【Java】:浅克隆和深克隆
创始人
2025-01-10 06:03:13
0次
克隆
克隆和赋值
- 克隆的结果是有多个相同的实体,各个对象指向不同的实体
- 而多个不同对象指向一个相同的实体不是克隆,而是赋值
克隆的过程
- 首先实例化一个 student1 对象
- 在堆里开辟了一块内存用来存储 age = 10 这个数据
- 调用 clone 方法
- 在堆中又开辟了一块内存储存和 student1 指向内存区域一模一样的内容
- 将克隆后的数据内存地址赋值给 student2
- student2 指向新克隆出来的区域

- 但若想访问
clone方法,需要满足:- 重写
clone方法,返回super.clone()- 虽然
Object类是所有类的父类,但它内部的clone方法是protected修饰的,只有在同包中才能访问,所以需要在新包中重写clone方法 return super.clone()的意思就是调用父类(Object类)中的clone方法
- 虽然
- 强制类型转换调用
clone方法的对象- 调用
clone方法后的返回类型是Object类,而调用clone方法的对象是Student类 - 父类
Object需要强制类型转换成子类Student
- 调用
- 需要抛出
CloneNotSuppertedException异常 - 自定义类型必须实现
Clonable接口- 这个接口中没有任何抽象方法
- 此时这个接口叫做空接口/标记接口
- 只有实现了这个克隆接口,才具备了可以被克隆的能力
- 重写
代码
class Student implements Cloneable{ public int age = 10; @Override //重写clone方法 protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student1 = new Student(); Student student2 = (Student)student1.clone(); System.out.println(student1.age); //输出:10 System.out.println(student2.age); //输出:10 } } 浅克隆/浅拷贝
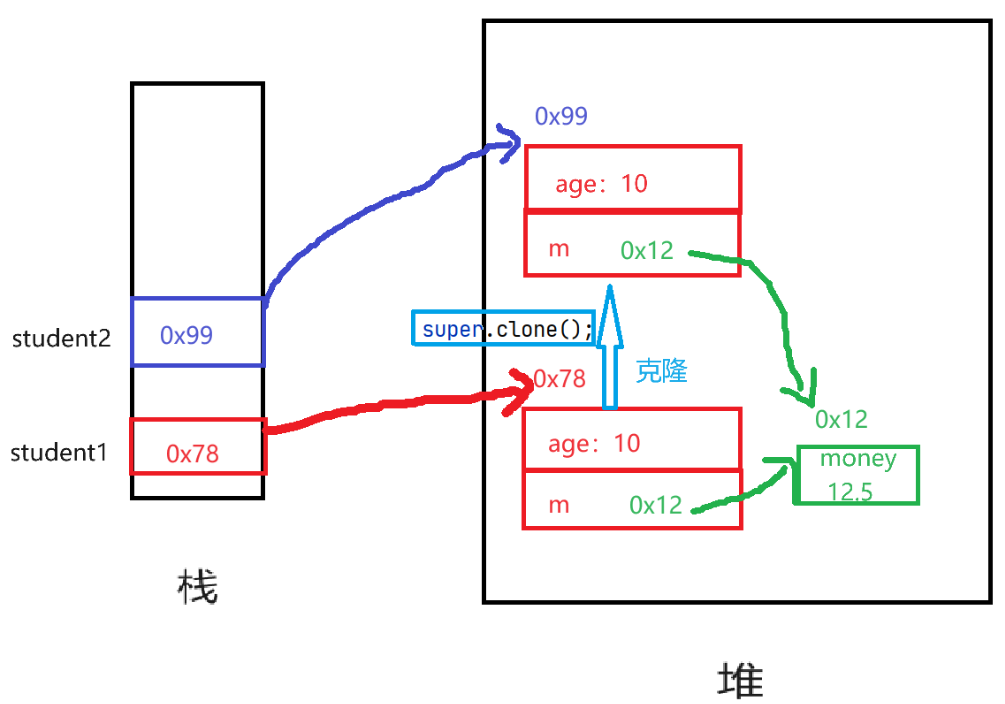
- 浅克隆创建一个新的对象,但只复制原始对象的基本数据类型的字段或引用(地址),而不赋值引用指向的对象
- 这意味着新对象和原始对象中的引用指向相同的对象
- 如果对原始对象的引用类型属性进行修改,浅克隆的对象也会受到影响,因为它们引用了相同的堆内存
浅克隆的实现
