牛客周赛 Round 51 (C++)
创始人
2025-01-10 06:34:10
0次
目录
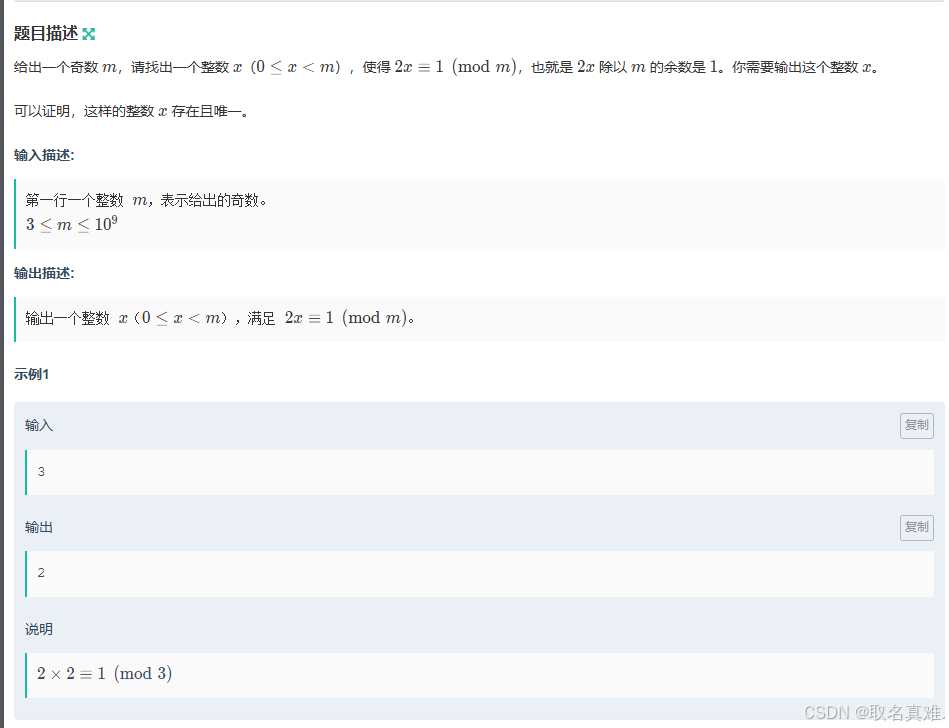
A-小红的同余_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
代码:
B-小红的三倍数_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
代码:
C-小红充电_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
代码:
D-小红的 gcd_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
代码:
E-小红走矩阵_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
代码:
F-小红的数组_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
代码:
A-小红的同余_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
通过二分查找答案即可
代码:
#include using namespace std; int m, ans; int judge(int x) { if ((2 * x) % m == 1) return 1; else return 0; } int main() { cin >> m; int l = 0, r = m; while (l < r) { int mid = (1 + l + r) >> 1; if (judge(mid)) { l = mid+1; ans = mid; } else r = mid-1; } cout << ans; } B-小红的三倍数_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)


思路:
为3的倍数的数有一个特点:各个位数相加的和为3的倍数,所以将所有数的各个位数加起来看和是否为3的倍数
代码:
#include using namespace std; int n; string s[110]; long long ans = 0; int main() { int n; cin >> n; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> s[i]; long long sum = 0; for (int j = 0; j < s[i].length(); j++) { sum += s[i][j] - '0'; } ans += sum % 3; } if (ans % 3 == 0) cout << "YES"; else cout << "NO"; } C-小红充电_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
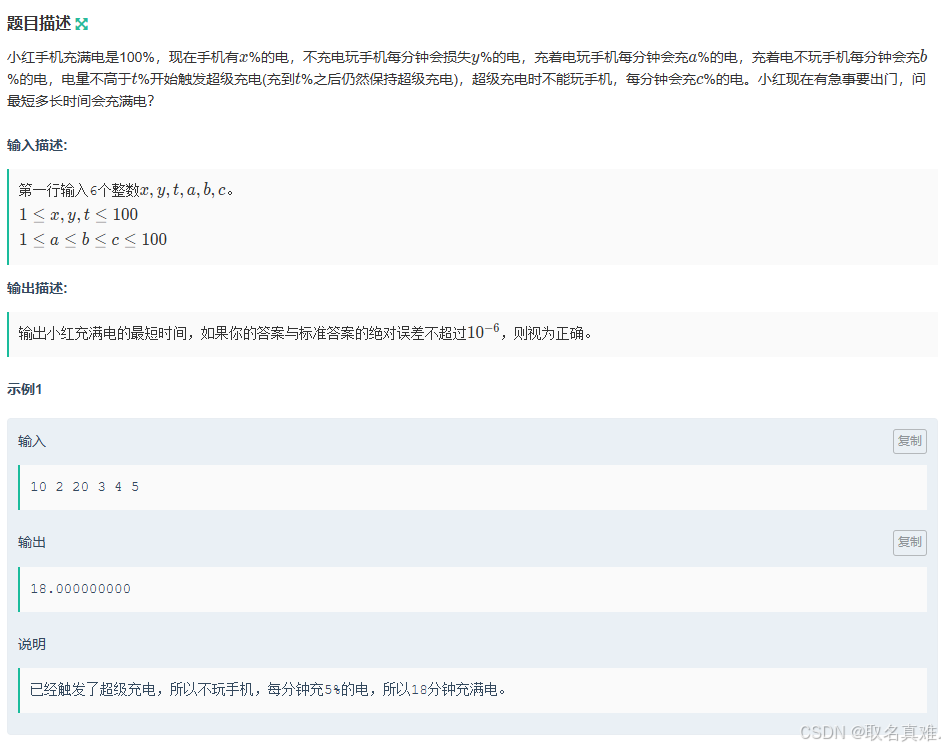
思路:
分两种情况讨论:第一种低于超级充电的触发条件,直接用C求即可;第二种高于超级充电触发条件,看是直接用B求所耗时间短 还是 先将电路用到低于超级充电触发条件然后用C求时间短。
代码:
#include using namespace std; int main() { double x, y, t, a, b, c; cin >> x >> y >> t >> a >> b >> c; double time; if (x <= t) { time = (100 - x) * 1.0 / c; } else { double ans1= (100 - x) * 1.0 / b; double ans2=(x-t)/y+ (100 - t) * 1.0 / c; time = min(ans1, ans2); } printf("%.9lf", time); } D-小红的 gcd_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
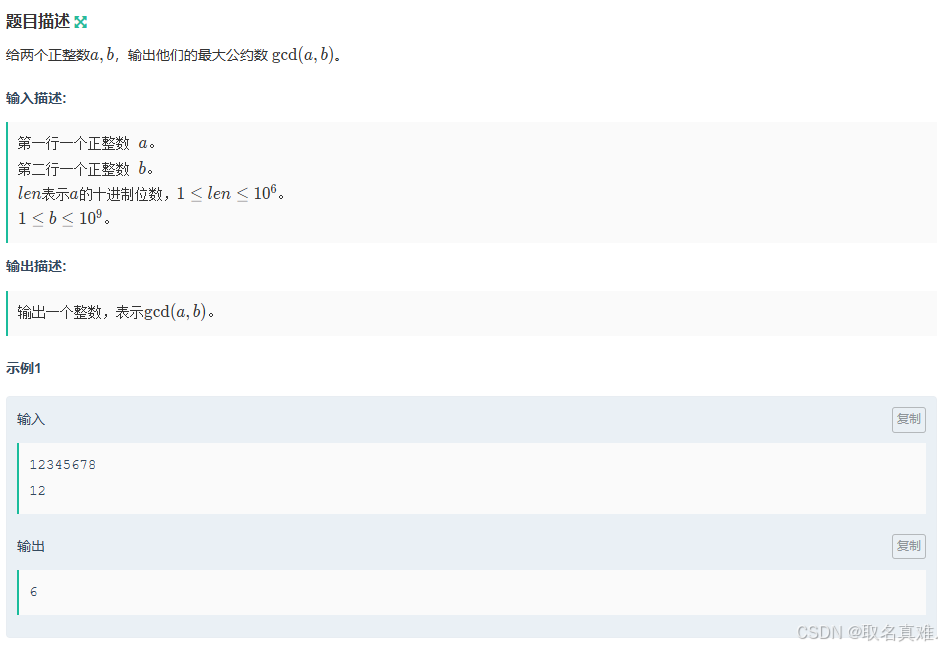
思路:
借用字符串来求,注意需要对每次求出来的值进行对b求余,不然会爆。
代码:
#include #define int long long using namespace std; int gcd(int a, int b) { return b > 0 ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } signed main() { string a; int b; cin >> a >> b; int x=0; int n = a.length(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { x *= 10; x += a[i] - '0'; x %= b; } int ans = gcd(x, b); cout << ans; return 0; } E-小红走矩阵_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)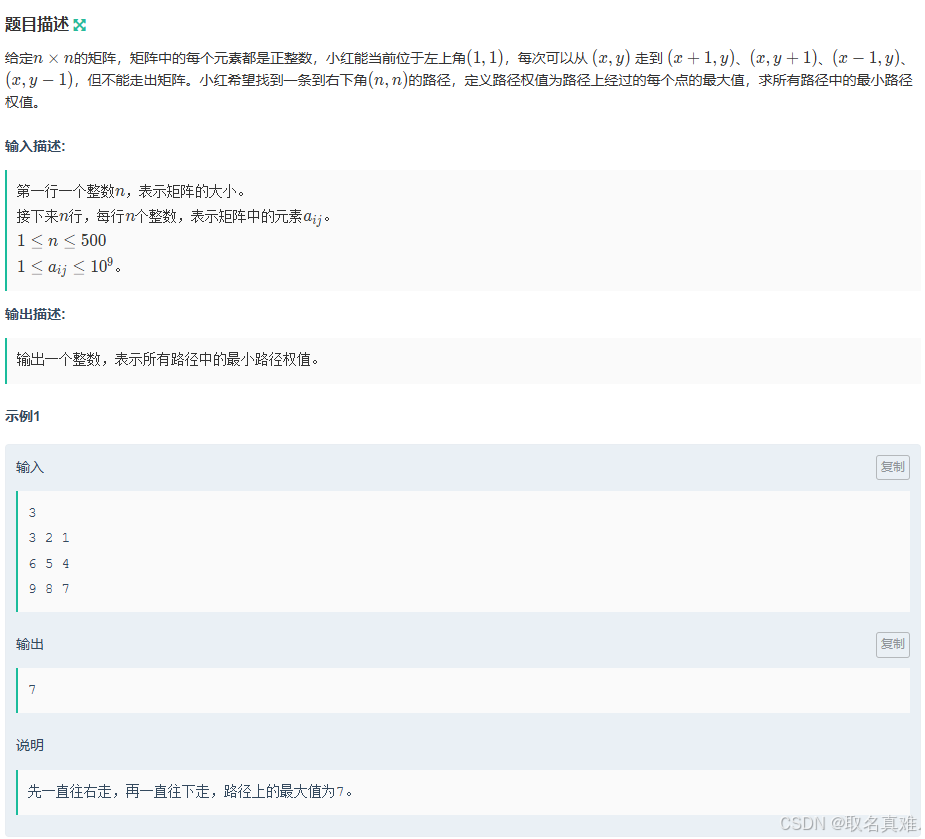
思路:
用二分法求答案,答案判断是否存在用深度搜索是否能走到终点
代码:
#include #include #define int long long using namespace std; int n, m, k; int s[510][510]; int dx[4] = { 1,0,0,-1 }; int dy[4] = { 0,1,-1,0 }; int flag = 0;//标志是否能走通迷宫 typedef struct node { int x, y; }node; node start, end1; int bfs(int ans) { queue q; if(s[1][1]>ans) return 0; q.push({1,1}); int book[510][510] = { 0 }; book[1][1]=1; while (!q.empty()) { int x = q.front().x;//取x坐标 int y = q.front().y;//取y坐标 