(自用)高性能网络编程
Epoll - Reactor 设计模式
以餐厅大点餐为例
Reactor优点

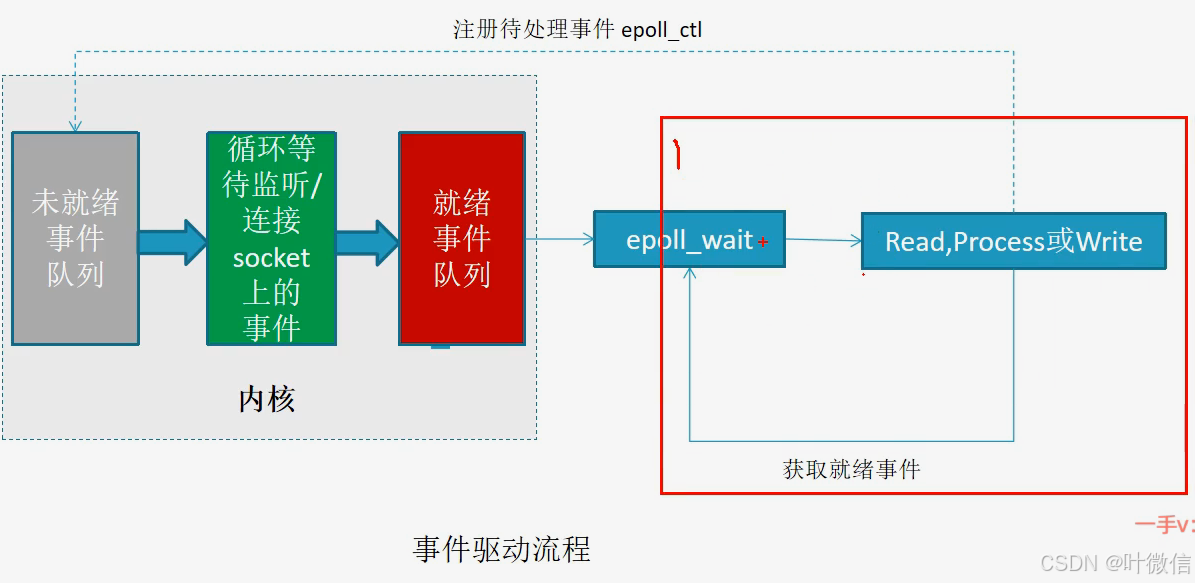
Epoll - IO多路复用
1.创建EPOLL 句柄
相关函数
epoll_create
#include int epoll_create(int size); 作用:
创建一个 epoll 实例
参数:
size 参数用于指定 epoll 实例中管理的文件描述符数量,不过该参数在现代 Linux 系统中已经被忽略,可以设置为任意值(除了 0)。
返回值:
如果创建成功,该文件描述符将是一个非负整数(用于后续的epoll操作);如果创建失败,该函数将返回 -1,并设置全局变量 errno 以指示错误原因。
2.向EPOLL对象中添加、修改或者删除感兴趣的事件
相关函数
epoll_ctl
#inclue int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event); 参数
epfd是epoll_create产生的epoll句柄(epoll_create的返回值)
fd表示操作的文件描述符
op取值:EPOLL_CTL_ADD 添加新的事件到epoll中
EPOLL_CTL_MOD 修改EPOLL中的事件
EPOLL_CTL_DEL 删除epoll中的事件
epoll_event结构体定义如下:
struct epoll_event{ __uint32_t events; epoll_data_t data; } typedef union epoll_data{//表示与事件相关的信息 void *ptr; int fd; uint32_t u32; uint64_t u64; }epoll_data_t events取值:
EPOLLIN 表示有数据可以读出(接受连接、关闭连接)
EPOLLOUT 表示连接可以写入数据发送(向服务器发起连接,连接成功事件) EPOLLERR 表示对应的连接发生错误
EPOLLHUP 表示对应的连接被挂起
3.收集在epoll监控的事件中已经发生的事件
#include int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event * events, int maxevents, int timeout); epfd: epoll的描述符。
events:则是分配好的 epoll_event结构体数组,epoll将会把发生的事件复制到 events数组中(events不可以是空指针,内核只负责把数据复制到这个 events数组中,不会去帮助我们在用户态中分配内存。内核这种做法效率很高)。
maxevents: 本次可以返回的最大事件数目,通常 maxevents参数与预分配的events数组的大小是相等的。
timeout: 表示在没有检测到事件发生时最多等待的时间(单位为毫秒),如果 timeout为0,立刻返回,不会等待。-1表示无限期阻塞
返回值
返回0表示监听超时
返回-1表示出错
大于0表示返回了需要处理的事件数
代码示例
用epoll实现了一个粗糙的http服务器
epoll_server.c
#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include // int fd; typedef struct _ConnectStat ConnectStat; typedef void(*response_handler) (ConnectStat * stat); struct _ConnectStat { int fd; char name[64]; char age[64]; struct epoll_event _ev; int status;//0 -未登录 1 - 已登陆 response_handler handler;//不同页面的处理函数 }; //http协议相关代码 ConnectStat * stat_init(int fd); void connect_handle(int new_fd); void do_http_respone(ConnectStat * stat); void do_http_request(ConnectStat * stat); void welcome_response_handler(ConnectStat * stat); void commit_respone_handler(ConnectStat * stat); const char *main_header = "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\nServer: Martin Server\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nConnection: Close\r\n"; static int epfd = 0; void usage(const char* argv) { printf("%s:[ip][port]\n", argv); } void set_nonblock(int fd) { int fl = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL); fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, fl | O_NONBLOCK); } int startup(char* _ip, int _port) //创建一个套接字,绑定,检测服务器 { //sock //1.创建套接字 int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (sock < 0) { perror("sock"); exit(2); } int opt = 1; setsockopt(sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt)); //2.