class Money { public double money = 12.5; } class Student implements Cloneable{ public int age = 10; public Money m = new Money(); @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student1 = new Student(); Student student2 = (Student)student1.clone(); System.out.println(student1.m.money); //输出:12.5 System.out.println(student2.m.money); //输出:12.5 System.out.println("========="); student1.m.money = 100; System.out.println(student1.m.money); //输出:100 System.out.println(student2.m.money); //输出:100 } } 观察输出结果可以发现:
- 将 student1 指向的对象m中的 money 成员改变后,student2 指向的对象中的 money 成员的值也变成了相同的值
所以可知:
- student1 和 student2 指向的 m 对象所指向的 money 成员是一样的
深拷贝/深克隆
若想在当 student1 修改 money 的值的时候,student2 中的 money 的值不变,就需要使用深克隆了
- 深克隆创建一个新的对象,并且递归地复制原始对象的所有字段和引用指向的对象,而不仅仅是复制引用本身
- 深克隆会确保新对象和原始对象之间的所有关系都是独立的
- 这意味着对新对象所做的修改不会影响到原始对象,因为他们拥有彼此独立的副本
深克隆的实现
- 深克隆的实现过程
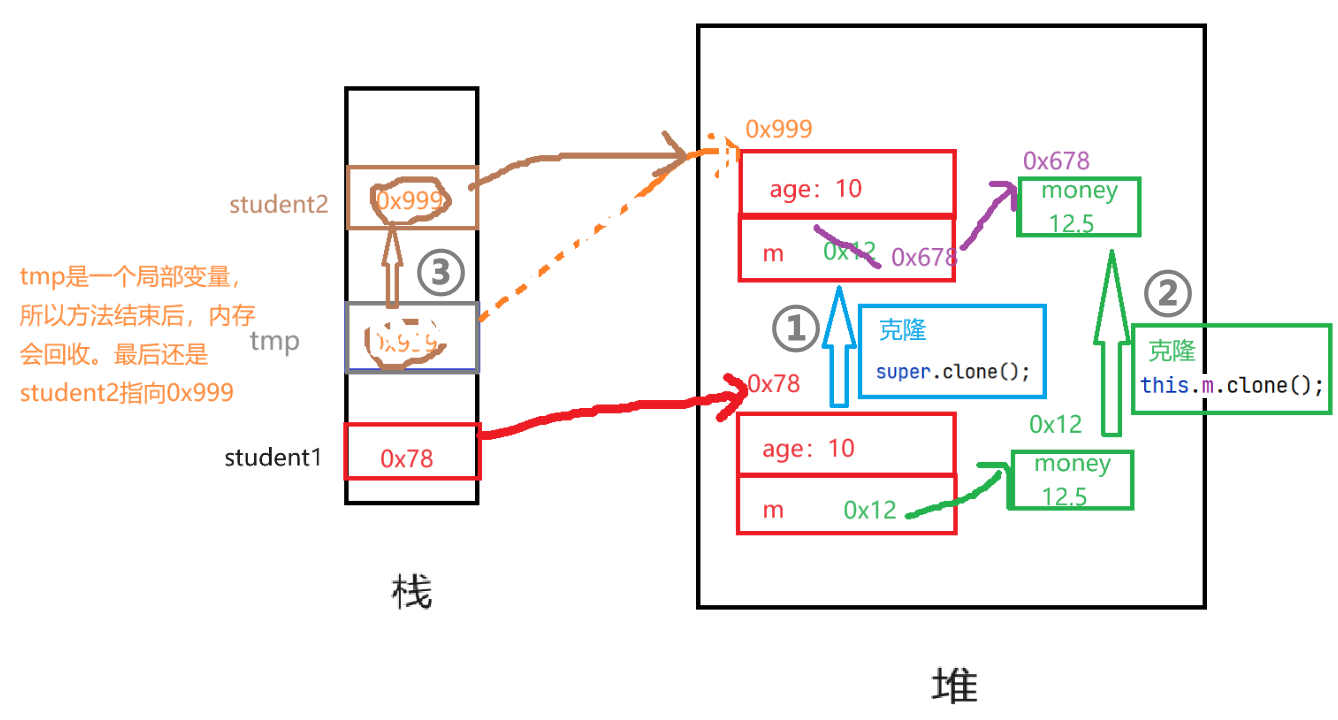
- 首先实例化一个
student1对象- 在堆里开辟了一块内存用来存储
age = 10和m这两个数据m是指向Money对象的指针或引用,这个Money对象里面有一个money = 12.5字段
- 在堆里开辟了一块内存用来存储
- 调用
clone方法- 在堆中又开辟了一块内存,存储和
student1一模一样的内容
- 在堆中又开辟了一块内存,存储和
- 将克隆后的数据所在堆中的地址赋值给
tmptmp指向新克隆出来的内容的地址
- 克隆实例化的对象
MoneyMoney类要支持clone方法- 要实现
Clonable接口 - 重写
clone方法
- 要实现
- 将克隆出来的对象的地址赋值给
tmp中的m- 至此,两个对象分别指向不同的两个内容相同的实体
- 实例中的引用变量间的修改也互不影响
- 返回
tmp- 将
tmp的指向地址赋值给student2,克隆完成
- 将
- 首先实例化一个
