【Elasticsearch】Elasticsearch集群管理在分布式环境中的应用
文章目录
- 📑引言
- 一、集群的基本组成与配置
- 1.1 集群结构
- 1.2 集群配置
- 二、索引和分片管理
- 2.1 索引管理
- 2.2 分片管理
- 三、高可用性和灾难恢复
- 3.1 高可用性
- 3.2 灾难恢复
- 四、性能调优
- 4.1 节点级别调优
- 4.2 索引和查询调优
- 五、安全管理
- 5.1 用户认证和权限管理
- 5.2 通信加密
- 五、小结
📑引言
Elasticsearch作为一个分布式搜索和分析引擎,被广泛应用于全文搜索、日志和监控、以及分析和可视化等多个领域。它基于Apache Lucene构建,具有高可扩展性、实时搜索、分析等特性。然而,在分布式环境下管理Elasticsearch集群并不是一件简单的任务,需要考虑到集群的节点配置、索引和分片管理、数据的高可用性和灾难恢复、性能调优等多方面的内容。本文将详细介绍如何在分布式环境中管理Elasticsearch集群,以确保其高效运行和稳定性。
一、集群的基本组成与配置
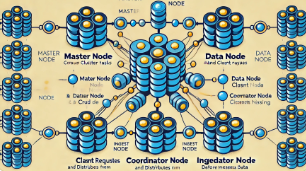
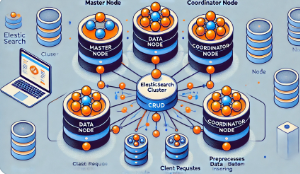
1.1 集群结构
Elasticsearch集群由一个或多个节点组成,其中每个节点是一个独立的服务器或虚拟机。一个集群内有一个或多个主节点(Master Node)、数据节点(Data Node)、协调节点(Coordinator Node)和处理节点(Ingest Node)。每种节点都有其特定的职责:
- 主节点:负责集群范围内的管理任务,如索引创建、删除、集群状态的更新等。
- 数据节点:存储实际的数据,并执行相关的CRUD(Create, Read, Update, Delete)操作和搜索请求。
- 协调节点:接收客户端请求,将请求分发到数据节点并汇总结果,通常不存储数据。
- 处理节点:在数据被索引之前,对数据进行预处理,如解析、变换等操作。
1.2 集群配置
配置Elasticsearch集群的基本步骤如下:
- 安装Elasticsearch:在所有节点上安装Elasticsearch,可以使用tar包、deb或rpm包进行安装。
- 配置elasticsearch.yml:配置文件位于
/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml,需要配置集群名称(cluster.name)、节点名称(node.name)、节点角色(node.master、node.data等)、网络绑定地址(network.host)等参数。 - 启动节点:配置完成后,启动Elasticsearch节点,可以使用
systemctl start elasticsearch命令。
以下是一个简单的elasticsearch.yml配置示例:
cluster.name: my-application node.name: node-1 node.master: true node.data: true network.host: 0.0.0.0 discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.1.1", "192.168.1.2"] cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2"] 二、索引和分片管理
2.1 索引管理
在Elasticsearch中,数据是以索引的形式存储的,每个索引包含多个文档。管理索引包括索引的创建、更新和删除等操作。可以使用Elasticsearch的REST API进行这些操作,例如:
- 创建索引:
PUT /my-index { "settings": { "number_of_shards": 3, "number_of_replicas": 2 } } - 删除索引:
DELETE /my-index - 更新索引设置:
PUT /my-index/_settings { "index": { "number_of_replicas": 1 } } 2.2 分片管理
分片(Shard)是Elasticsearch中分散数据的一种方式。每个索引可以被分割成多个分片,每个分片本质上是一个独立的Lucene索引。分片有两种类型:主分片(Primary Shard)和副本分片(Replica Shard)。
- 主分片:存储原始数据,每个索引至少有一个主分片。
- 副本分片:主分片的拷贝,用于数据的高可用性。
管理分片时需要注意以下几点:
- 分片数量的选择:分片数量在索引创建时决定,一旦创建就无法更改。需要根据数据量和查询并发量来选择合适的分片数量。
- 分片的再平衡:当集群中的节点发生变化时,Elasticsearch会自动重新分配分片,以确保数据均衡分布。
三、高可用性和灾难恢复
3.1 高可用性
为了确保Elasticsearch集群的高可用性,主要需要关注以下几个方面:
- 多主节点配置:确保集群中至少有三个主节点,以避免主节点故障时集群无法选举新的主节点。
- 副本分片配置:每个主分片至少配置一个副本分片,确保在主分片故障时数据不丢失。
- 跨区域部署:在多个数据中心或可用区之间分布节点,防止单点故障导致整个集群不可用。
3.2 灾难恢复
灾难恢复(Disaster Recovery)是指在出现数据丢失或系统崩溃等严重故障时,能够快速恢复数据和服务。Elasticsearch提供了多种机制来实现灾难恢复:
- 快照和恢复:定期对索引进行快照(Snapshot),并将快照存储到远程存储(如S3、HDFS)中。在灾难发生时,可以通过快照进行数据恢复。