填充本地 sockaddr_in 结构体(设置本地的IP地址和端口) struct sockaddr_in local; local.sin_port = htons(_port); local.sin_family = AF_INET; local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip); //3.bind()绑定 if (bind(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0) { perror("bind"); exit(3); } //4.listen()监听 检测服务器 if (listen(sock, 5) < 0) { perror("listen"); exit(4); } //sleep(1000); return sock; //这样的套接字返回 } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 3) //检测参数个数是否正确 { usage(argv[0]); exit(1); } int listen_sock = startup(argv[1], atoi(argv[2])); //创建一个绑定了本地 ip 和端口号的套接字描述符 //1.创建epoll epfd = epoll_create(256); //可处理的最大句柄数256个 if (epfd < 0) { perror("epoll_create"); exit(5); } struct epoll_event _ev; //epoll结构填充 ConnectStat * stat = stat_init(listen_sock); _ev.events = EPOLLIN; //初始关心事件为读 _ev.data.ptr = stat; //_ev.data.fd = listen_sock; // //2.托管 epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, listen_sock, &_ev); //将listen sock添加到epfd中,关心读事件 struct epoll_event revs[64]; int timeout = -1; int num = 0; int done = 0; while (!done) { //epoll_wait()相当于在检测事件 switch ((num = epoll_wait(epfd, revs, 64, timeout))) //返回需要处理的事件数目 64表示 事件有多大 { case 0: //返回0 ,表示监听超时 printf("timeout\n"); break; case -1: //出错 perror("epoll_wait"); break; default: //大于零 即就是返回了需要处理事件的数目 { struct sockaddr_in peer; socklen_t len = sizeof(peer); int i; for (i = 0; i < num; i++) { ConnectStat * stat = (ConnectStat *)revs[i].data.ptr; int rsock = stat->fd; //准确获取哪个事件的描述符 if (rsock == listen_sock && (revs[i].events) && EPOLLIN) //如果是初始的 就接受,建立链接 { int new_fd = accept(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len); if (new_fd > 0) { printf("get a new client:%s:%d\n", inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr), ntohs(peer.sin_port)); //sleep(1000); connect_handle(new_fd); } } else // 接下来对num - 1 个事件处理 { if (revs[i].events & EPOLLIN) { do_http_request((ConnectStat *)revs[i].data.ptr); } else if (revs[i].events & EPOLLOUT) { do_http_respone((ConnectStat *)revs[i].data.ptr); } else { } } } } break; }//end switch }//end while return 0; } ConnectStat * stat_init(int fd) { ConnectStat * temp = NULL; temp = (ConnectStat *)malloc(sizeof(ConnectStat)); if (!temp) { fprintf(stderr, "malloc failed. reason: %m\n"); return NULL; } memset(temp, '\0', sizeof(ConnectStat)); temp->fd = fd; temp->status = 0; //temp->handler = welcome_response_handler; } //初始化连接,然后等待浏览器发送请求 void connect_handle(int new_fd) { ConnectStat *stat = stat_init(new_fd); set_nonblock(new_fd); stat->_ev.events = EPOLLIN; stat->_ev.data.ptr = stat; epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, new_fd, &stat->_ev); //二次托管 } void do_http_respone(ConnectStat * stat) { stat->handler(stat); } void do_http_request(ConnectStat * stat) { //读取和解析http 请求 char buf[4096]; char * pos = NULL; //while header \r\n\r\ndata ssize_t _s = read(stat->fd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); if (_s > 0) { buf[_s] = '\0'; printf("receive from client:%s\n", buf); pos = buf; //Demo 仅仅演示效果,不做详细的协议解析 if (!strncasecmp(pos, "GET", 3)) { stat->handler = welcome_response_handler; } else if (!strncasecmp(pos, "Post", 4)) { //获取 uri printf("---Post----\n"); pos += strlen("Post"); while (*pos == ' ' || *pos == '/') ++pos; if (!strncasecmp(pos, "commit", 6)) {//获取名字和年龄 int len = 0; printf("post commit --------\n"); pos = strstr(buf, "\r\n\r\n"); char *end = NULL; if (end = strstr(pos, "name=")) { pos = end + strlen("name="); end = pos; while (('a' <= *end && *end <= 'z') || ('A' <= *end && *end <= 'Z') || ('0' <= *end && *end <= '9')) end++; len = end - pos; if (len > 0) { memcpy(stat->name, pos, end - pos); stat->name[len] = '\0'; } } if (end = strstr(pos, "age=")) { pos = end + strlen("age="); end = pos; while ('0' <= *end && *end <= '9') end++; len = end - pos; if (len > 0) { memcpy(stat->age, pos, end - pos); stat->age[len] = '\0'; } } stat->handler = commit_respone_handler; } else { stat->handler = welcome_response_handler; } } else { stat->handler = welcome_response_handler; } //生成处理结果 html ,write stat->_ev.events = EPOLLOUT; //stat->_ev.data.ptr = stat; epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, stat->fd, &stat->_ev); //二次托管 } else if (_s == 0) //client:close { printf("client: %d close\n", stat->fd); epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, stat->fd, NULL); close(stat->fd); free(stat); } else { perror("read"); } } void welcome_response_handler(ConnectStat * stat) { const char * welcome_content = "\ \n\ \n\ \n\ This is a test \n\ \n\ \n\ \n\
\n\ 大家好,欢迎来到奇牛学院VIP 课!
\n\ \n\ \n\ \n\ "; char sendbuffer[4096]; char content_len[64]; strcpy(sendbuffer, main_header); snprintf(content_len, 64, "Content-Length: %d\r\n\r\n", (int)strlen(welcome_content)); strcat(sendbuffer, content_len); strcat(sendbuffer, welcome_content); printf("send reply to client \n%s", sendbuffer); write(stat->fd, sendbuffer, strlen(sendbuffer)); stat->_ev.events = EPOLLIN; //stat->_ev.data.ptr = stat; epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, stat->fd, &stat->_ev); } void commit_respone_handler(ConnectStat * stat) { const char * commit_content = "\ \n\ \n\ \n\ This is a test \n\ \n\ \n\ \n\
\n\ 欢迎学霸同学 %s ,你的芳龄是 %s!
