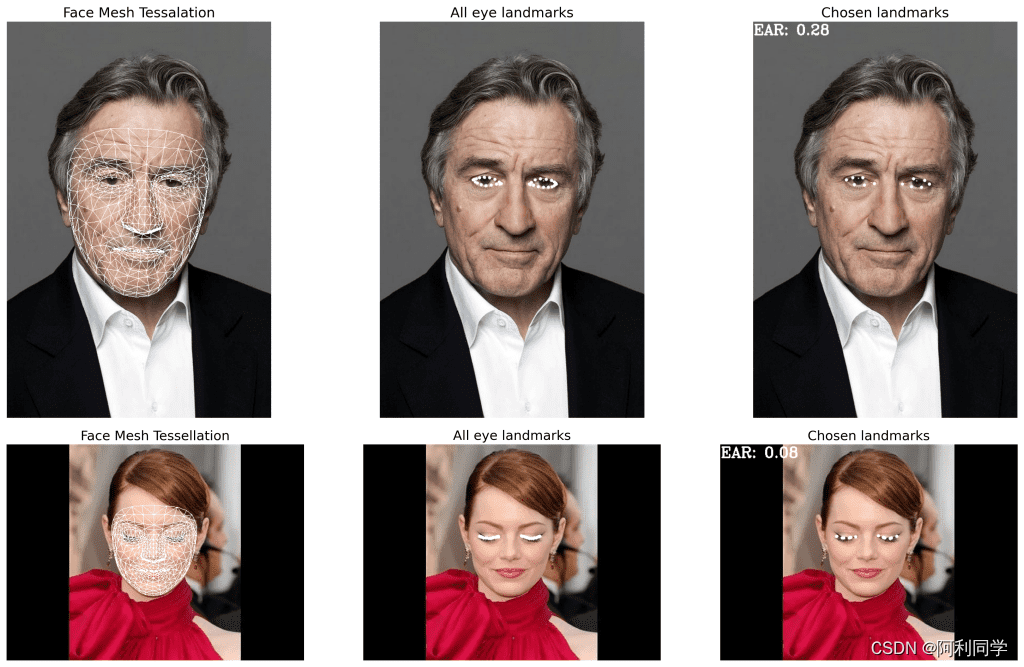
车牌识别
- 用python3+opencv3做的中国车牌识别
- 包括算法和客户端界面,只有2个文件,一个是界面代码,一个是算法代码
- 点击即可出结果,方便易用!
链接:车牌识别
大致的UI界面如下,点击输入图片,右侧即可出现结果!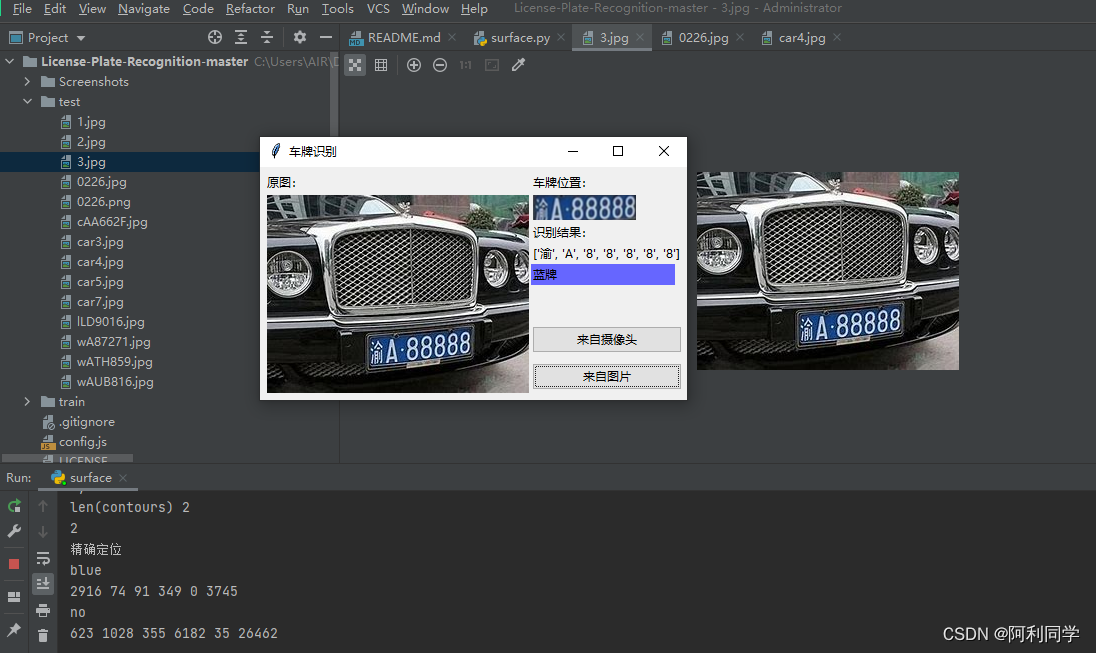
代码
额外说明:算法代码只有500行,测试中发现,车牌定位算法的参数受图像分辨率、色偏、车距影响。
--->qq 1309399183----------<代码交流 def from_pic(self): self.thread_run = False self.pic_path = askopenfilename(title="选择识别图片", filetypes=[("jpg图片", "*.jpg")]) if self.pic_path: img_bgr = predict.imreadex(self.pic_path) self.imgtk = self.get_imgtk(img_bgr) self.image_ctl.configure(image=self.imgtk) resize_rates = (1, 0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5, 0.4) for resize_rate in resize_rates: print("resize_rate:", resize_rate) r, roi, color = self.predictor.predict(img_bgr, resize_rate) if r: break #r, roi, color = self.predictor.predict(img_bgr, 1) self.show_roi(r, roi, color) 图像去雾去雨+目标检测+单目测距结合
- 0.0实时感知本车周围物体的距离对高级驾驶辅助系统具有重要意义,当判定物体与本车距离小于安全距离时便采取主动刹车等安全辅助功,
- 0.1这将进一步提升汽车的安全性能并减少碰撞的发生。上一章本文完成了目标检测任务,接下来需要对检测出来的物体进行距离测量。
- 1.首先描述并分析了相机成像模型,推导了图像的像素坐标系与世界坐标系之间的关系。
- 2.其次,利用软件标定来获取相机内外参数并改进了测距目标点的选取。
- 3.最后利用测距模型完成距离的测量并对采集到的图像进行仿真分析和方法验证。
传送门链接------------->:单目测距
代码
for path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset: img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device) img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32 img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0 if img.ndimension() == 3: img = img.unsqueeze(0) # Warmup if device.type != 'cpu' and (old_img_b != img.shape[0] or old_img_h != img.shape[2] or old_img_w != img.shape[3]): old_img_b = img.shape[0] old_img_h = img.shape[2] old_img_w = img.shape[3] for i in range(3): model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0] # Inference t1 = time_synchronized() with torch.no_grad(): # Calculating gradients would cause a GPU memory leak pred = model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0] t2 = time_synchronized() distance=object_point_world_position(u, v, h, w, out_mat, in_mat): 路径规划
本节针对越野场景路径规划问题,采用栅格法建立障碍物、威胁物和越野道路模型,模拟真实的越野环境场景。
引入方向变化惩罚和局部区域复杂度惩罚来优化A算法,使算法规划出的路径更平滑,算法效率更高效。
采用改进 Floyd 算法对路径进行双向平滑,并且进行了防碰撞处理,来确保规划出路径的安全可靠性。
仿真结果表明,所改进的 A算法与传统算法相比较,效率提高了 30%,拐点数减少了4
倍,所提算法能够在越野环境多重因素综合影响以及不同车辆性能和任务的要求下快速的规划出安全的路径。
传送门链接---------------->:A star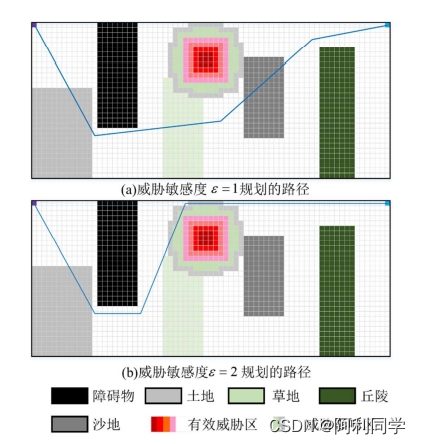
代码
###############创建A-Star类############ class AStar: # 描述AStar算法中的节点数据 class Node: #初始化 def __init__(self, point, startPoint,endPoint, g=0,w=1,p=1): self.point = point # 自己的坐标 self.father = None # 父节点 self.g = g # g值,g值在用到的时候会重新算 # 计算h值,采用曼哈顿距离 #self.h = (abs(endPoint.x - point.x) + abs(endPoint.y - point.y)) * 10 #采用欧几里得距离 #self.h = math.pow((math.pow((endPoint.x - point.x),2) + math.pow((endPoint.y - point.y),2)),0.5)*10 #采用对角距离 pp=(1-p)+0.2*math.exp((math.pow((math.pow((endPoint.x - point.x),2) + math.pow((endPoint.y - point.y),2)),0.5))/(math.pow((math.pow((endPoint.x - startPoint.x),2) + math.pow((endPoint.y - startPoint.y),2)),0.5))) Diagonal_step = min((endPoint.x - point.x),(endPoint.y - point.y)) straight_step = (abs(endPoint.x - point.x) + abs(endPoint.y - point.y)) - 2*Diagonal_step self.h =(straight_step + math.pow(2,0.5)*Diagonal_step)*10*pp #print(pp) #初始化A-start def __init__(self, map2d, startPoint, endPoint, passTag=1.0):#map2d地图信息,startPoint起点, endPoint终点, passTag=1.0为不可行驶区域 # 开启表 self.openList = [] # 关闭表 self.closeList = [] # 寻路地图 self.map2d = map2d # 起点终点 if isinstance(startPoint, Point) and isinstance(endPoint, Point): self.startPoint = startPoint self.endPoint = endPoint else: self.startPoint = Point(*startPoint) self.endPoint = Point(*endPoint) # 不可行走标记 self.passTag = passTag def getMinNode(self): """ 获得openlist中F值最小的节点 :return: Node """ currentNode = self.openList[0] for node in self.openList: if node.g + node.h < currentNode.g + currentNode.h: currentNode = node return currentNode#返回最小代价的点 停车位检测
- 基于深度学习的鱼眼图像中的停车点检测和分类是为二维物体检测而开发的。我们的工作增强了预测关键点和方框的能力。这在许多场景中很有用,因为对象不能用右上的矩形“紧密”表示。
- 一个这样的例子,道路上的任何标记,由于透视效果,在现实世界中的对象矩形不会在图像中保持矩形,所以关键点检测显得格外重要。鱼眼图像还呈现了观察到这种现象的另一种场景,由于鱼眼宽广的视角,可以扑捉更多画像
链接:停车位检测

代码
#全部代码可加qq1309399183 def train(): #parses command line args args = parse_args() #parses args from file if args.config_file is not None: cfg_from_file(args.config_file) if (args.FIX_MODEL_CHECKPOINT): args.FIX_MODEL_CHECKPOINT = args.FIX_MODEL_CHECKPOINT.replace(" ", "") args.FIX_MODEL_CHECKPOINT = args.FIX_MODEL_CHECKPOINT.replace("=", "") cfg.RESUME_CHECKPOINT = args.FIX_MODEL_CHECKPOINT cfg.CHECK_PREVIOUS = False if (os.path.exists(cfg.RESUME_CHECKPOINT) == False): print('Exiting the process as asked model for resuming is not found') exit() if (args.RESUME_CHECKPOINT): cfg.RESUME_CHECKPOINT = args.RESUME_CHECKPOINT if (args.LOG_DIR): cfg.EXP_DIR = args.LOG_DIR cfg.LOG_DIR = cfg.EXP_DIR if (args.PHASE): cfg.PHASE = [] cfg.PHASE.append(args.PHASE) if (args.EVAL_METHOD): cfg.DATASET.EVAL_METHOD = args.EVAL_METHOD #for backward compatibility if cfg.DATASET.DATASET == 'psd': cfg.DATASET.DATASET = 'tiod' if cfg.DATASET.BGR_OR_RGB == True: #cfg.DATASET.PIXEL_MEANS = (123.68, 116.78, 103.94) #cfg.DATASET.PIXEL_MEANS = (123, 117, 104) cfg.DATASET.PIXEL_MEANS = (128.0, 128.0, 128.0) # simpler mean subtraction to keep data in int8 after mean subtraction print("cfg: ", cfg) for phase in cfg.PHASE: cfg_dir = cfg.LOG_DIR + '/' + phase + '_cfg/' os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(cfg_dir), exist_ok=True) shutil.copy(args.config_file, cfg_dir) # to making every run consistent # TII np.random.seed(100) torch.manual_seed(100) torch.cuda.manual_seed(100) random.seed(100) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(999) torch.backends.cudnn.enabled = False train_model() if __name__ == '__main__': train() 图像雾去雨与目标检测
- 针对不同的天气则采取不同的图像前处理方法来提升图像质量。
- 雾天天气 时,针对当下求解的透射率会导致去雾结果出现光晕、伪影现象,本文采用加权最小二乘法细化透射率透。
- 针对四叉树法得到的大气光值不精确的问题,改进四叉树法来解决上述问题。将上述得到的透射率和大气光值代入大气散射模型完成去雾处理;
- 在图像处理后加入目标检测,提高了目标检测精度以及目标数量。
下图展现了雾天处理后的结果
图第一列为雾霾图像,第二列为没有加入图像处理的目标检测结果图,第三列为去雾后的目标检测结果图。

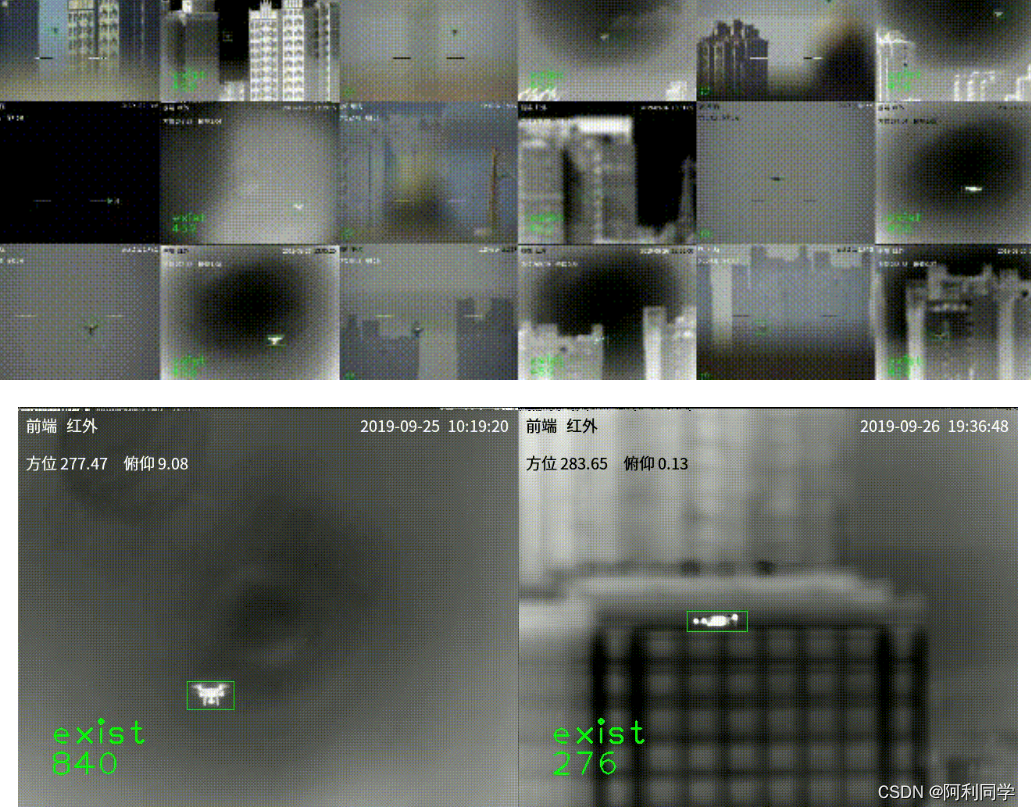
无人机检测
- 反无人机目标检测与跟踪的意义在于应对无人机在现实世界中可能带来的潜在威胁,并保障空域安全。以下是这方面的几个重要意义:
- 空域安全:无人机的广泛应用给空域安全带来了新的挑战。通过开展反无人机目标检测与跟踪研究,可以及时发现和追踪潜在的无人机入侵行为,确保空域的安全和秩序。
- 防范恶意活动:无人机技术的快速发展也为一些恶意活动提供了新的工具和手段,如无人机进行窥探、非法监听、破坏等。反无人机目标检测与跟踪的研究可以帮助及时发现和阻止这些恶意活动,维护社会的稳定和安全
。
传送门链接-------------->:无人机检测