# 创建快照仓库 PUT /_snapshot/my_backup { "type": "fs", "settings": { "location": "/mount/backups/my_backup" } } # 创建快照 PUT /_snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1 { "indices": "my-index", "ignore_unavailable": true, "include_global_state": false } # 恢复快照 POST /_snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1/_restore { "indices": "my-index", "ignore_unavailable": true, "include_global_state": false } - 跨集群复制:在不同集群之间复制索引数据,确保在一个集群发生故障时,另一个集群能够继续提供服务。
PUT /_ccr/auto_follow/my_auto_follow_pattern { "remote_cluster": "remote_cluster", "leader_index_patterns": ["my-leader-index-*"], "follow_index_pattern": "my-follower-index-{{leader_index}}" } 四、性能调优
4.1 节点级别调优
- JVM配置:确保给Elasticsearch分配足够的堆内存(Heap Memory),但不超过系统内存的50%。同时,配置合理的垃圾回收机制(GC)。
# 在jvm.options文件中配置 -Xms16g -Xmx16g - 磁盘I/O优化:使用SSD作为存储介质,配置RAID 0提高I/O性能,同时确保磁盘空间充足,避免因磁盘空间不足导致集群无法写入数据。
4.2 索引和查询调优
- 索引优化:通过减少字段类型(如text和keyword类型)、禁用不必要的功能(如_source字段存储)来减少索引的大小和复杂度。
PUT /my-index { "mappings": { "_source": { "enabled": false }, "properties": { "message": { "type": "text", "index": true } } } } - 查询优化:使用分页(pagination)、过滤(filter)等技术来减少查询的计算量。尽量使用term查询代替全文搜索查询,以提高查询速度。
GET /my-index/_search { "query": { "term": { "user.id": "kimchy" } } } 五、安全管理
Elasticsearch集群的安全管理包括用户认证、权限管理和通信加密等方面。
5.1 用户认证和权限管理
- 用户认证:通过配置Elasticsearch的X-Pack插件,实现用户认证功能,可以使用内置用户、LDAP或Active Directory进行用户认证。
# 配置elasticsearch.yml xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.authc.realms.native.native1: order: 0 - 权限管理:通过配置角色(Role)和角色映射(Role Mapping),实现基于角色的访问控制。
# 配置角色 PUT /_security/role/my_role { "cluster": ["all"], "indices": [ { "names": ["my-index"], "privileges": ["read", "write"] } ] } # 配置角色映射 POST /_security/role_mapping/my_role_mapping { "roles": ["my_role"], "rules": { "field": { "username": "kimchy" } }, "enabled": true } 5.2 通信加密
- HTTP通信加密:使用SSL/TLS加密
Elasticsearch节点与客户端之间的通信,确保数据在传输过程中不被窃取。
# 配置elasticsearch.yml xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled: true xpack.security.http.ssl.keystore.path: certs/elastic-certificates.p12 xpack.security.http.ssl.truststore.path: certs/elastic-certificates.p12 - 节点间通信加密:配置节点间通信加密,确保Elasticsearch节点之间的数据传输安全。
# 配置elasticsearch.yml xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode: certificate xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.path: certs/elastic-certificates.p12 xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.path: certs/elastic-certificates.p12 五、小结
在分布式环境下管理Elasticsearch集群是一项复杂且充满挑战的任务,需要在集群配置、索引和分片管理、高可用性和灾难恢复、性能调优以及安全管理等多个方面进行深入的了解和优化。通过合理的配置和管理,可以充分发挥Elasticsearch的性能和可靠性,满足各种业务需求。