\n\ \n\ \n\ \n"; char sendbuffer[4096]; char content[4096]; char content_len[64]; int len = 0; len = snprintf(content, 4096, commit_content, stat->name, stat->age); strcpy(sendbuffer, main_header); snprintf(content_len, 64, "Content-Length: %d\r\n\r\n", len); strcat(sendbuffer, content_len); strcat(sendbuffer, content); printf("send reply to client \n%s", sendbuffer); write(stat->fd, sendbuffer, strlen(sendbuffer)); stat->_ev.events = EPOLLIN; //stat->_ev.data.ptr = stat; epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, stat->fd, &stat->_ev); } 注意:
1.由accept函数产生的listen_sock只有一个,可以把它看作是一个信箱;epoll_wait函数监听的文件描述符只有两种可能:
a.监听客户端连接发起的listen_sock(唯一)
b.与客户端建立连接的文件描述符(每个客户端独对应一个)
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) { ConnectStat* stat = (ConnectStat*)revs[i].data.ptr;//获取函数参数 int rsock = stat->fd; //准确获取哪个事件的描述符 //listen_sock只能有一个(代表信箱) if (rsock == listen_sock && (revs[i].events) && EPOLLIN) //如果是初始的 就接受,建立链接 { int new_fd = accept(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len); if (new_fd > 0) { printf("get a new client:%s:%d\n", inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr), ntohs(peer.sin_port)); //sleep(1000); connect_handle(new_fd); } } else // 接下来对num - 1 个事件处理 { if (revs[i].events & EPOLLIN) { do_http_request((ConnectStat*)revs[i].data.ptr); } else if (revs[i].events & EPOLLOUT) { do_http_respone((ConnectStat*)revs[i].data.ptr); } else { } } }上面这段代码遍历就绪事件的数组revs[],判断事件对应的文件描述符是否是listen_sock:
a.若是listen_sock,则表示有客户端要建立连接,则调用accept函数接收连接,并调用connect_handle函数添加新的事件。
void connect_handle(int new_fd) { ConnectStat* stat = stat_init(new_fd); set_nonblock(new_fd); stat->_ev.events = EPOLLIN; stat->_ev.data.ptr = stat; epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, new_fd, &stat->_ev); //二次托管 }b.若不是listen_sock,则是已经建立连接的事件,则调用request和response函数,接收客户端传来的数据或者对客户端进行回应
if (revs[i].events & EPOLLIN) { do_http_request((ConnectStat*)revs[i].data.ptr); } else if (revs[i].events & EPOLLOUT) { do_http_respone((ConnectStat*)revs[i].data.ptr); } else { }request表示从客户端读取数据并处理,response表示对客户端进行回应。
do_http_request函数如下:
void do_http_request(ConnectStat* stat) { //读取和解析http 请求 char buf[4096]; char* pos = NULL; //while header \r\n\r\ndata ssize_t _s = read(stat->fd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); if (_s > 0) { buf[_s] = '\0'; printf("receive from client:%s\n", buf); pos = buf; //Demo 仅仅演示效果,不做详细的协议解析 if (!strncasecmp(pos, "GET", 3)) { stat->handler = welcome_response_handler; } else if (!strncasecmp(pos, "Post", 4)) { //获取 uri printf("---Post----\n"); pos += strlen("Post"); while (*pos == ' ' || *pos == '/') ++pos; if (!strncasecmp(pos, "commit", 6)) {//获取名字和年龄 int len = 0; printf("post commit --------\n"); pos = strstr(buf, "\r\n\r\n"); char* end = NULL; if (end = strstr(pos, "name=")) { pos = end + strlen("name="); end = pos; while (('a' <= *end && *end <= 'z') || ('A' <= *end && *end <= 'Z') || ('0' <= *end && *end <= '9')) end++; len = end - pos; if (len > 0) { memcpy(stat->name, pos, end - pos); stat->name[len] = '\0'; } } if (end = strstr(pos, "age=")) { pos = end + strlen("age="); end = pos; while ('0' <= *end && *end <= '9') end++; len = end - pos; if (len > 0) { memcpy(stat->age, pos, end - pos); stat->age[len] = '\0'; } } stat->handler = commit_respone_handler; } else { stat->handler = welcome_response_handler; } } else { stat->handler = welcome_response_handler; } //生成处理结果 html ,write stat->_ev.events = EPOLLOUT; //stat->_ev.data.ptr = stat; epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, stat->fd, &stat->_ev); //二次托管 } else if (_s == 0) //client:close { printf("client: %d close\n", stat->fd); epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, stat->fd, NULL); close(stat->fd); free(stat); } else { perror("read"); } } 调用read从客户端读取数据并分析:
1.读取长度若为0,表示客户端已经关闭,删除对应的事件并关闭描述符
2.读取长度不为0,根据客户端发送的不同请求(GET/POST)设置事件对应的执行函数,并将事件改成EPOLLOUT表示向客户端输出数据。
do_http_response函数代码如下:
void do_http_respone(ConnectStat* stat) { stat->handler(stat); }很简单,执行事件数据函数(该函数由do_http_request在分析客户端发来的请求时设置)。
水平触发和边缘触发
Level_triggered(水平触发):当被监控的文件描述符上有可读写事件发生时,epoll_wait()会通知处理程序去读写。如果这次没有把数据一次性全部读写完(如读写缓冲区太小),那么下次调用 epoll_wait()时,它还会通知你在上没读写完的文件描述符上继续读写,当然如果你一直不去读写,它会一直通知你!!!如果系统中有大量你不需要读写的就绪文件描述符,而它们每次都会返回,这样会大大降低处理程序检索自己关心的就绪文件描述符的效率!!!