q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)//遍历四个方向 { int tx = x + dx[i]; int ty = y + dy[i]; if (tx<1 || ty<1 || tx>n || ty>n || book[tx][ty] == 1 || s[tx][ty] > ans)//是否越界,是否走过,是否可走 continue; else { book[tx][ty] = 1; q.push({ tx,ty}); if(tx==n&&ty==n) return 1; } } } return 0; } signed main() { cin >> n ; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { cin >> s[i][j]; } int l = 1, r = 1e9; while (l < r) { int mid = (l + r) >> 1; if (bfs(mid)) r = mid; else l = mid + 1; } cout << l; return 0; } F-小红的数组_牛客周赛 Round 51 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
用线段树存正数时的绝对值最大和负数时的绝对值最大,相当于建了两棵树。
需要加一句 ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0) 不然会超时。
代码:
#include #define lc u<<1 #define rc u<<1|1 using namespace std; const int N = 5e5 + 10; typedef long long ll; struct node { int l, r; ll sum, lm, rm, m; ll fsum, flm, frm, fm; }tr[N << 2]; int n, q; ll a[N], b[N]; void pushup(node& u, node& l, node& r) { u.sum = l.sum + r.sum; u.lm = max(l.lm, l.sum + r.lm); u.rm = max(r.rm, r.sum + l.rm); u.m = max(l.m, max(r.m, l.rm + r.lm)); u.fsum = l.fsum + r.fsum; u.flm = max(l.flm, l.fsum + r.flm); u.frm = max(r.frm, r.fsum + l.frm); u.fm = max(l.fm, max(r.fm, l.frm + r.flm)); } void pushup(int u) { pushup(tr[u], tr[lc], tr[rc]); } void build(int u, int l, int r) { if (l == r)tr[u] = { l,l,a[l],a[l],a[l],a[l],b[l],b[l],b[l],b[l] }; else { tr[u] = { l,r }; int mid = (l + r) >> 1; build(lc, l, mid), build(rc, mid + 1, r); pushup(u); } } node query(int u, int l, int r) { if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r)return tr[u]; int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1; if (l > mid)return query(rc, l, r); else if (r <= mid)return query(lc, l, r); else { node res; node L = query(lc, l, r); node R = query(rc, l, r); pushup(res, L, R); return res; } } signed main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0); cin >> n; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; b[i] = -a[i]; } cin >> q; build(1, 1, n); while (q--) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; node t = query(1, a, b); cout << max(t.m, t.fm) << '\n'; } return 0; } 相关内容
热门资讯
第四分钟了解“一起宁德钓蟹黑科...
第四分钟了解“一起宁德钓蟹黑科技辅助软件推荐”必备开挂辅助挂-其实存在有挂1、任何一起宁德钓蟹黑科技...
8分钟俱乐部!hhpoker免...
8分钟俱乐部!hhpoker免费透视脚本,永胜联盟会封号(插件透视开挂辅助教程)1、完成hhpoke...
两分钟了解“传送屋激k有挂”安...
两分钟了解“传送屋激k有挂”安装开挂辅助插件-一直是有挂亲,关键说明,传送屋激k有挂赛季回归,传送屋...
九分钟精通!wpk透视辅助靠谱...
您好,wpk透视是真的假的这款游戏可以开挂的,确实是有挂的,需要了解加去威信【136704302】很...
第4分钟了解“越局吧可以看到别...
第4分钟了解“越局吧可以看到别人底牌”专业开挂辅助神器-一直真的有挂亲,关键说明,越局吧可以看到别人...
第六分钟理解!德普之星可以开辅...
第六分钟理解!德普之星可以开辅助,新道游科技透视免费版下载(AI透视开挂辅助教程)1、让任何用户在无...
透视数据"werpl...
透视数据"werplan可以作弊"揭露开挂作弊辅助助手(本然有挂)是一款可以让一直输的玩家,快速成为...
五分钟了解“微信小程序多乐跑得...
五分钟了解“微信小程序多乐跑得快破解”靠谱开挂辅助挂-都是真的有挂1、打开软件启动之后找到中间准星的...
7分钟指导!德普之星有透视辅助...
7分钟指导!德普之星有透视辅助,衢州都莱辅助器下载地址(大神透视开挂辅助app)1、完成衢州都莱辅助...
透视了解"德州透视是...
透视了解"德州透视是真的"揭露开挂作弊辅助软件(总是是有挂)相信很多朋友都在电脑上玩过德州透视是真的...