class Money implements Cloneable{ public double money = 12.5; @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } class Student implements Cloneable{ public int age = 10; public Money m = new Money(); @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student tmp = (Student) super.clone(); tmp.m = (Money)this.m.clone(); return tmp; } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student1 = new Student(); Student student2 = (Student)student1.clone(); System.out.println(student1.m.money); //输出:12.5 System.out.println(student2.m.money); //输出:12.5 System.out.println("========="); student1.m.money = 100; System.out.println(student1.m.money); //输出:100 System.out.println(student2.m.money); //输出:12.5 } } 相关内容
热门资讯
每日必看教程!凑一桌关春天辅助...
每日必看教程!凑一桌关春天辅助器可以安装(透视)wepoker辅助器软件下载(关于开挂辅助脚本)是一...
玩家实测!闲逸助手下载2.4....
玩家实测!闲逸助手下载2.4.0(透视)wepoker黑侠辅助器正版下载(分享开挂辅助安装);wep...
我来分享!友玩广西辅助联系方式...
我来分享!友玩广西辅助联系方式(透视)哈糖大菠萝能开挂吗(必备开挂辅助助手);是一款可以让一直输的玩...
总算了解!小闲辅助神器(透视)...
总算了解!小闲辅助神器(透视)德普之星私人局透视(曝光开挂辅助助手);德普之星私人局透视是一种具有地...
技术分享!美猴王辅助(透视)购...
您好:购买的wpk辅助在哪里下载这款游戏可以开挂的,确实是有挂的,很多玩家在这款游戏中打牌都会发现很...
一起来讨论!玉兔辅助器(透视)...
一起来讨论!玉兔辅助器(透视)德州圈脚本(总结开挂辅助软件);1、不需要AI权限,帮助你快速的进行德...
让我来分享经验!了解科技南通长...
让我来分享经验!了解科技南通长牌辅助神器(透视)wepoker透视脚本下载(科普开挂辅助神器);1....
盘点十款!手机字牌辅助脚本工具...
您好,手机字牌辅助脚本工具这款游戏可以开挂的,确实是有挂的,需要了解加微【485275054】很多玩...
玩家必看攻略!雀友会广东潮汕麻...
玩家必看攻略!雀友会广东潮汕麻雀开挂(透视)wepoker看底牌(关于开挂辅助器);1、这是跨平台的...
一分钟揭秘!微信边锋辅助(透视...
一分钟揭秘!微信边锋辅助(透视)wpk俱乐部有没有辅助(了解开挂辅助安装);相信小伙伴都知道这个微信...