设置方式: 默认即水平触发
Edge_triggered(边缘触发):当被监控的文件描述符上有可读写事件发生时,epoll_wait()会通知处理程序去读写。如果这次没有把数据全部读写完(如读写缓冲区太小),那么下次调用epoll_wait()时,它不会通知你,也就是它只会通知你一次,直到该文件描述符上出现第二次可读写事件才会通知你!!!这种模式比水平触发效率高,系统不会充斥大量你不关心的就绪文件描述符!!! 设置方式: stat->_ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET
关键问题
如何解决事件与 连接socket句柄挂钩,快速完成检索?
如何突破 系统默认状态最多允许 1024 个连接限制?
cmd输入
ulimit -a差距查看open files

表示进程可打开的文件句柄数最大值
使用
ulimit -n 100000进行修改
epoll 监听的事件没有超时处理机制,如何处理?
参考epoll框架
高并发epoll的封装
源代码在Github仓库中:

本来想传的,弄了半天一直传不上给我整笑了😓
代码剖析
global.h
struct _fde { unsigned int type;//类型 u_short local_port;//本地端口 u_short remote_port;//远程端口 struct in_addr local_addr;//本地地址 char ipaddr[16]; /* dotted decimal address of peer */ PF *read_handler;//读处理函数指针 void *read_data;//读的数据 PF *write_handler;//写处理的函数指针 void *write_data;//写的数据 PF *timeout_handler;//超时处理的... time_t timeout;//超时阈值 void *timeout_data; };定义了和文件描述符相关的信息
extern fde *fd_table;fd_table数组用来保存每一个文件句柄的信息.
eg:fd_table[1] 表示fd=1对应的文件句柄的信息
/*系统时间相关,设置成全局变量,供所有模块使用*/ extern struct timeval current_time; extern double current_dtime; extern time_t sys_curtime;定义了一些时间变量,用于超时处理.
/* epoll 相关接口实现 */ extern void do_epoll_init(int max_fd); extern void do_epoll_shutdown(); extern void epollSetEvents(int fd, int need_read, int need_write); extern int do_epoll_select(int msec);定义了epoll相关的一些接口.
/*框架外围接口*/ void comm_init(int max_fd); extern int comm_select(int msec); extern inline void comm_call_handlers(int fd, int read_event, int write_event); void commUpdateReadHandler(int fd, PF * handler, void *data); void commUpdateWriteHandler(int fd, PF * handler, void *data);定义了框架的外围接口
com_epoll.c
定义了一些全局变量:
/* epoll structs */ static int kdpfd; static struct epoll_event events[MAX_EVENTS];//传入epoll_wait做参数 static int epoll_fds = 0;//目前在监听的文件句柄总数 static unsigned *epoll_state; /* 保存每个epoll 的事件状态 */为什么这里要设置epoll_state数组?

我们可以调用epoll_ctl函数来添加、修改、删除事件,但是对于具体的事件监听状态是难以获知的。
我们需要设置一个数组来获取每一个文件句柄对应的事件状态,以便进行修改(setEpollEvnet函数)
static const char * epolltype_atoi(int x)//把epolltpye类型转为字符串类型 { switch (x) { case EPOLL_CTL_ADD: return "EPOLL_CTL_ADD"; case EPOLL_CTL_DEL: return "EPOLL_CTL_DEL"; case EPOLL_CTL_MOD: return "EPOLL_CTL_MOD"; default: return "UNKNOWN_EPOLLCTL_OP"; } }将epoll_wait的相关命令转变为对应的字符形式
void do_epoll_init(int max_fd) { kdpfd = epoll_create(max_fd); if (kdpfd < 0) fprintf(stderr,"do_epoll_init: epoll_create(): %s\n", xstrerror()); //fd_open(kdpfd, FD_UNKNOWN, "epoll ctl"); //commSetCloseOnExec(kdpfd); epoll_state = calloc(max_fd, sizeof(*epoll_state));//状态数组,保存每一个event的状态 //epoll_state[fd] 访问fd对应事件的状态 }对于epoll_create进行分装,传入最大文件描述符 ,
并初始化数组epoll_state用来存放每一个事件的状态:

void do_epoll_shutdown() { close(kdpfd); kdpfd = -1; safe_free(epoll_state); }关闭epoll句柄,并释放事件状态数组所占内存。
void epollSetEvents(int fd, int need_read, int need_write) { int epoll_ctl_type = 0; struct epoll_event ev; assert(fd >= 0); debug(5, 8) ("commSetEvents(fd=%d)\n", fd); memset(&ev, 0, sizeof(ev)); ev.events = 0; ev.data.fd = fd; if (need_read) ev.events |= EPOLLIN; if (need_write) ev.events |= EPOLLOUT; if (ev.events)//EPOLLHUP、EPOLLERR为必设状态 ev.events |= EPOLLHUP | EPOLLERR; //自动判断epoll_ctl的op类型 if (ev.events != epoll_state[fd]) { /* If the struct is already in epoll MOD or DEL, else ADD */ if (!ev.events) { epoll_ctl_type = EPOLL_CTL_DEL; } else if (epoll_state[fd]) { epoll_ctl_type = EPOLL_CTL_MOD; } else { epoll_ctl_type = EPOLL_CTL_ADD; } //更新数组 epoll_state[fd] = ev.events; if (epoll_ctl(kdpfd, epoll_ctl_type, fd, &ev) < 0) { debug(5, 1) ("commSetEvents: epoll_ctl(%s): failed on fd=%d: %s\n", epolltype_atoi(epoll_ctl_type), fd, xstrerror()); } switch (epoll_ctl_type) { case EPOLL_CTL_ADD: epoll_fds++; break; case EPOLL_CTL_DEL: epoll_fds--; break; default: break; } } }实现对于epoll_ctl函数的封装
由传入的need_read、need_write参数决定事件是要读还是写,并且无论是读还是写,
无论是读还是写都设置EPOLLHUP和EPOLLERR
- EPOLLHUP:表示该文件描述符的连接被挂起,通常是指连接断开或者对方关闭连接。
- EPOLLERR:表示该文件描述符发生错误,例如连接出现错误、连接被重置等。
数组epoll_state中存储了在调用epollSetEvents之前,fd对应的事件状态,这里通过比较事件状态的新值(存储在新创建的ev中)和旧值(存储在event_state数组中)来决定是新增、修改或删除事件状态:
//自动判断epoll_ctl的op类型 if (ev.events != epoll_state[fd]) { /* If the struct is already in epoll MOD or DEL, else ADD */ if (!ev.events) {//新事件状态为0,则要进行删除 epoll_ctl_type = EPOLL_CTL_DEL; } else if (epoll_state[fd]) {//新、旧事件状态不为0,则要进行修改 epoll_ctl_type = EPOLL_CTL_MOD; } else {//旧事件状态为0,则进行添加 epoll_ctl_type = EPOLL_CTL_ADD; }并且要更新epoll_state数组实现同步:
epoll_state[fd] = ev.events;最后调用epoll_ctl函数,并更新一些全局变量:
if (epoll_ctl(kdpfd, epoll_ctl_type, fd, &ev) < 0) { debug(5, 1) ("commSetEvents: epoll_ctl(%s): failed on fd=%d: %s\n", epolltype_atoi(epoll_ctl_type), fd, xstrerror()); } switch (epoll_ctl_type) { case EPOLL_CTL_ADD: epoll_fds++; break; case EPOLL_CTL_DEL: epoll_fds--; break; default: break; }int do_epoll_select(int msec) { int i; int num; int fd; struct epoll_event *cevents; /*if (epoll_fds == 0) { assert(shutting_down); return COMM_SHUTDOWN; } statCounter.syscalls.polls++; */ num = epoll_wait(kdpfd, events, MAX_EVENTS, msec); if (num < 0) { getCurrentTime(); if (ignoreErrno(errno))//可以忽略的错误 return COMM_OK; debug(5, 1) ("comm_select: epoll failure: %s\n", xstrerror()); return COMM_ERROR; } //statHistCount(&statCounter.select_fds_hist, num); if (num == 0) return COMM_TIMEOUT; //num表示事件就绪的句柄数目 for (i = 0, cevents = events; i < num; i++, cevents++) { fd = cevents->data.fd; comm_call_handlers(fd, cevents->events & ~EPOLLOUT, cevents->events & ~EPOLLIN);//是否有读事件?是否有写事件? } return COMM_OK; } 对epoll_wait函数进行封装:
a.epoll_wait返回值<0表示出错,判断是否是可忽略的错误,若是可忽略的错误则返回COMM_OK,否则返回COMM_ERROR
b.返回值=0表示超时,返回COMM_TIMEOUT
c.返回值num>0表示有事件可以处理,可处理的事件会放在events数组中0~num-1的位置,遍历数组,执行相应的事件处理函数
comm_call_handlers函数如下:
inline void comm_call_handlers(int fd, int read_event, int write_event) { fde *F = &fd_table[fd]; debug(5, 8) ("comm_call_handlers(): got fd=%d read_event=%x write_event=%x F->read_handler=%p F->write_handler=%p\n" ,fd, read_event, write_event, F->read_handler, F->write_handler); if (F->read_handler && read_event) { PF *hdl = F->read_handler; void *hdl_data = F->read_data; /* If the descriptor is meant to be deferred, don't handle */ debug(5, 8) ("comm_call_handlers(): Calling read handler on fd=%d\n", fd); //commUpdateReadHandler(fd, NULL, NULL); hdl(fd, hdl_data); } if (F->write_handler && write_event) { PF *hdl = F->write_handler; void *hdl_data = F->write_data; //commUpdateWriteHandler(fd, NULL, NULL); hdl(fd, hdl_data); } } 为fd对应的事件执行相应的读处理/写处理函数
common.c
time_t getCurrentTime(void)//获取时间戳,用来做超时处理 { gettimeofday(¤t_time, NULL); current_dtime = (double) current_time.tv_sec + (double) current_time.tv_usec / 1000000.0; return sys_curtime = current_time.tv_sec; } 获取当前时间戳,并以秒为单位返回(用来做超时处理);同时还将时间戳以双精度浮点数的形式存储在current'_dtime中
current_time.tv_usec/1000000.0表示将微秒转换为秒
int commSetTimeout(int fd, int timeout, PF * handler, void *data)//设置超时处理函数 { fde *F; debug(5, 3) ("commSetTimeout: FD %d timeout %d\n", fd, timeout); assert(fd >= 0); assert(fd < Biggest_FD); F = &fd_table[fd]; if (timeout < 0) {//表示不执行超时处理 F->timeout_handler = NULL; F->timeout_data = NULL; return F->timeout = 0; } assert(handler || F->timeout_handler); if (handler || data) { F->timeout_handler = handler; F->timeout_data = data; } return F->timeout = sys_curtime + (time_t) timeout; }设置超时处理函数:
timeout的单位是秒,timeout<0表示不进行超时处理
超时的时间设置为当前的时间+timeout(当时间达到了F->timeout就执行超时处理函数)
int comm_select(int msec) { static double last_timeout = 0.0; int rc; double start = current_dtime; debug(5, 3) ("comm_select: timeout %d\n", msec); if (msec > MAX_POLL_TIME) msec = MAX_POLL_TIME; //statCounter.select_loops++; /* Check timeouts once per second */ if (last_timeout + 0.999 < current_dtime) { last_timeout = current_dtime; checkTimeouts();//checkTimeouts一秒钟调用一次 } else { int max_timeout = (last_timeout + 1.0 - current_dtime) * 1000; if (max_timeout < msec) msec = max_timeout; } //comm_select_handled = 0; rc = do_epoll_select(msec); getCurrentTime(); //statCounter.select_time += (current_dtime - start); if (rc == COMM_TIMEOUT) debug(5, 8) ("comm_select: time out\n"); return rc; } 执行一个事件选择操作,控制超时时间,实时更新时间戳,并执行相应的超时检查和处理。
重点是下面这一部分:
/* Check timeouts once per second */ if (last_timeout + 0.999 < current_dtime) { last_timeout = current_dtime; checkTimeouts();//checkTimeouts一秒钟调用一次 } else { int max_timeout = (last_timeout + 1.0 - current_dtime) * 1000; if (max_timeout < msec) msec = max_timeout; } //comm_select_handled = 0; rc = do_epoll_select(msec); getCurrentTime();这一部分保证了checkTimeouts函数(处理超时事件)每秒执行一次
static void checkTimeouts(void)//处理超时事件 { int fd; fde *F = NULL; PF *callback; for (fd = 0; fd <= Biggest_FD; fd++) { F = &fd_table[fd]; /*if (!F->flags.open) continue; */ if (F->timeout == 0) continue; if (F->timeout > sys_curtime) continue; debug(5, 5) ("checkTimeouts: FD %d Expired\n", fd); if (F->timeout_handler) { debug(5, 5) ("checkTimeouts: FD %d: Call timeout handler\n", fd); callback = F->timeout_handler; F->timeout_handler = NULL; callback(fd, F->timeout_data); } else { debug(5, 5) ("checkTimeouts: FD %d: Forcing comm_close()\n", fd); comm_close(fd); } } } 如果有事件超时,则执行处理函数
void commUpdateReadHandler(int fd, PF * handler, void *data) { fd_table[fd].read_handler = handler; fd_table[fd].read_data = data; epollSetEvents(fd,1,0); //设置读事件 } void commUpdateWriteHandler(int fd, PF * handler, void *data) { fd_table[fd].write_handler = handler; fd_table[fd].write_data = data; epollSetEvents(fd,0,1); }主要是对事件的处理函数进行注册;
fd_table[fd].read_handler = handler;//指定事件对应的读处理函数
fd_table[fd].read_data = data;//指定事件对应的读处理函数的参数
epollSetEvents(fd,1,0); //设置读事件
LIBEVENT框架——解决了C10K问题
C10K 问题:并发能力突破不了1万连接
libevent是一个轻量级的开源的高性能的事件触发的网络库,适用于windows、linux、bsd等多种平台,内部使用select、epoll、kqueue等系统调用管理事件机制。
它被众多的开源项目使用,例如大名鼎鼎的memcached等。
特点:
事件驱动,高性能;
轻量级,专注于网络(相对于ACE);
开放源码,代码相当精炼、易读;
跨平台,支持Windows、Linux、BSD和Mac OS;
支持多种I/O多路复用技术(epoll、poll、dev/poll、select和kqueue等),在不同的操作系统下,做了多路复用模型的抽象,可以选择使用不同的模型,通过事件函数提供服务;
支持I/O,定时器和信号等事件;
采用Reactor模式
libevent是一个典型的reactor模式的实现。
普通的函数调用机制:程序调用某个函数,函数执行,程序等待,函数将结果返回给调用程序(如果含有函数返回值的话),也就是顺序执行的。
Reactor模式的基本流程:应用程序需要提供相应的接口并且注册到reactor反应器上,如果相应的事件发生的话,那么reactor将自动调用相应的注册的接口函数(类似于回调函数)通知你,所以libevent是事件触发的网络库。
libevent的功能
Libevent提供了事件通知,io缓存事件,定时器,超时,异步解析dns,事件驱动的http server以及一个rpc框架。
事件通知:当文件描述符可读可写时将执行回调函数。
IO缓存:缓存事件提供了输入输出缓存,能自动的读入和写入,用户不必直接操作io。
定时器:libevent提供了定时器的机制,能够在一定的时间间隔之后调用回调函数。
信号:触发信号,执行回调。
异步的dns解析:libevent提供了异步解析dns服务器的dns解析函数集。
事件驱动的http服务器:libevent提供了一个简单的,可集成到应用程序中的HTTP服务器。
RPC客户端服务器框架:libevent为创建RPC服务器和客户端创建了一个RPC框架,能自动的封装和解封数据结构。
libevent实战
上一篇:类和对象(二)
